(Press-News.org) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive form of blood cancer. It is caused by mutations in a large number of genes that are acquired in the course of a person’s life. One of these genes – the tumor suppressor gene TP53 – plays a key role. Normally, TP53 helps to prevent the development of tumors. Blood cancer patients in whom this gene is mutated, however, face an extremely poor prognosis, as their genes are resistant to conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Intensive research is therefore being carried out into new therapeutic approaches, such as CAR (chimeric antigen receptor) T-cells, which are already being used successfully for other cancers of the blood.
Mutation in blood cancer cells weakens immunotherapy defense cells
An international research team led by Professors Markus Manz and Steffen Boettcher from the University of Zurich (UZH) and the Department of Medical Oncology and Hematology at the University Hospital Zurich (USZ) has now shown that TP53-mutant AML cells are also significantly more resistant to a new type of immunotherapy – CAR T-cell therapy – than AML cells without the mutated gene. “The reason for the poorer effect of CAR T-cells with mutated TP53 is that these immune cells are exhausted more quickly and are therefore less active against the cancer cells,” says Steffen Boettcher, chief of service at USZ.
In CAR T-cell therapy, certain immune cells – the T-cells – are extracted from a patient’s blood. These immune cells are then genetically modified in the lab so that they form numerous new contact points (CARs) on their surface. Reintroduced into the patient, these CAR T-cells are able to recognize certain surface structures on the tumor cells, which enables the CAR T-cells to identify the cancer cells and destroy them in a targeted manner. Various CAR T-cell products are currently being tested against AML in early clinical trials.
Concomitant pharmacotherapies or advanced CAR T-cells are effective against resistant cancer cells
In their study, the researchers not only examined the mechanism underlying the resistance of mutated AML cells to CAR T-cell immunotherapy; they also found out how the endurance of CAR T-cells can be increased and a weak point of TP53-mutant AML cells can be exploited to overcome this resistance. Through additional pharmacological concomitant therapies or further genetic improvement of the CAR T-cells, they were able to drastically increase the effectiveness of CAR T-cells against TP53-mutant AML cells to the point where there was no longer any therapeutic difference compared to non-mutated AML cells.
“This proof-of-principle study shows that concurrent pharmacological therapies and genetically engineered CAR T-cells are promising strategies to develop more effective and tolerable immunotherapies for patients with TP53-mutant AML,” says head of clinic Markus Manz.
END
An immunotherapy to overcome resistant leukemia
2024-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The irony of smoking to stay thin: smoking increases belly fat
2024-03-21
The worry of gaining weight is a common excuse for smokers not to quit. A new study published today in the scientific journal Addiction has found that both starting smoking and lifetime smoking may increase abdominal fat, especially visceral fat: the unhealthy fat deep inside the abdomen that is linked to a higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and dementia.
Smokers tend to have lower body weights than non-smokers, but they also have more abdominal fat, and more abdominal visceral fat. Visceral fat is hard to see; you can have ...
Healing eyes with contact lenses
2024-03-21
A cross-disciplinary University of Waterloo team has developed a new contact lens material that could act as a bandage for corneal wounds while releasing drugs in a controlled manner to help the eye heal faster.
Typically, corneal abrasion patients spend seven to 10 days wearing a clear, oxygen-permeable bandage contact lens, often instilled with eyedrops containing antibiotics. However, the one-time antibiotic application makes it difficult to ensure enough drugs stay on the eye for sustained treatment.
“It’s a targeted-release drug delivery ...
Excess temperatures cause low flocking concerns
2024-03-21
High temperatures during critical periods of the reproductive cycle of sheep result in 2.1 million fewer lambs produced in Australia each year, costing sheep farmers an estimated $97 million annually.
The work, funded by Meat and Livestock Australia and conducted by a transdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Adelaide and South Australian Research Development Institute (SARDI), found that days above 32°C during the week of mating caused the significant loss of potential lambs.
Published in Nature Food, the study found annual losses of potential lambs would increase to 2.5 million if median global warming increased ...
