(Press-News.org) Archaeological analysis of a near unique animal cemetery discovered in London nearly 30 years ago has revealed the international scale of horse trading by the elites of late medieval and Tudor England.
Using advanced archaeological science techniques, including studying chemical composition, researchers have been able to identify the likely origins of several physically elite horses and the routes they took to reach British shores during the formative years of their life.
These animals – akin to modern supercars – were sourced from a variety of locations across Europe specifically for their height and strength and imported for use in jousting tournaments and as status symbols of 14th- to 16th-century life. They include three of the tallest animals known from late medieval England, standing up to 1.6 metres or 15.3 hands high, which while quite small by modern standards would have been very impressive for their day.
The skeletons of the horses were recovered from a site under the modern-day Elverton Street in the City of Westminster, which was excavated in advance of building works in the 1990s. In medieval times, the cemetery would have been located outside the walled City of London but was close to the royal palace complex at Westminster.
The research, led by the University of Exeter, and funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council, is published in the latest edition of Science Advances.
“The chemical signatures we measured in the horse’s teeth are highly distinctive and very different to anything we would expect to see in a horse that grew up in the UK,” said Dr Alex Pryor, Senior Lecturer in Archaeology and lead researcher. “These results provide direct and unprecedented evidence for a variety of horse movement and trading practices in the Middle Ages. Representatives for the King and other medieval London elites were scouring horse trading markets across Europe seeking out the best quality horses they could find and bringing them to London. It’s quite possible that the horses were ridden in the jousting contests we know were held in Westminster, close to where the horses were buried.”
In the first experiment of its kind to be conducted on medieval horse remains, the researchers took 22 molar teeth from 15 individual animals and drilled out portions of the enamel for isotope analysis. By measuring isotope ratios of the elements strontium, oxygen and carbon present within the teeth and comparing the results with known ranges in different geographies, the team was able to identify the potential origin of each horse – and accurately rule out others, including prime European horse-breeding centres such as Spain and southern Italy.
Dr Pryor said that at least half of the horses had diverse international origins, possibly Scandinavia, the Alps and other northern and eastern European locations. The results, the researchers conclude, were consistent with the breeding patterns of royal stud farms, where horses would reside until their second or third year, before they would either be broken and trained or sent elsewhere to be sold.
Physical analysis of the teeth revealed wear suggestive of heavy use of a curb bit, often employed with elite animals, especially those groomed for war and tournaments after the 14th century. Bit wear on two of the mares also suggested they were used under saddle or in harness and for breeding. And analysis of the skeletons revealed many of them to be well above average size, with several instances of fused lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae indicative of a life of riding and hard work.
“The finest medieval horses were like modern supercars – inordinately expensive and finely tuned vehicles that proclaimed their owner’s status,” added Professor Oliver Creighton, a medieval specialist at the University of Exeter and part of the research team. “And at Elverton Street, our research team seem to have found evidence for horses used in jousting – the sport of kings, in which riders showcased their fighting skills and horsemanship on elite mounts.
“The new findings provide a tangible archaeological signature of this trade, emphasising its international scale. It is apparent that the medieval London elite were explicitly targeting the highest quality horses they could find at a European scale.”
The paper, Isotopic biographies reveal horse rearing and trading networks in medieval London, can be accessed via Science Advances.
END
Tudor era horse cemetery in Westminster revealed as likely resting place for elite imported animals
2024-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers uncover protein interactions controlling fertility in female mice
2024-03-22
Francis Crick Institute press release
Under strict embargo: 18:00hrs GMT Friday 22 March 2024
Peer reviewed
Experimental study
Animals
Researchers uncover protein interactions controlling fertility in female mice
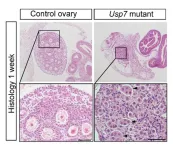
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have shed light on the proteins controlling the development of ovaries in mice before and after birth. This could lead to a better understanding of how female infertility develops.
Following their research identifying the gene responsible for initiating the development ...
Scientists explore complex pattern of tipping points in the Atlantic’s current system
2024-03-22
An international team of scientists have warned against relying on nature providing straightforward ‘early warning’ indicators of a climate disaster, as new mathematical modelling shows new fascinating aspects of the complexity of the dynamics of climate.
It suggests that the climate system could be more unpredictable than previously thought.
By modelling the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, one of the main ocean current systems, the team which included mathematicians from the University of Leicester have found that the stability of ...
