(Press-News.org) An “anti-hunger” molecule produced after vigorous exercise is responsible for the moderate weight loss caused by the diabetes medication metformin, according to a new study in mice and humans. The molecule, lac-phe, was discovered by Stanford Medicine researchers in 2022.
The finding, made jointly by researchers at Stanford Medicine and at Harvard Medical School, further cements the critical role the molecule, called lac-phe, plays in metabolism, exercise and appetite. It may pave the way to a new class of weight loss drugs.
“Until now, the way metformin, which is prescribed to control blood sugar levels, also brings about weight loss has been unclear,” said Jonathan Long, PhD, an assistant professor of pathology. “Now we know that it is acting through the same pathway as vigorous exercise to reduce hunger. Understanding how these pathways are controlled may lead to viable strategies to lower body mass and improve health in millions of people.”
Long and Mark Benson, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, are co-senior authors of the study, which will be published March 18 in Nature Metabolism. Postdoctoral scholar Shuke Xiao, PhD, is the lead author of the study.
Many people with diabetes who are prescribed metformin lose around 2% to 3% of their body weight within the first year of starting the drug. Although this amount of weight loss is modest when compared with the 15% or more often seen by people taking semaglutide drugs such as Ozempic and Wegovy, the discoveries that led to those drugs also grew from observations of relatively minor, but reproducible, weight loss in people taking first-generation versions of the medications.
Post-workout appetite loss
When Long and colleagues at Baylor University discovered lac-phe in 2022, they were on the hunt for small molecules responsible for curtailing hunger after vigorous exercise. What they found was a Frankenbaby of lactate — a byproduct of muscle fatigue — and an amino acid called phenylalanine. They dubbed the hybrid molecule lac-phe and went on to show that it’s not only more abundant after exercise but it also causes people (as well as mice and even racehorses) to feel less hungry immediately after a hard workout.
“There is an intimate connection between lac-phe production and lactate generation,” Long said. “Once we understood this relationship, we started to think about other aspects of lactate metabolism.”
Metformin was an obvious candidate because as it stimulates the breakdown of glucose (thus reducing blood sugar levels) it can trigger the generation of lactate.
The researchers found that obese laboratory mice given metformin had increased levels of lac-phe in their blood. They ate less than their peers and lost about 2 grams of body weight during the nine-day experiment.
Long and his colleagues also analyzed stored blood plasma samples from people with Type 2 diabetes before and 12 weeks after they had begun taking metformin to control their blood sugar. They saw significant increases in the levels of lac-phe in people after metformin compared with their levels before treatment. Finally, 79 participants in a large, multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis who were also taking metformin had significantly higher levels of lac-phe circulating in their blood than those who were not taking the drug.
“It was nice to confirm our hunch experimentally,” Long said. “The magnitude of effect of metformin on lac-phe production in mice was as great as or greater than what we previously observed with exercise. If you give a mouse metformin at levels comparable to what we prescribe for humans, their lac-phe levels go through the roof and stay high for many hours.”
Further research revealed that lac-phe is made by intestinal epithelial cells in the animals; blocking the ability of mice to make lac-phe erased the appetite suppression and weight loss previously observed.
Finally, a statistical analysis of the people in the atherosclerosis study who lost weight during the several-year study and follow-up period found a meaningful association between metformin use, lac-phe production and weight loss.
“The fact that metformin and sprint exercise affect your body weight through the same pathway is both weird and interesting,” Long said. “And the involvement of the intestinal epithelial cells suggests a layer of gut-to-brain communication that deserves further exploration. Are there other signals involved?”
Long noted that, while semaglutide drugs are injected into the bloodstream, metformin is an oral drug that is already prescribed to millions of people. “These findings suggest there may be a way to optimize oral medications to affect these hunger and energy balance pathways to control body weight, cholesterol and blood pressure. I think what we’re seeing now is just the beginning of new types of weight loss drugs.”
Researchers from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Colorado, the University of Virginia and the Broad Institute contributed to the work.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health (grants GM113854, K08HL145095, DK124265, DK136526, HHSN2682015000031, HSN26800004, UM1DK078616 and 1R01HL151855), a Stanford School of Medicine’s Dean’s Fellowship and the American Heart Association.
END
Weight loss caused by common diabetes drug tied to “anti-hunger” molecule in study
A Stanford Medicine study found that metformin, a commonly prescribed diabetes drug associated with moderate weight loss, stimulates production of lac-phe, a molecule abundant after exercise.
2024-03-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Intermittent food intake activates a 'GPS gene' in liver cells, thus completing the development of the liver after birth
2024-03-18
After birth, liver cells acquire different functions depending on their location. CNIO researchers have discovered that this specialization occurs with the onset of oral food intake, which is intermittent.
The alternation of periods with and without nutrients activates the mTOR gene and causes liver cells to specialize, which completes liver maturation.
