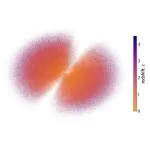
(Press-News.org) Astronomers have charted the largest-ever volume of the universe with a new map of active supermassive black holes living at the centers of galaxies. Called quasars, the gas-gobbling black holes are, ironically, some of the universe’s brightest objects.
The new map logs the location of about 1.3 million quasars in space and time, the furthest of which shone bright when the universe was only 1.5 billion years old. (For comparison, the universe is now 13.7 billion years old.)
“This quasar catalog is different from all previous catalogs in that it gives us a three-dimensional map of the largest-ever volume of the universe,” says map co-creator David Hogg, a senior research scientist at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics in New York City and a professor of physics and data science at New York University. “It isn’t the catalog with the most quasars, and it isn’t the catalog with the best-quality measurements of quasars, but it is the catalog with the largest total volume of the universe mapped.”
Hogg and his colleagues present the map in a paper published March 18 in The Astrophysical Journal. The paper’s lead author, Kate Storey-Fisher, is a postdoctoral researcher at the Donostia International Physics Center in Spain.
The scientists built the new map using data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia space telescope. While Gaia’s main objective is to map the stars in our galaxy, it also inadvertently spots objects outside the Milky Way, such as quasars and other galaxies, as it scans the sky.
“We were able to make measurements of how matter clusters together in the early universe that are as precise as some of those from major international survey projects — which is quite remarkable given that we got our data as a ‘bonus’ from the Milky Way–focused Gaia project,” Storey-Fisher says.
Quasars are powered by supermassive black holes at the centers of galaxies and can be hundreds of times as bright as an entire galaxy. As the black hole’s gravitational pull spins up nearby gas, the process generates an extremely bright disk and sometimes jets of light that telescopes can observe.
The galaxies that quasars inhabit are surrounded by massive halos of invisible material called dark matter. By studying quasars, astronomers can learn more about dark matter, such as how much it clumps together.
Astronomers can also use the locations of distant quasars and their host galaxies to better understand how the cosmos expanded over time. For example, scientists have already compared the new quasar map with the oldest light in our cosmos, the cosmic microwave background. As this light travels to us, it is bent by the intervening web of dark matter — the same web mapped out by the quasars. By comparing the two, scientists can measure how strongly matter clumps together.
“It has been very exciting to see this catalog spurring so much new science,” Storey-Fisher says. “Researchers around the world are using the quasar map to measure everything from the initial density fluctuations that seeded the cosmic web to the distribution of cosmic voids to the motion of our solar system through the universe.”
The team used data from Gaia’s third data release, which contained 6.6 million quasar candidates, and data from NASA’s Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. By combining the datasets, the team removed contaminants such as stars and galaxies from Gaia’s original dataset and more precisely pinpointed the distances to the quasars. The team also created a map showing where dust, stars and other nuisances are expected to block our view of certain quasars, which is critical for interpreting the quasar map.
“This quasar catalog is a great example of how productive astronomical projects are,” says Hogg. “Gaia was designed to measure stars in our own galaxy, but it also found millions of quasars at the same time, which give us a map of the entire universe.”
ABOUT THE FLATIRON INSTITUTE
The Flatiron Institute is the research division of the Simons Foundation. The institute's mission is to advance scientific research through computational methods, including data analysis, theory, modeling and simulation. The institute's Center for Computational Astrophysics creates new computational frameworks that allow scientists to analyze big astronomical datasets and to understand complex, multi-scale physics in a cosmological context.
END
Largest-ever map of universe’s active supermassive black holes released
The new map includes around 1.3 million quasars from across the visible universe and could help scientists better understand the properties of dark matter
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Despite protection urban hawks still face an array of threats
2024-03-18
Life can be hard for a raptor. If you’re a teenager from the city, it’s even harder. That’s according to a new study published in the Journal of Raptor Research titled “Causes of Death of Female Cooper’s Hawks (Accipiter cooperii) from an Urban Setting in New Mexico, USA,” conducted by Brian A. Millsap and his colleagues at the US Fish and Wildlife Service. Over the course of 11 years, his research team affixed GPS transmitters to 158 female Cooper’s hawks in the Albuquerque area. Of those, 88 died and were found, allowing the researchers to investigate cause of death. The ...
Middle-aged Americans lonelier than European counterparts
2024-03-18
Middle-aged adults in the U.S. tend to report significantly higher levels of loneliness than their European counterparts, possibly due in part to weaker family ties and greater income inequality, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Loneliness is gaining attention globally as a public health issue because elevated loneliness increases one’s risk for depression, compromised immunity, chronic illness and mortality,” said lead author Frank Infurna, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at Arizona State ...
