● Background
A superconductor is a material in which electrons pair up at low temperatures, resulting in zero electrical resistance. It is used as a material for powerful electromagnets in medical MRI and other applications. They are also deemed crucial as tiny logic elements in quantum computers that operate at cryogenic temperatures, and there is a need to elucidate the properties of superconductors at cryogenic temperatures when they are microminiaturized.
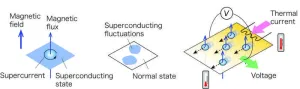
Atomically thin two-dimensional superconductors are strongly affected by fluctuations and thus exhibit properties that differ significantly from those of thicker superconductors. There are two types of fluctuations: thermal (classical), which is more pronounced at high temperatures, and quantum, which is more important at very low temperatures, and the latter causes a variety of interesting phenomena. For example, when a magnetic field is applied perpendicularly to a two-dimensional superconductor at absolute zero and increased, a transition occurs from zero resistance superconductivity to an insulator with localized electrons. This phenomenon is called the magnetic field-induced superconductor-insulator transition and is a typical example of a quantum phase transition4 caused by quantum fluctuations. However, it has been known since the 1990s that for samples with relatively weak localization effects, an anomalous metallic state appears in the intermediate magnetic field region where the electrical resistance is several orders of magnitude lower than the normal state. The origin of this anomalous metallic state is thought to be a liquid-like state in which magnetic flux lines (Fig. 1 left) that penetrate into the superconductor move around due to quantum fluctuations. However, this prediction has not been substantiated because most previous experiments on two-dimensional superconductors have used electrical resistivity measurements that examine the voltage response to current, making it difficult to distinguish between voltage signals originating from the motion of magnetic flux lines and those originating from the scattering of normal-conducting electrons.
A research team led by Assistant Professor Koichiro Ienaga and Professor Satoshi Okuma of the Department of Physics, School of Science at Tokyo Tech reported in Physical Review Letters in 2020 that quantum motion of magnetic flux lines occurs in an anomalous metallic state by using the thermoelectric effect, in which voltage is generated with respect to heat flow (temperature gradient) rather than current. However, to further clarify the origin of the anomalous metallic state, it is necessary to elucidate the mechanism by which the superconducting state is destroyed by quantum fluctuation and transitions to the normal (insulating) state. In this study, they performed measurements aimed at detecting the superconducting fluctuation state (center of Fig. 1), which is a precursor state of superconductivity and is thought to exist in the normal state.
● Research results
In this study, a molybdenum-germanium (MoxGe1-x) thin films with an amorphous structure5, known as a two-dimensional superconductor with uniform structure and disorder, was fabricated and used. It is 10 nanometers thick (one nanometer is one billionth of a meter) and promises to have the fluctuation effects characteristic of two-dimensional systems. Since fluctuation signals cannot be detected by electrical resistivity measurements because they are buried in the signal of normal-conducting electron scattering, we performed thermoelectric effect measurements, which can detect two types of fluctuations: (1) superconducting fluctuations (fluctuations in the amplitude of superconductivity) and (2) magnetic flux line motion (fluctuations in the phase of superconductivity). When a temperature difference is applied in the longitudinal direction of the sample,the superconducting fluctuations and the motion of the magnetic flux lines generate a voltage in the transverse direction. In contrast, normal electron motion generates voltage primarily in the longitudinal direction. Especially in samples such as amorphous materials, where electrons do not move easily, the voltage generated by electrons in the transverse direction is negligible, so the fluctuation contribution alone can be selectively detected by measuring the transverse voltage (Fig. 1, right).