The finding is the result of an investigation into the consequences of sedentary lifestyles and overeating in today’s society, where the body ...
Scientists reveal chemical structural analysis in a whiff of smell
2024-03-18
Scents, such as coffee, flowers, or freshly-baked pumpkin pie, are created by odor molecules released by various substances and detected by our noses. In essence, we are smelling molecules, the basic unit of a substance that retains its physical and chemical properties.
A research team led by Dr. ZHOU Wen from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has discovered that this process of "smelling" involves an analysis of submolecular structural features.
The study was published online in Nature Human Behaviour on March 18.
In this study, the ...
Using light to produce medication and plastics more efficiently
2024-03-18
Anyone who wants to produce medication, plastics or fertilizer using conventional methods needs heat for chemical reactions – but not so with photochemistry, where light provides the energy. The process to achieve the desired product also often takes fewer intermediate steps. Researchers from the University of Basel are now going one step further and are demonstrating how the energy efficiency of photochemical reactions can be increased tenfold. More sustainable and cost-effective applications are now tantalizingly close.
Industrial chemical reactions ...
Mapping the evolution of urinary tract cancer cells
2024-03-18
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have performed the most comprehensive analysis to date of cancer of the ureters or the urine-collection cavities in the kidney, known as upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). The study, which compared the characteristics of primary and metastatic tumors, provides new insights into the biology of these aggressive cancers and potential ways to treat them.
In the study, which appeared March 18 in Nature Communications, the researchers examined tissue samples from 44 primary and metastatic UTUC tumors. They compared gene mutations ...
Implantable sensor could lead to timelier Crohn’s treatment
2024-03-18
· Temperature sensor warns of disease flareups, tracks disease progression in real time
· Currently no way to quickly detect inflammation, leading to invasive surgeries
· Strategy could be useful in ulcerative colitis, another inflammatory bowel disease
CHICAGO --- A team of Northwestern University scientists has developed the first wireless, implantable temperature sensor to detect inflammatory flareups in patients with Crohn’s disease. The approach offers long-term, real-time monitoring and ...
Glucose levels affect cognitive performance in people with type 1 diabetes differently
2024-03-18
A new study led by researchers at McLean Hospital (a member of Mass General Brigham) and Washington State University used advances in digital testing to demonstrate that naturally occurring glucose fluctuations impact cognitive function in people with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). Results showed that cognition was slower in moments when glucose was atypical – that is, considerably higher or lower than someone’s usual glucose level. However, some people were more susceptible to the cognitive effects of large glucose fluctuations than others.
“In trying to understand how diabetes impacts the brain, our research shows that it is important to consider not only how people ...
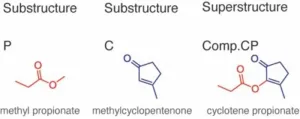
Mimicking exercise with a pill
2024-03-18
NEW ORLEANS, March 18, 2024 — Doctors have long prescribed exercise to improve and protect health. In the future, a pill may offer some of the same benefits as exercise. Now, researchers report on new compounds that appear capable of mimicking the physical boost of working out — at least within rodent cells. This discovery could lead to a new way to treat muscle atrophy and other medical conditions in people, including heart failure and neurodegenerative disease.
The researchers will present their ...
New composite decking could reduce global warming effects of building materials
2024-03-18
NEW ORLEANS, March 18, 2024 — Buildings and production of the materials used in their construction emit a lot of carbon dioxide (CO2), a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming and climate change. But storing CO2 in building materials could help make them more environmentally friendly. Scientists report that they have designed a composite decking material that stores more CO2 than is required to manufacture it, providing a “carbon-negative” option that meets building codes and is less expensive than standard composite decking.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society ...
Artificial mucus identifies link to tumor formation
2024-03-18
NEW ORLEANS, March 18, 2024 – During cold and flu season, excess mucus is a common, unpleasant symptom of illness, but the slippery substance is essential to human health. To better understand its many roles, researchers synthesized the major component of mucus, the sugar-coated proteins called mucins, and discovered that changing the mucins of healthy cells to resemble those of cancer cells made healthy cells act more cancer-like.
The researcher will present her results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2024 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in person March 17-21; it features nearly 12,000 ...
Study explores homeless women’s experiences of ‘period poverty’
2024-03-18
Research from the University of Southampton has identified common issues women face when experiencing periods while homeless.
A review of research published in Women and Health has found homeless women experienced practical challenges in managing menstruation alongside feelings of embarrassment and shame, with many ‘making do’ due to inadequate provision.
The researchers say it’s high time to address the provision of menstrual health resources as a basic human right.
Dr Stephanie Barker, a teaching fellow at the University of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Weight loss caused by common diabetes drug tied to “anti-hunger” molecule in studyA Stanford Medicine study found that metformin, a commonly prescribed diabetes drug associated with moderate weight loss, stimulates production of lac-phe, a molecule abundant after exercise.