(Press-News.org) Embargoed press materials are now available for Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Top scientists and educators in the field will gather at the meeting, March 23–26 in San Antonio.
Reporters are invited to attend an exciting lineup of in-person scientific sessions in San Antonio or access press materials electronically. Register now or find more information in the #DiscoverBMB newsroom. Please note that only a limited number of complementary on-site press passes will be issued, so advance registration is recommended.
Explore the schedule at a glance, searchable schedule, award lectures or symposium sessions to see all the exciting research that will be covered at #DiscoverBMB.
Featured research findings are highlighted below, with embargo times noted:
African catfish skin mucus yields promising antibacterial compound (3/24, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Peptide extracted from farmed fish could help fight antimicrobial-resistant infections
Researchers uncover key biomolecule involved in whooping cough infection (3/25, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Potential drug and vaccine strategies could target crucial glycan to fight pertussis
Study suggests that estrogen may drive nicotine addiction in women (3/25, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Findings open the door to targeted therapies for controlling nicotine use
New compound offers hope for deadly tropical disease (3/24, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Schistosomiasis drug candidate overcomes limitations of current treatment
Study suggests statins could help fight gum disease (3/25, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Common cholesterol drug shown to affect immune cells that drive periodontal inflammation
More than meets the eye: Researchers uncover the microbial secrets of dry eye (3/26, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Insights into the ocular microbiome could have implications beyond eye health
Study links long-term consumption of reused deep-fried oil with increased neurodegeneration (3/25, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Animal study suggests the grease disrupts liver–gut–brain connections
How might diabetes lead to Alzheimer’s? Study suggests the liver is key (3/23, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Researchers trace a path from the gut to the brain and say managing diabetes could help to prevent dementia
New surfactant could improve lung treatments for premature babies (3/24, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Researchers report progress toward an alternative to animal-derived formulation
Bedrest may affect cholesterol dynamics differently depending on age (3/24, 4:30 p.m. CDT)
Unraveling physical inactivity’s effects on the body could lead to new ways to mitigate its negative effects
Follow #DiscoverBMB on Facebook, X, Instagram and LinkedIn.
About the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB)
The ASBMB is a nonprofit scientific and educational organization with more than 12,000 members worldwide. Founded in 1906 to advance the science of biochemistry and molecular biology, the society publishes three peer-reviewed journals, advocates for funding of basic research and education, supports science education at all levels, and promotes the diversity of individuals entering the scientific workforce. www.asbmb.org
END
Discover BMB 2024 press materials available now
Get the latest molecular life science research news at the ASBMB’s annual meeting
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
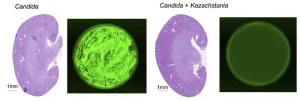
Newly identified yeast could prevent fungal infections by outcompeting rivals, study suggests
2024-03-18
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel have identified a yeast that could be used to prevent invasive candidiasis, a major cause of death in hospitalized and immunocompromised patients. The study, to be published March 18 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), shows that the novel yeast lives harmlessly in the intestines of mice and humans and can displace the yeast responsible for candidiasis, Candida albicans.
Millions of microbial species live within or on the human body, many of them being harmless or even beneficial to human health. The microscopic yeast C. albicans is commonly found in the intestines ...
NIH studies find severe symptoms of “Havana Syndrome,” but no evidence of MRI-detectable brain injury or biological abnormalities
2024-03-18
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE
Monday, March, 18,2024
10 a.m. EDT
Contact:
NIH Office of Communications and Public Liaison
NIH News Media Branch
301-496-5787
NIH studies find severe symptoms of “Havana Syndrome,” but no evidence of MRI-detectable brain injury or biological abnormalities
Compared to healthy volunteers, affected U.S. government personnel did not exhibit differences that would explain symptoms
Using advanced imaging techniques and in-depth clinical assessments, a research team at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found no significant evidence of MRI-detectable brain injury, nor differences in most clinical measures compared to ...
Clinical, biomarker, and research tests among US government personnel and their family members involved in anomalous health incidents
2024-03-18
About The Study: In this exploratory study, there were no significant differences between individuals reporting anomalous health incidents and matched control participants with respect to most clinical, research, and biomarker measures, except for objective and self-reported measures of imbalance and symptoms of fatigue, posttraumatic stress, and depression. This study did not replicate the findings of previous studies, although differences in the populations included and the timing of assessments limit direct comparisons. ...
