(Press-News.org) In order for plants to grow, they absorb water and nutrients through their roots. In doing so, they rely on tiny helpers: bacteria and fungi in particular are found in a thin layer around the roots. These microbes also ward off organisms that are harmful to the plant, just as the "microbiome" in the human gut helps determine whether we fall ill or stay healthy.
An international research team led by the University of Bonn and with the participation of the IPK Leibniz Institute has now demonstrated on maize plants that the genetic make-up of the host plant has a significant influence on the composition of the root microbes. "It was shown that the root microbiome is strongly dependent on stress conditions such as nutrient or water deficiency," says Dr. Yong Jiang, one of the first authors of the study and a scientist in IPK's research group “Quantitative Genetics”.
The genetic make-up of different maize varieties varies greatly. Regional varieties are adapted to very different environmental conditions, depending on whether they are grown in the cooler highlands or warmer lowlands of South America. "The centuries-long selection of maize varieties adapted to the local climate led to very different genotypes, which we were able to use for the study," says Dr. Peng Yu, head of the junior research group "Functional Root Biology" at the University of Bonn.
The research team has now analysed 129 maize varieties. These were grown under "normal" conditions and under a lack of phosphorus, nitrogen and water. In addition, the DNA of microbes from 3,168 samples taken from the layer around the roots, which is just a few millimetres thick, was sequenced.
The role of the genetic material in the root was revealed under stress conditions. Nutrient and water deficiency also had an influence on the composition of the microbes. However, under the same stress conditions, differences in the microbiome of the maize varieties were nevertheless revealed. "We have shown that certain maize genes interact with certain bacteria," explains Dr. Peng Yu.
The international research team was even able to use data on the growing conditions at the place of origin of a particular maize variety and its genetic make-up to predict which key organisms occur in the microbiome at the root. Bacteria of the genus Massilia stood out in particular: "It was striking that only a few specimens of these microbes were present when there was a sufficient supply of nitrogen," explains Prof. Dr. Gabriel Schaaf from the Ecophysiology of Plant Nutrition department at INRES and member of the PhenoRob Cluster of Excellence at the University of Bonn. If, on the other hand, nitrogen was scarce, many Massilia were found at the roots. The team then "inoculated" maize roots with this bacterium. This showed that the plants subsequently formed many more lateral roots and thus significantly improved their nutrient and water uptake.
In further investigations, the researchers discovered that the root attracts Massilia bacteria with flavones. This is a plant pigment that stimulates the formation of lateral roots with the help of the bacteria. "However, the prerequisite for this was that the maize plant had a microtubule-binding gene," says Dr. Peng Yu.
"For this study, we also opened up the toolbox of quantitative genetics for microbiome research," explains IPK scientist Dr. Yong Jiang. "We were surprised by the large proportion of the genetic component in the formation of the microbiome." The results can be used by both science and breeding. "They can serve as a basis for investigating further agroecological issues and for developing new maize varieties that are better adapted to climate change based on the genome and microbiome data."
END
Research team identifies genetic contribution to the composition of the microbiome around maize roots
2024-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change disrupts vital ecosystems in the Alps
2024-03-21
Reduced snow cover and shifting vegetation patterns in the Alps, both driven by climate change, are having major combined impacts on biodiversity and functioning of ecosystems in the high mountains, according to new research published today.
Mountain ranges covering vast areas of the world are warming much faster than surrounding lowland areas, triggering huge reductions in snow cover and rapid upward movement of dwarf-shrubs, such as heather.
Scientists at The University of Manchester have found that these changes are disrupting the timing of crucial alpine ecosystem functions performed by ...
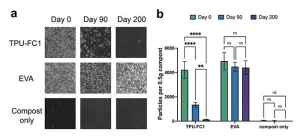
Say hello to biodegradable microplastics
2024-03-21
Microplastics are tiny, nearly indestructible fragments shed from everyday plastic products. As we learn more about microplastics, the news keeps getting worse. Already well-documented in our oceans and soil, we’re now discovering them in the unlikeliest of places: our arteries, lungs and even placentas. Microplastics can take anywhere from 100 to 1,000 years to break down and, in the meantime, our planet and bodies are becoming more polluted with these materials every day.
Finding viable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics and microplastics has never been more important. New research from scientists ...
