(Press-News.org) There were multiple unsafe sleep practices at play in more than three-quarters of Sudden Unexpected Infant Deaths reported in 23 jurisdictions between 2011 and 2020, a new study reveals. The researchers say the findings underscore the need for more comprehensive safe-sleep education for new parents, including from healthcare providers.
Of 7,595 infant deaths reviewed, almost 60% of the infants were sharing a sleep surface, such as a bed, when they died. This practice is strongly discouraged by sleep experts, who warn that a parent or other bed partner could unintentionally roll over and suffocate the baby.
Infants who died while sharing a sleep surface were typically younger (less than 3 months old), non-Hispanic Black, publicly insured, and either in the care of a parent at the time of death or being supervised by someone impaired by drugs or alcohol. These infants were typically found in an adult bed, chair or couch instead of the crib or bassinet recommended by sleep experts.
“The large number of hazardous sleep practices for both infants who were sharing a sleep surface and sleeping alone at the time of death is alarming,” said researcher Fern Hauck, MD, MS, a safe-sleep expert at UVA Health and the University of Virginia School of Medicine. “These are known risk factors for SUID [Sudden Unexpected Infant Death], and tells us that we need to do a better job of working with families to increase acceptance of the recommendations to create safer sleep spaces for their infants.”
Sudden Unexpected Infant Deaths
To better understand the factors contributing to SUID and improve safe-sleep messaging, Hauck and her collaborators analyzed data from the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s SUID Case Registry. That data reflects localities from Alaska to Wyoming, including the Tidewater area of Virginia.
Examining the registry allowed the researchers to obtain important insights on the prevalence of practices such as prenatal smoking, a known risk factor for SUID, and breastfeeding, which is thought to have a protective benefit. More than 36% of mothers of infants who died had smoked while pregnant. This percentage was higher among moms who bed shared than those who didn’t, 41.4% to 30.5%. Both bed sharers and non-bed sharers had breastfed at similar rates.
The researchers note that it was rare for bedsharing to be the only risk factor present during a child’s death. The findings highlight the need for better public education about safe-sleep practices, and for care providers to take a more active role in teaching new parents about the practices, the researchers say.
“Our findings support comprehensive safe sleep counseling for every family at every encounter beyond just asking where an infant is sleeping,” the researchers write in a new paper in the journal Pediatrics.
In addition to helping parents understand safe-sleep practices, care providers should take steps to ensure parents can follow those practices once they leave the hospital. For example, some families may not have the means to purchase a crib or bassinet; a hospital might direct them to resources to help with that.
“SUID deaths in the U.S. are still higher than in most other countries, and this is unacceptable,” Hauck said. “Clinicians and others caring for infants need to have thoughtful conversations with families at risk to understand the barriers to following safe-sleep guidelines and find ways to work together to overcome them.”
About the SUID Research Team
The SUID research team consisted of Alexa B. Erck Lambert, Carrie K. Shapiro-Mendoza, Sharyn E. Parks, Carri Cottengim, Meghan Faulkner and Hauck. The researchers have no financial interest in the work.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog
END
Multiple unsafe sleep practices found in most sudden infant deaths
2024-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson’s Institute for Data Science in Oncology announces appointment of inaugural IDSO Affiliates
2024-03-22
HOUSTON ― The Institute for Data Science in Oncology (IDSO) at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the appointment of its inaugural cohort of IDSO Affiliates. These 33 talented scientists, clinicians and staff bring diverse expertise to help IDSO leadership and focus area co-leads advance collaborative data science projects and align the institute’s efforts with MD Anderson’s mission to end cancer.
“We are proud to welcome these exceptional individuals to the growing IDSO community, and we look forward ...
B4C@TiB2 core–shell structural units show outstanding toughening effect for Al2O3 ceramics
2024-03-22
Toughening has always been an important research direction of structure ceramics. The addition of secondary phases to the ceramic matrix to prepare composite ceramics is an effective toughening pathway in the field of structure ceramics. Both phase-type and microstructure of the secondary phases play a decisive role in the toughening effect of the ceramic matrix. Being different from the conventional independent phase as the secondary phase, B4C@TiB2 core–shell structural unit has been purposely designed as an innovative kind of secondary phase to toughen the Al2O3 ceramic matrix, providing a new concept for the toughening studies of structural ceramics.
A ...