Dr. Sujuan Ba and the National Foundation for Cancer Research have been awarded the 2024 Pioneer in Medicine Award at the 21st Annual GFC Awards Gala
2024-03-18
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) is proud to announce that both the organization and our CEO, Dr. Sujuan Ba, have been honored with the "2024 Pioneer in Medicine Award" by the World Brain Mapping Foundation and the Society for Brain Mapping and Therapeutics. The award was presented to Dr. Ba at the 21st Annual GFC Awards Gala on Friday, March 15th, 2024. This recognition highlights a significant landmark in NFCR's over 50 years of impact in charting new pathways through research to find ...
Breathe, don’t vent: Turning down the heat is key to managing anger
2024-03-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Venting about a source of anger might feel good in the moment, but it’s not effective at reducing the rage, new research suggests.
Instead, techniques often used to address stress – deep breathing, mindfulness, meditation, yoga or even counting to 10 – have been shown to be more effective at decreasing anger and aggression.
Researchers analyzed over 150 studies involving more than 10,000 participants and found that what really works to reduce anger is lowering physiological arousal – in other words, turning down the heat. Activities that increased arousal overall ...
A wetter world recorded in Australian coral colony
2024-03-18
Images
When climate scientists look to the future to determine what the effects of climate change may be, they use computer models to simulate potential outcomes such as how precipitation will change in a warming world.
But University of Michigan scientists are looking at something a little more tangible: coral.
Examining samples from corals in the Great Barrier Reef, the researchers discovered between 1750 and present day, as the global climate warmed, wet-season rainfall in that part of the world increased by about 10%, and the rate of extreme rain events more than doubled. Their results are published in Nature, Communications Earth and Environment.
"Climate scientists ...
Weight loss caused by common diabetes drug tied to “anti-hunger” molecule in study
2024-03-18
An “anti-hunger” molecule produced after vigorous exercise is responsible for the moderate weight loss caused by the diabetes medication metformin, according to a new study in mice and humans. The molecule, lac-phe, was discovered by Stanford Medicine researchers in 2022.
The finding, made jointly by researchers at Stanford Medicine and at Harvard Medical School, further cements the critical role the molecule, called lac-phe, plays in metabolism, exercise and appetite. It may pave the way to a new class of weight loss drugs.
“Until now, the way metformin, which is prescribed to control blood sugar ...
Intermittent food intake activates a 'GPS gene' in liver cells, thus completing the development of the liver after birth
2024-03-18
After birth, liver cells acquire different functions depending on their location. CNIO researchers have discovered that this specialization occurs with the onset of oral food intake, which is intermittent.
The alternation of periods with and without nutrients activates the mTOR gene and causes liver cells to specialize, which completes liver maturation.
The finding is the result of an investigation into the consequences of sedentary lifestyles and overeating in today’s society, where the body ...
Scientists reveal chemical structural analysis in a whiff of smell
2024-03-18
Scents, such as coffee, flowers, or freshly-baked pumpkin pie, are created by odor molecules released by various substances and detected by our noses. In essence, we are smelling molecules, the basic unit of a substance that retains its physical and chemical properties.
A research team led by Dr. ZHOU Wen from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has discovered that this process of "smelling" involves an analysis of submolecular structural features.
The study was published online in Nature Human Behaviour on March 18.
In this study, the ...
Using light to produce medication and plastics more efficiently
2024-03-18
Anyone who wants to produce medication, plastics or fertilizer using conventional methods needs heat for chemical reactions – but not so with photochemistry, where light provides the energy. The process to achieve the desired product also often takes fewer intermediate steps. Researchers from the University of Basel are now going one step further and are demonstrating how the energy efficiency of photochemical reactions can be increased tenfold. More sustainable and cost-effective applications are now tantalizingly close.
Industrial chemical reactions ...
Mapping the evolution of urinary tract cancer cells
2024-03-18
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have performed the most comprehensive analysis to date of cancer of the ureters or the urine-collection cavities in the kidney, known as upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). The study, which compared the characteristics of primary and metastatic tumors, provides new insights into the biology of these aggressive cancers and potential ways to treat them.
In the study, which appeared March 18 in Nature Communications, the researchers examined tissue samples from 44 primary and metastatic UTUC tumors. They compared gene mutations ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Jeonbuk National University researchers explore metal oxide electrodes as a new frontier in electrochemical microplastic detection
Cannabis: What is the profile of adults at low risk of dependence?
Medical and materials innovations of two women engineers recognized by Sony and Nature
Blood test “clocks” predict when Alzheimer’s symptoms will start
Second pregnancy uniquely alters the female brain
Study shows low-field MRI is feasible for breast screening
Nanodevice produces continuous electricity from evaporation
Call me invasive: New evidence confirms the status of the giant Asian mantis in Europe
Scientists discover a key mechanism regulating how oxytocin is released in the mouse brain
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
[Press-News.org] Largest-ever map of universe’s active supermassive black holes releasedThe new map includes around 1.3 million quasars from across the visible universe and could help scientists better understand the properties of dark matter