University College Dublin seeking to appoint a Full Professor of Data Science for Weather and Climate
2024-03-22
As part of a new multi-million-euro academic research programme at University College Dublin (UCD) funded by Met Éireann (the Irish National Meteorological Service) to support the further development of weather and climate services for Ireland using data science and Artificial Intelligence (AI), UCD is seeking to appoint a Full Professor of Data Science for Weather and Climate.
This exciting new senior academic post is a permanent position in the UCD School of Mathematics and Statistics arising from a funding award of €5 million over five years from Met Éireann, ...
Scientists uncover evidence that microplastics are contaminating archaeological remains
2024-03-22
Researchers have for the first time discovered evidence of microplastic contamination in archaeological soil samples.
The team discovered tiny microplastic particles in deposits located more than seven metres deep, in samples dating back to the first or early second century and excavated in the late 1980s.
Preserving archaeology in situ has been the preferred approach to managing historical sites for a generation. However, the research team say the findings could prompt a rethink, with the tiny particles potentially compromising the preserved remains.
Microplastics are small plastic particles, ranging from 1μm (one thousandth of a millimetre) ...
Toronto researchers devise new way to find proteins for targeted treatment of disease
2024-03-22
Researchers at the University of Toronto and Sinai Health have created a new platform to identify proteins that can be co-opted to control the stability of other proteins — a new but largely unrealized approach to the treatment of disease.
The researchers developed a method to interrogate the entire human proteome for ‘effector’ proteins, which can influence the stability of other proteins via induced proximity. The study marks the first time researchers have searched for effector proteins on this scale, and has identified many new effectors that could be used therapeutically.
“We found more than 600 new effector proteins in 14,000 ...
Researchers invent artificial intelligence model to design new superbug-fighting antibiotics
2024-03-22
Attention editors: Under embargo by the journal Nature Machine Intelligence until Friday, March 22, 12 p.m. eastern
Hamilton, ON, Mar. 22, 2024 – Researchers at McMaster University and Stanford University have invented a new generative artificial intelligence model which can design billions of new antibiotic molecules that are inexpensive and easy to build in the laboratory.
The worldwide spread of drug-resistant bacteria has created an urgent need for new antibiotics, but even modern AI methods are limited ...
An avocado a day may improve overall diet quality, researchers report
2024-03-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Eating one avocado per day may improve overall diet quality, according to a team led by researchers in Penn State’s Department of Nutritional Sciences. Poor diet quality is a risk factor for many diseases, including heart disease, and many American adults have poor diet quality and do not meet key dietary recommendations provided by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
This study was led by Kristina Petersen, associate professor of nutritional sciences, and Penny ...
CU researchers describe tools to better understand CaMKII, a protein involved in brain and heart disease
2024-03-22
AURORA, Colo. (March 22, 2024) – The health impacts of a complex protein that plays a major role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease and heart conditions can be lessened by three kinds of drug inhibitors, according to scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
In an overview of the protein and the inhibitors published today in the journal Cell Reports, the CU researchers discussed the best ways to use the interventions.
The protein, CaMKII, is ubiquitous in cells throughout the body but is perhaps best known for its prominent role in the brain and the heart. It is critical in learning and memory but if misregulated can ...
Theoretical physicist Carlo Rovelli to receive 2024 Lewis Thomas Prize
2024-03-22
From photons to atheism to Churchill’s extraterrestrial musings, the stunning breadth of Carlo Rovelli’s work has spurred readers to think deeply about the intersection of science and culture, transforming staggering complexity into widely accessible writing along the way.
For this artful ability to educate and engage, Rovelli will be presented with the 2024 Lewis Thomas Prize for Writing about Science at The Rockefeller University on April 9. Named after its first recipient, noted physician-scientist and essayist Lewis Thomas, the prize was ...
Your dog understands that some words “stand for” objects
2024-03-22
It’s no surprise that your dog can learn to sit when you say “sit” and come when called. But a study appearing March 22 in the journal Current Biology has made the unexpected discovery that dogs generally also know that certain words “stand for” certain objects. When dogs hear those words, brain activity recordings suggest they activate a matching mental representation in their minds.
“Dogs do not only react with a learned behavior to certain words,” says Marianna Boros (@FamDogProject) of the Department of Ethology at the Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary, one of the paper’s co-first authors. “They also don’t ...