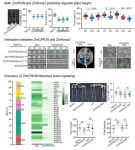
The maize ZmCPK39-ZmKnox2 module regulates plant height
2024-03-21
This study was led by Professor Mingliang Xu (College of Agronomy and Biotechnology, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China). Through phylogenic analysis, the authors identified a gene encoding a calcium-dependent protein kinase, ZmCPK39, as a candidate gene for plant height regulation in maize. The function of ZmCPK39 in controlling plant height has been verified using gene editing technology. Compared to the wild-type ND101, knockout of ZmCPK39 significantly reduced plant height by 40%.
The authors further ...
New route to recyclable polymers from plants
2024-03-21
Cellulose, abundantly available from plant biomass, can be converted into molecules used to make a new class of recyclable polymers, to sustainably replace some plastics.
Researchers at Hokkaido University have taken a significant step forward in the drive to make recyclable yet stable plastics from plant materials. This is a key requirement to reduce the burden of plastic pollution in the environment. They developed a convenient and versatile method to make a variety of polymers from chemicals derived from plant cellulose; crucially, these polymers can be fully recycled. The method was published in the journal ACS Macro Letters.
Cellulose is one of the most abundant ...
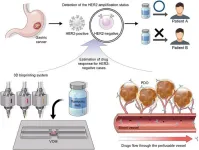
Revolutionizing gastric cancer treatment through personalized 3D bioprinting
2024-03-21
Gastric cancer ranks among the most widespread diseases in Asian populations, with South Koreans experiencing the third-highest incidence globally in 2020, as reported by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Recently, a collaborative research effort between Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and Yonsei University achieved advancement in the realm of precision personalized medicine for gastric cancer. By using 3D bioprinting to accurately replicate the biological environment surrounding gastric cancer cells, the researchers have achieved a significant ...
How neural inhibition could reduce alcohol use
2024-03-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Neuroscientists at Scripps Research have found that inhibiting neurons involved in the body’s stress response may reduce alcohol consumption in people who have both post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD)—even if they still experience trauma-related anxiety.
The findings were published March 21 in Molecular Psychiatry. These discoveries are helping untangle the complex role that stress and trauma play in neurological disorders like PTSD and AUD, while also informing the development of new treatment options for people who experience both these conditions simultaneously.
“Traumatic ...
The Lancet: Dramatic declines in global fertility rates set to transform global population patterns by 2100
2024-03-21
Embargoed access to the paper and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
By 2050, over three-quarters (155 of 204) of countries will not have high enough fertility rates to sustain population size over time; this will increase to 97% of countries (198 of 204) by 2100.
Pronounced shifts in patterns of livebirths are also predicted, with the share of the world’s live births nearly doubling in low-income regions from 18% in 2021 to 35% in 2100; and sub-Saharan Africa accounting for one in every two children born on the planet by 2100.
In low-income settings with higher fertility rates, better access to contraceptives and female education ...
NHS needs 32 billion cash injection to recover shortfall and help tackle current crisis
2024-03-21
The NHS needs an immediate cash injection of around £8.5bn a year over the next four years to make up a £32bn shortfall in funding and help tackle the current crisis, especially in areas such as waiting times, access to primary care, workforce and capital investment, say experts in the second report of The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS.
John Appleby and colleagues argue that, while the government’s recent spring budget funding pledges are a start, they “certainly will not make up the significant shortfall that the NHS ...
Many publicly accessible AI assistants lack adequate safeguards to prevent mass health disinformation
2024-03-21
Effective processes for reporting and responding to safeguard vulnerabilities are also lacking, warn experts
Many publicly accessible artificial intelligence (AI) assistants lack adequate safeguards to consistently prevent the mass generation of health disinformation across a broad range of topics, warn experts in The BMJ today.
They call for enhanced regulation, transparency, and routine auditing to help prevent advanced AI assistants from contributing to the generation of health disinformation.
Large language models (LLMs) are a form of generative AI that have the potential to greatly improve many aspects of society, including ...