(Press-News.org) Among the many confounding symptoms in patients recovering from a COVID-19 infection are memory loss and difficulty learning. Yet little is known about the mechanisms of cognitive impairments like these, commonly called brain fog.
In a new study, researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have identified a mechanism that causes neurological problems in mice infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19. The researchers also found a treatment that helped prevent these changes. Sarah Lutz, assistant professor of anatomy and cell biology in the College of Medicine, led the research, which was published in the journal Brain.
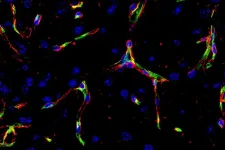
The team focused on the blood-brain barrier, which plays a role in other neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. Normally, this barrier protects the brain from potentially harmful cells or molecules circulating in the bloodstream. But the infected mice, researchers found, had leaky blood-brain barrier vessels and impaired memory or learning.
To understand why, the researchers looked at blood vessels from the brains of infected mice to see which genes were most altered. They found a significant decrease in a signaling pathway called Wnt/beta-catenin, which helps maintain the health of the blood-brain barrier and protects the brain from damage.
With these results, the team explored whether a gene therapy that stimulates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway could prevent brain damage in mice who were infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Indeed, it did just that.
“They had less blood-brain barrier leakage and less immune cell infiltration of the brain, which led to improvements in learning and memory,” Lutz said.
Because age is a risk factor for cognitive impairment in humans with COVID-19, the team focused on older mice in their research. They specifically tracked mild infections in the mice. Mild, rather than severe, infections account for most COVID-19 cases in humans today, thanks to the vaccine. Yet even mild infections can cause cognitive impairment, Lutz said.
While the research is a long way from establishing a therapy for humans to prevent post-infection cognitive impairments, this study is an important step on that path, Lutz said.
“Anytime you can identify a molecular mechanism that contributes to a disease, you’re learning about basic biology and what causes disease in general,” she said. “This research suggests that improving blood-brain barrier integrity could have benefits in preventing complications of COVID-19.”
One major lesson from the COVID-19 pandemic is that even mild infections can profoundly affect organs, including the brain, explained Dr. Jalees Rehman, the Benjamin Goldberg Professor and head of the UIC Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics and a co-author on the study.
“There is a need for more research on respiratory infections that can affect the brain,” Rehman said. “The good news is that by studying the molecular signals activated by the infection as well as during the subsequent inflammation when the immune system responds to infection, one can develop new targeted therapies which prevent further damage to the brain and other organs.”
The other UIC authors of the study are Troy Trevino, Avital Fogel, Guliz Otkiran, Seshadri Niladhuri, Mark Sanborn, Jacob Class, Ali Almousawi and Justin Richner.
Written by Emily Stone
END
Research offers hope for preventing post-COVID ‘brain fog’ by targeting brain’s blood vessels
2024-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Non-culturable Legionella identified with sequencing
2024-03-21
Highlights:
Legionnaires’ disease is a rare and dangerous respiratory tract infection.
Diagnoses and surveillance usually require culturing isolates.
A new study shows how whole genome sequencing could be used when culturing isn’t an option.
The work points to new avenues for public health surveillance of infectious diseases.
Washington, D.C.—Legionnaires’ disease (LD), a rare and severe type of pneumonia, is a respiratory infection caused by species of Legionella bacteria. One of the most accurate ways to diagnose LD is to perform culture on samples from a patient’s lower respiratory tract, but those samples are difficult ...
Immune cells identified as key players in brain health
2024-03-21
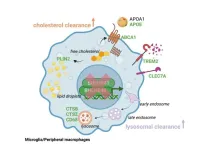
New York, NY [March 21, 2024]—Using novel genetic and genomic tools, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have shed light on the role of immune cells called macrophages in lipid-rich tissues like the brain, advancing our understanding of Alzheimer’s and other diseases. The study, published in the March 6 online issue of Nature Communications [DOI: 0.1038/s41467-024-46315-7], represents a step forward in understanding immune cell regulation and its impact on disease progression.
The researchers initially studied genes controlling macrophages, also referred ...