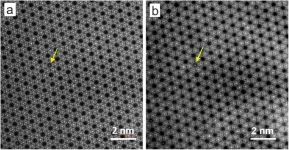
New method for analyzing nanoporous materials
2024-03-21
In addition to their main components, the properties of crystalline and nanoporous materials often depend crucially on guest atoms or ions that are embedded in the tiny pores of their lattice structure. This applies to high-tech materials used in sensor or separation technology as well as to natural materials. The bluish gemstone aquamarine, for example, would be colourless without such guest components. Determining the type and position of guest components is difficult, as many materials react sensitively to the radiation emissions ...
An immunotherapy to overcome resistant leukemia
2024-03-21
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive form of blood cancer. It is caused by mutations in a large number of genes that are acquired in the course of a person’s life. One of these genes – the tumor suppressor gene TP53 – plays a key role. Normally, TP53 helps to prevent the development of tumors. Blood cancer patients in whom this gene is mutated, however, face an extremely poor prognosis, as their genes are resistant to conventional chemotherapeutic agents. Intensive research is therefore being carried out into new therapeutic approaches, ...
The irony of smoking to stay thin: smoking increases belly fat
2024-03-21
The worry of gaining weight is a common excuse for smokers not to quit. A new study published today in the scientific journal Addiction has found that both starting smoking and lifetime smoking may increase abdominal fat, especially visceral fat: the unhealthy fat deep inside the abdomen that is linked to a higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and dementia.
Smokers tend to have lower body weights than non-smokers, but they also have more abdominal fat, and more abdominal visceral fat. Visceral fat is hard to see; you can have ...
Healing eyes with contact lenses
2024-03-21
A cross-disciplinary University of Waterloo team has developed a new contact lens material that could act as a bandage for corneal wounds while releasing drugs in a controlled manner to help the eye heal faster.
Typically, corneal abrasion patients spend seven to 10 days wearing a clear, oxygen-permeable bandage contact lens, often instilled with eyedrops containing antibiotics. However, the one-time antibiotic application makes it difficult to ensure enough drugs stay on the eye for sustained treatment.
“It’s a targeted-release drug delivery ...
Excess temperatures cause low flocking concerns
2024-03-21
High temperatures during critical periods of the reproductive cycle of sheep result in 2.1 million fewer lambs produced in Australia each year, costing sheep farmers an estimated $97 million annually.
The work, funded by Meat and Livestock Australia and conducted by a transdisciplinary team of researchers from the University of Adelaide and South Australian Research Development Institute (SARDI), found that days above 32°C during the week of mating caused the significant loss of potential lambs.
Published in Nature Food, the study found annual losses of potential lambs would increase to 2.5 million if median global warming increased ...
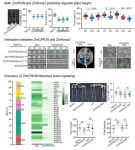
The maize ZmCPK39-ZmKnox2 module regulates plant height
2024-03-21
This study was led by Professor Mingliang Xu (College of Agronomy and Biotechnology, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China). Through phylogenic analysis, the authors identified a gene encoding a calcium-dependent protein kinase, ZmCPK39, as a candidate gene for plant height regulation in maize. The function of ZmCPK39 in controlling plant height has been verified using gene editing technology. Compared to the wild-type ND101, knockout of ZmCPK39 significantly reduced plant height by 40%.
The authors further ...
New route to recyclable polymers from plants
2024-03-21
Cellulose, abundantly available from plant biomass, can be converted into molecules used to make a new class of recyclable polymers, to sustainably replace some plastics.
Researchers at Hokkaido University have taken a significant step forward in the drive to make recyclable yet stable plastics from plant materials. This is a key requirement to reduce the burden of plastic pollution in the environment. They developed a convenient and versatile method to make a variety of polymers from chemicals derived from plant cellulose; crucially, these polymers can be fully recycled. The method was published in the journal ACS Macro Letters.
Cellulose is one of the most abundant ...
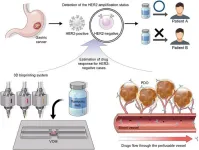
Revolutionizing gastric cancer treatment through personalized 3D bioprinting
2024-03-21
Gastric cancer ranks among the most widespread diseases in Asian populations, with South Koreans experiencing the third-highest incidence globally in 2020, as reported by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. Recently, a collaborative research effort between Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) and Yonsei University achieved advancement in the realm of precision personalized medicine for gastric cancer. By using 3D bioprinting to accurately replicate the biological environment surrounding gastric cancer cells, the researchers have achieved a significant ...