The thermoelectric effect was measured in a variety of magnetic fields and in a variety of temperatures ranging from much higher than the superconducting transition temperature of 2.4 K (Kelvin) to very low temperature of 0.1 K (1/3000 of 300 K, the room temperature), which is close to absolute zero. That reveals that superconducting fluctuations survive not only in the liquid region of the magnetic flux (dark red region in Fig. 2), where superconducting phase fluctuations are more pronounced, but also over a wide temperature-magnetic field region farther outwards that is considered to be the normal-state region, where superconductivity is destroyed (the high-temperature and high-magnetic field region above the upper convex solid line in Fig. 2). Notably, the crossover line between thermal (classical) and quantum fluctuations was successfully detected for the first time (thick solid line in Fig. 2). The value of the magnetic field when the crossover line reaches absolute zero likely corresponds to the quantum critical point where quantum fluctuations are strongest, and that point (white circle in Fig. 2) is clearly located inside the magnetic field range where an anomalous metallic state was observed in the electrical resistance. It was not possible to detect the existence of this quantum critical point from electrical resistivity measurements until now. This result reveals that the anomalous metallic state in a magnetic field at absolute zero in two-dimensional superconductors, which has remained unresolved for 30 years, originates from the existence of the quantum critical point. In other words, the anomalous metallic state is a broadened quantum critical ground state for the superconductor-insulator transition.
● Social impact
The thermoelectric effect measurements obtained for amorphous conventional superconductors can be regarded as standard data for the thermoelectric effect on superconductors, since they capture purely the effect of fluctuations in superconductivity without the contribution of normal-state electrons. The thermoelectric effect is important in terms of its application to electric cooling systems, etc., and there is a need to develop materials that exhibit a large thermoelectric effect at low temperatures to extend the limit of cooling temperatures. Anomalously large thermoelectric effects have been reported at low temperatures in certain superconductors, and comparison with the present data may provide a clue to their origin.
● Future development
Of academic interest that will be developed in this study is demonstrating the theoretical prediction that in two-dimensional superconductors with stronger localization effects than the present sample, the magnetic flux lines will be in a quantum condensed state6. Moving forward, we plan to deploy experiments using the methods of this study with the aim of detecting them.
The results of this study were published online in Nature Communications on March 16th, 2024.
[Terms]
Fluctuations in superconductivity: The strength of superconductivity is not uniform and fluctuates in time and space. It is normal for thermal fluctuations to occur, but near absolute zero, quantum fluctuations occur based on the quantum mechanical uncertainty principle.
Thermoelectric effect: An effect of exchanging thermal and electrical energy. A voltage is generated when a temperature difference is applied, while a temperature difference is produced when a voltage is applied. The former is being studied for application as a power generation device and the latter as a cooling device. In this study, it is used as a method to detect fluctuations in superconductivity.
Two-dimensional superconductivity: A very thin superconductor. When the thickness becomes thinner than the distance between the pairs of electrons responsible for superconductivity, the effect of fluctuations in superconductivity becomes stronger, and the properties of the superconductors are very different from those of thicker superconductors.
Quantum critical point, quantum phase transition: A phase transition that occurs at absolute zero when a parameter such as a magnetic field is changed is called a quantum phase transition, and is distinguished from a phase transition caused by a temperature change. The quantum critical point is the phase transition point where a quantum phase transitions occur and where quantum fluctuations are strongest.
Amorphous structure: A structure of material in which atoms are arranged in an irregular manner and which has no crystalline structure.
Quantum condensed state: A state in which a large number of particles fall into the lowest energy state and behave as a singular macroscopic wave. In the superconducting state, many pairs of electrons are condensed. Liquid helium also condenses when cooled to 2.17 K, producing a superfluidity with zero viscosity.
About Tokyo Institute of Technology
Tokyo Tech stands at the forefront of research and higher education as the leading university for science and technology in Japan. Tokyo Tech researchers excel in fields ranging from materials science to biology, computer science, and physics. Founded in 1881, Tokyo Tech hosts over 10,000 undergraduate and graduate students per year, who develop into scientific leaders and some of the most sought-after engineers in industry. Embodying the Japanese philosophy of “monotsukuri,” meaning “technical ingenuity and innovation,” the Tokyo Tech community strives to contribute to society through high-impact research.
https://www.titech.ac.jp/english/
END