Rose essential oil: A safe pesticide for organic agriculture
2024-03-21
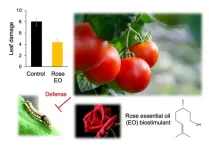
Plants-derived essential oils (EOs) find applications in various industries, such as detergents, cosmetics, pharmacology, and food additives. Moreover, EOs have an exceptional safety profile, and their numerous bioactivities greatly benefit human health. Beyond these benefits, EOs have also been found to illicit insect-repellent responses by inducing neurotoxic effects.
Terpenoids are abundant in plant EOs and have garnered widespread attention as they can regulate plant defense responses by regulating the expression of defense genes. For example, soybean and komatsuna plants, when grown near mint, experience a significant improvement in defense properties ...
Researchers identify novel genetic variants associated with Alzheimer’s disease
2024-03-21
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Identifying genetic variants and the role they play in predisposing people to Alzheimer’s disease can help researchers better understand how to treat the neurodegenerative condition for which there is currently no cure. A new study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) and UTHealth Houston School of Public Health has identified several genetic variants that may influence Alzheimer’s disease risk, putting researchers one step closer to uncovering biological pathways to target for future treatment and prevention.
Published in the journal Alzheimer’s ...
Research team identifies genetic contribution to the composition of the microbiome around maize roots
2024-03-21
In order for plants to grow, they absorb water and nutrients through their roots. In doing so, they rely on tiny helpers: bacteria and fungi in particular are found in a thin layer around the roots. These microbes also ward off organisms that are harmful to the plant, just as the "microbiome" in the human gut helps determine whether we fall ill or stay healthy.
An international research team led by the University of Bonn and with the participation of the IPK Leibniz Institute has now demonstrated on maize plants that the genetic make-up of the host plant has a significant influence on the composition of the root microbes. "It was shown ...
Climate change disrupts vital ecosystems in the Alps
2024-03-21
Reduced snow cover and shifting vegetation patterns in the Alps, both driven by climate change, are having major combined impacts on biodiversity and functioning of ecosystems in the high mountains, according to new research published today.
Mountain ranges covering vast areas of the world are warming much faster than surrounding lowland areas, triggering huge reductions in snow cover and rapid upward movement of dwarf-shrubs, such as heather.
Scientists at The University of Manchester have found that these changes are disrupting the timing of crucial alpine ecosystem functions performed by ...
Say hello to biodegradable microplastics
2024-03-21
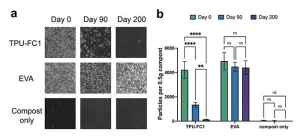
Microplastics are tiny, nearly indestructible fragments shed from everyday plastic products. As we learn more about microplastics, the news keeps getting worse. Already well-documented in our oceans and soil, we’re now discovering them in the unlikeliest of places: our arteries, lungs and even placentas. Microplastics can take anywhere from 100 to 1,000 years to break down and, in the meantime, our planet and bodies are becoming more polluted with these materials every day.
Finding viable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics and microplastics has never been more important. New research from scientists ...
New method for analyzing nanoporous materials
2024-03-21
In addition to their main components, the properties of crystalline and nanoporous materials often depend crucially on guest atoms or ions that are embedded in the tiny pores of their lattice structure. This applies to high-tech materials used in sensor or separation technology as well as to natural materials. The bluish gemstone aquamarine, for example, would be colourless without such guest components. Determining the type and position of guest components is difficult, as many materials react sensitively to the radiation emissions ...
An immunotherapy to overcome resistant leukemia
2024-03-21
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive form of blood cancer. It is caused by mutations in a large number of genes that are acquired in the course of a person’s life. One of these genes – the tumor suppressor gene TP53 – plays a key role. Normally, TP53 helps to prevent the development of tumors. Blood cancer patients in whom this gene is mutated, however, face an extremely poor prognosis, as their genes are resistant to conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Intensive research is therefore being carried out into new therapeutic approaches, ...
The irony of smoking to stay thin: smoking increases belly fat
2024-03-21
The worry of gaining weight is a common excuse for smokers not to quit. A new study published today in the scientific journal Addiction has found that both starting smoking and lifetime smoking may increase abdominal fat, especially visceral fat: the unhealthy fat deep inside the abdomen that is linked to a higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and dementia.
Smokers tend to have lower body weights than non-smokers, but they also have more abdominal fat, and more abdominal visceral fat. Visceral fat is hard to see; you can have ...