Neuroimaging findings in US government personnel and their family members involved in anomalous health incidents
2024-03-18
About The Study: In this exploratory neuroimaging study, there were no significant differences in imaging measures of brain structure or function between individuals reporting anomalous health incidents and matched control participants after adjustment for multiple comparisons. U.S. government personnel stationed internationally have reported anomalous health incidents, with some individuals experiencing persistent debilitating symptoms.
Authors: Carlo Pierpaoli, M.D., Ph.D., of the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering in ...
Can used coffee grounds help clean up environmental toxins?
2024-03-18
Global coffee consumption generates millions of tons of spent coffee grounds each year, which can be damaging to wildlife and the environment. However, new research published in the Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology reveals that spent coffee grounds could be repurposed to act as a powerful adsorbent of bentazone, a herbicide commonly used in agriculture that is highly neurotoxic.
In the study, investigators found that when they used zinc chloride to activate the carbon from spent coffee grounds, the activated carbon showed a 70% efficiency in bentazone removal. ...
Largest-ever map of universe’s active supermassive black holes released
2024-03-18
Astronomers have charted the largest-ever volume of the universe with a new map of active supermassive black holes living at the centers of galaxies. Called quasars, the gas-gobbling black holes are, ironically, some of the universe’s brightest objects.
The new map logs the location of about 1.3 million quasars in space and time, the furthest of which shone bright when the universe was only 1.5 billion years old. (For comparison, the universe is now 13.7 billion years old.)
“This quasar catalog is different from all previous catalogs in that it gives us a three-dimensional map of the largest-ever volume of the universe,” says map co-creator David Hogg, a ...
Despite protection urban hawks still face an array of threats
2024-03-18
Life can be hard for a raptor. If you’re a teenager from the city, it’s even harder. That’s according to a new study published in the Journal of Raptor Research titled “Causes of Death of Female Cooper’s Hawks (Accipiter cooperii) from an Urban Setting in New Mexico, USA,” conducted by Brian A. Millsap and his colleagues at the US Fish and Wildlife Service. Over the course of 11 years, his research team affixed GPS transmitters to 158 female Cooper’s hawks in the Albuquerque area. Of those, 88 died and were found, allowing the researchers to investigate cause of death. The ...
Middle-aged Americans lonelier than European counterparts
2024-03-18
Middle-aged adults in the U.S. tend to report significantly higher levels of loneliness than their European counterparts, possibly due in part to weaker family ties and greater income inequality, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Loneliness is gaining attention globally as a public health issue because elevated loneliness increases one’s risk for depression, compromised immunity, chronic illness and mortality,” said lead author Frank Infurna, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at Arizona State ...
Dr. Sujuan Ba and the National Foundation for Cancer Research have been awarded the 2024 Pioneer in Medicine Award at the 21st Annual GFC Awards Gala
2024-03-18
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) is proud to announce that both the organization and our CEO, Dr. Sujuan Ba, have been honored with the "2024 Pioneer in Medicine Award" by the World Brain Mapping Foundation and the Society for Brain Mapping and Therapeutics. The award was presented to Dr. Ba at the 21st Annual GFC Awards Gala on Friday, March 15th, 2024. This recognition highlights a significant landmark in NFCR's over 50 years of impact in charting new pathways through research to find ...
Breathe, don’t vent: Turning down the heat is key to managing anger
2024-03-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Venting about a source of anger might feel good in the moment, but it’s not effective at reducing the rage, new research suggests.
Instead, techniques often used to address stress – deep breathing, mindfulness, meditation, yoga or even counting to 10 – have been shown to be more effective at decreasing anger and aggression.
Researchers analyzed over 150 studies involving more than 10,000 participants and found that what really works to reduce anger is lowering physiological arousal – in other words, turning down the heat. Activities that increased arousal overall ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
[Press-News.org] Discover BMB 2024 press materials available nowGet the latest molecular life science research news at the ASBMB’s annual meeting