Opto-RANK: A light switch for osteoclasts
2024-03-21
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan – Drinking milk helps your bones grow big and strong; but what if direct exposure to light could help too? Now, researchers from Japan report that lighting up bone tissue could help treat bone disease.
In a study published last month in Scientific Reports, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have revealed that a treatment approach based on light could help activate bones to repair themselves.
Bones are constantly being remodeled through the action of osteoclasts, which break down bone tissue, and osteoblasts, which create new bone tissue. Both cell types develop from immature precursor cells, and controlling their activity is a promising approach for treating bone growth disorders.
“Previous studies have used optogenetics, in which target molecules are activated by light, to induce or enhance specific cellular functions,” says the co-senior author of the study Takao Nakata. “However, optogenetics tools have not yet been used to generate mature differentiated cells from their precursors, such as osteoclasts from monocytes/macrophages.”
In this study, the researchers constructed a light-activated form of RANK, an important signaling protein in osteoclast differentiation. They then expressed this optogenetic protein, called Opto-RANK, in macrophages and activated it with light to see if the cells would start to behave like osteoclasts.
“The results were very clear,” explains Tomohiro Ishii, co-senior author. “Opto-RANK responded to blue light activation by forming active clusters that recruited TRAF6, a crucial molecule that regulates osteoclast differentiation.”
In addition, the light-activated cells exhibited activation of three genes that are normally expressed in maturing osteoclasts. The cells also formed many small pits, which is a feature of mature osteoclasts that helps them break down bone tissue.
“Our findings suggest that Opto-RANK can be used to induce macrophage differentiation into osteoclasts and stimulate local bone resorption when activated by blue light,” says Nakata.
The precise control of Opto-RANK activity that can be achieved with light activation could make it a powerful tool for cell therapy, such as the treatment of abnormal calcification diseases and orthodontic issues. In addition, Opto-RANK could be useful beyond bone biology, as RANK signaling is involved in other important functions, such as immunity, body temperature regulation, and tumor development.
###
The article, “Development of an optogenetics tool, Opto‑RANK, for control of osteoclast differentiation using blue light,” was published in Scientific Reports at DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-52056-w
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-03-21
We are used to computers getting faster and faster, but complicated calculations involving lots of data can take a very long time, even today.
This applies to calculations of chemical reactions, how proteins assume different three-dimensional forms and so-called phase transitions, where one chemical substance transitions from one state to another, such as from solid to liquid form.
These types of results are often very important – for example, in the chemical industry.
Down from one year to ten days
These complicated calculations can take years to perform, and access to the most ...
2024-03-21
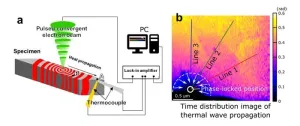
1. A NIMS research team has developed a technique that enables the nanoscale observation of heat propagation paths and behavior within material specimens. This was achieved using a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) capable of emitting a pulsed electron beam and a nanosized thermocouple—a high-precision temperature measurement device developed by NIMS.
2. Public interest in energy conservation and recycling has grown considerably in recent years. This change has inspired scientists to develop next-generation materials/devices capable of controlling and utilizing heat with a high degree of precision, including thermoelectric devices able to ...
2024-03-21
They published their work on Mar. 15th in Energy Material Advances.
"It is highly necessary to design highly conductive and high-performance materials for application in alkaline ion batteries," said paper author Xijun Xu, associate Professor at the College of Chemical Engineering and Light Industry, Guangdong University of Technology.
"In recent years, with the development of large-scale power systems such as electric vehicles, the demand for secondary batteries has gradually shifted towards high power and low cost. Furthermore, in light of the increasing energy and environmental concerns, the exploration of green and renewable ...
2024-03-21
They published their work on Mar. 15th in Energy Material Advances.
"The development of cost-effective and high-performance RP anode materials for LIBs/SIBs is imperative," said paper author Hailei Zhao, professor with the Beijing Key Lab of New Energy Materials and Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, "Despite RP shows a great potential, the inherent poor electrical conductivity of RP (~10-14 S cm-1) and significant volume changes during charge/discharge processes (> 300%) compromise its cycling stability."
Zhao explained that the poor electrical conductivity ...
2024-03-21
In a Finnish outcrop nestled between some of Northern Europe's oldest mountains, researchers have found traces of a previously hidden part of Earth's crust that points more than three billion years back in time and north towards Greenland.
These traces were found in the mineral zircon, which after chemical analyses, indicated to researchers from the Department of Geosciences and Natural Resource Management that the "foundation" upon which Denmark and Scandinavia rest, was probably 'born' from Greenland approximately 3.75 billion years ago.
"Our data suggest that the oldest part of Earth's crust beneath Scandinavia originates ...
2024-03-21
Among the many confounding symptoms in patients recovering from a COVID-19 infection are memory loss and difficulty learning. Yet little is known about the mechanisms of cognitive impairments like these, commonly called brain fog.
In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have identified a mechanism that causes neurological problems in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19. The researchers also found a treatment that helped prevent these changes. Sarah Lutz, assistant professor of anatomy and cell biology in the College of Medicine, led the research, ...
2024-03-21
Highlights:
Legionnaires’ disease is a rare and dangerous respiratory tract infection.
Diagnoses and surveillance usually require culturing isolates.
A new study shows how whole genome sequencing could be used when culturing isn’t an option.
The work points to new avenues for public health surveillance of infectious diseases.
Washington, D.C.—Legionnaires’ disease (LD), a rare and severe type of pneumonia, is a respiratory infection caused by species of Legionella bacteria. One of the most accurate ways to diagnose LD is to perform culture on samples from a patient’s lower respiratory tract, but those samples are difficult ...
2024-03-21
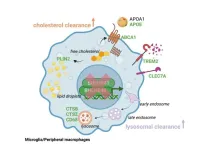
New York, NY [March 21, 2024]—Using novel genetic and genomic tools, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have shed light on the role of immune cells called macrophages in lipid-rich tissues like the brain, advancing our understanding of Alzheimer’s and other diseases. The study, published in the March 6 online issue of Nature Communications [DOI: 0.1038/s41467-024-46315-7], represents a step forward in understanding immune cell regulation and its impact on disease progression.
The researchers initially studied genes controlling macrophages, also referred ...
2024-03-21
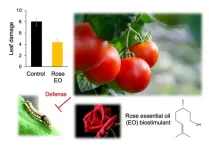
Plants-derived essential oils (EOs) find applications in various industries, such as detergents, cosmetics, pharmacology, and food additives. Moreover, EOs have an exceptional safety profile, and their numerous bioactivities greatly benefit human health. Beyond these benefits, EOs have also been found to illicit insect-repellent responses by inducing neurotoxic effects.
Terpenoids are abundant in plant EOs and have garnered widespread attention as they can regulate plant defense responses by regulating the expression of defense genes. For example, soybean and komatsuna plants, when grown near mint, experience a significant improvement in defense properties ...
2024-03-21
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Identifying genetic variants and the role they play in predisposing people to Alzheimer’s disease can help researchers better understand how to treat the neurodegenerative condition for which there is currently no cure. A new study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) and UTHealth Houston School of Public Health has identified several genetic variants that may influence Alzheimer’s disease risk, putting researchers one step closer to uncovering biological pathways to target for future treatment and prevention.
Published in the journal Alzheimer’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Opto-RANK: A light switch for osteoclasts