Messenger RNAs with multiple “tails” could lead to more effective therapeutics
2024-03-22
Messenger RNA (mRNA) made its big leap into the public limelight during the pandemic, thanks to its cornerstone role in several COVID-19 vaccines. But mRNAs, which are genetic sequences that instruct the body to produce proteins, are also being developed as a new class of drugs. For mRNAs to have broad therapeutic uses, however, the molecules will need to last longer in the body than those that make up the COVID vaccines.
Researchers from the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and MIT have engineered a ...
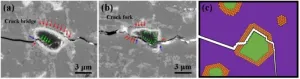
3D images reveal link between crack complexity and material toughness
2024-03-22
The last time you dropped a favorite mug or sat on your glasses, you may have been too preoccupied to take much notice of the intricate pattern of cracks that appeared in the broken object. But capturing the formation of such patterns is the specialty of John Kolinski and his team at the Laboratory of Engineering Mechanics of Soft Interfaces (EMSI) in EPFL’s School of Engineering. They aim to understand how cracks propagate in brittle solids, which is essential for developing and testing safe and cost-effective composite materials for use in construction, sports, and aerospace engineering.
But traditional mechanics approaches to analyzing crack formation assume ...
Decommissioned offshore structures could offer only limited ecological benefits
2024-03-22
Decommissioned offshore structures offer limited long-term ecological benefits if they are simply left in the ocean to serve as artificial reefs, a new study suggests.
The research, published in the journal Nature Sustainability, saw researchers carrying out a comprehensive analysis of existing studies into the environmental impacts of marine artificial structures – including oil and gas platforms and offshore wind farms – all over the world.
It highlighted that such installations can offer some ecological benefits – including increasing the diversity and abundance of fish species – in areas where the ...
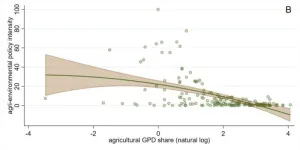
All countries’ agri-environmental policies at a glance
2024-03-22
There can be no analysis without data. In this spirit, researchers from the University of Bonn and the Swiss Federal Institution of Technology (ETH) Zurich have published a database containing over 6,000 agri-environmental policies, thus enabling their peers as well as policymakers and businesses to seek answers to all manner of different questions. The researchers have used two examples to demonstrate how this can be done: how a country’s economic development is linked to its adoption of agri-environmental policies and how such policies impact soil erosion. Their study has now been published in “Nature Food.” Embargo: Don´t publish before March 22, ...
Bees need food up to a month earlier than provided by recommended pollinator plants
2024-03-22
Embargoed until 08:00 AM GMT / 04:00 AM ET Friday 22 March 2024
Bees need food up to a month earlier than provided by recommended pollinator plants
Plant species which are recommended as ‘pollinator friendly’ in Europe begin flowering up to a month too late for bees, resulting in low colony survival and low production of queens.
This is the first time that research has quantified the decline in colony survival and queen production due to a shortage of early season food.
Enhancing ...
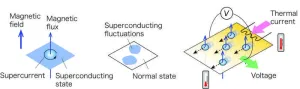
Discovery of a hidden quantum critical point in two-dimensional superconductors
2024-03-22
Weak fluctuations in superconductivity1, a precursor phenomenon to superconductivity, have been successfully detected by a research group of Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech). This breakthrough was achieved by measuring the thermoelectric effect2 in superconductors over a wide range of magnetic fields and over a wide range of temperatures from much higher than the superconducting transition temperature to very low temperatures near absolute zero. This revealed the full picture of fluctuations in superconductivity ...
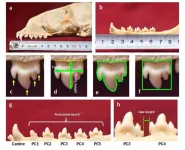
Multi-cusped postcanine teeth are associated with zooplankton feeding in phocid seals.
2024-03-22
The morphology of an animal's teeth often reflects its diet. A well-known example of a mammal that feeds in the water is the crabeater seal (Lobodon carcinophaga), which consumes large amounts of zooplankton. Crabeater seals have complex, jagged teeth, which are believed to function as a sieve to retain krill in their mouths and filter it from seawater. Furthermore, recent studies have shown that the Baikal seal (Pusa sibirica) also preys on large quantities of zooplankton and possesses distinctive jagged teeth. Thus, while behavioral observations and tooth morphology studies suggest a ...
Outcomes after stem cell transplant in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia have improved since 2000
2024-03-22
Bottom Line: Among patients over 65 who received an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT) for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) between 2000 and 2021, leukemia-free and overall survival improved significantly over time.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)
Author: Ali Bazarbachi, MD, PhD, senior author of the study and a professor at the American University of Beirut in Lebanon
Background: AML ...