(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. – The famous work ethic of honey bees might spell disaster for these busy crop pollinators as the climate warms, new research indicates.
Flying shortens the lives of bees, and worker honey bees will fly to find flowers whenever the weather is right, regardless of how much honey is already in the hive. Using climate and bee population models, researchers found that increasingly long autumns with good flying weather for bees raises the likelihood of colony collapse in the spring.
The study, published in Scientific Reports, focused on the Pacific Northwest but holds implications for hives across the U.S. The researchers also modeled a promising mitigation: putting colonies into indoor cold storage, so honey bees will cluster in their hive before too many workers wear out.
“This is a case where a small amount of warming, even in the near future, will make a big impact on honey bees,” said lead author Kirti Rajagopalan, a Washington State University climate researcher. “It’s not like this is something that can be expected 80 years from now. It is a more immediate impact that needs to be planned for.”
For this study, researchers ran simulations through a honey bee population dynamics model using climate projections for 2050 and the end of the century at 2100. They found that honey bee colonies that spend the winter outside in many areas of the Pacific Northwest would likely experience spring colony collapses in both the near- and long-term scenarios. This also occurred under a simulation where climate change continued as it is progressing now and one where greenhouse gas emissions were reduced in the near future.
Worker honey bees will forage for food whenever temperatures rise above about 50 degrees Fahrenheit. When it gets colder, they cluster in the hive, huddling with other bees, eating honey reserves and shivering, which helps keep the bees warm. In the spring, the adult worker bees start flying again. That means they also start dying. If too many older worker bees die before their replacements emerge ready to forage, the whole colony can collapse. Scientists have estimated this happens when there are fewer than 5,000 to 9,000 adult bees in the hive.
This study found that colonies wintering outside in colder areas like Omak in the far north of Washington state might still do all right under climate change. But for honey bee colonies in many other places, like Richland, Washington near the border of Oregon, staying outside in the winter would mean the spring hive population would plummet to fewer than 9,000 adults by 2050 and less than 5,000 by the end of the century.
The authors note that the simulations just looked at seasonal factors like temperature, wind and the amount of daylight, making them fairly conservative models.
“Our simulations are showing that even if there is no nutritional stress, no pathogens, no pesticides – just the conditions in fall and winter are enough to compromise the age structure of a colony. So when the hive comes out of winter, the bees are dying faster than they're being born,” said co-author Gloria DeGrandi-Hoffman, a research leader at the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Carl Hayden Bee Research Center.
The researchers also simulated a potential mitigation, placing honey bee hive boxes in cold storage so the bees start to cluster earlier and save workers. For instance, in the Richland scenarios, by the end of the century, having bees in cold storage from October to April would boost the spring hive population to over 15,000 compared to around 5,000 to 8,000 if they were kept outside.
A relatively new practice, cold storage is gaining popularity among commercial beekeepers to help manage bee health and for the logistics involved in moving hives to California to pollinate almond trees in February, an event that draws more than two million hives from across the country.
“A lot of beekeepers are already practicing this management technique of storing bees indoors because it has a lot of immediate potential to help in a number of ways,” said co-author Brandon Hopkins, a WSU entomologist. “These findings demonstrate that there are additional benefits to this practice for the survival of colonies in a changing climate.”
This research received support from the Washington Department of Agriculture’s Specialty Crop Block Grant.
END
Honey bees at risk for colony collapse from longer, warmer fall seasons
Cold storage for colonies could help mitigate climate change effects
2024-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
20,000 years of shared history on the Persian plateau
2024-03-25
All present day non African human populations are the result of subdivisions that took place after their ancestors left Africa at least 60.000 years ago. How long did it take for these separations to take place? Almost 20.000 years, during which they were all part of a single population. Where did they live for all this time? We don’t know, yet.
This is a conversation that could have taken place one year ago, now it is possible to give clearer answers to these questions thanks to the study recently published in Nature Communications (1) led by the researchers from the University ...
New UM study reveals unintended consequences of fire suppression
2024-03-25
MISSOULA – The escalation of extreme wildfires globally has prompted a critical examination of wildfire management strategies. A new study from the University of Montana reveals how fire suppression ensures that wildfires will burn under extreme conditions at high severity, exacerbating the impacts of climate change and fuel accumulation.
The study used computer simulations to show that attempting to suppress all wildfires results in fires burning with more severe ecological impacts, with accelerated increases in burned area beyond those expected from fuel accumulation or climate change.
“Fire suppression has unintended consequences,” said lead author Mark Kreider, a Ph.D. ...
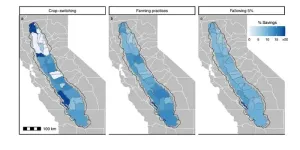
Small changes can yield big savings in agricultural water use
2024-03-25
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — While Hollywood and Silicon Valley love the limelight, California is an agricultural powerhouse, too. Agricultural products sold in the Golden State totaled $59 billion in 2022. But rising temperatures, declining precipitation and decades of over pumping may require drastic changes to farming. Legislation to address the problem could even see fields taken out of cultivation.
Fortunately, a study out of UC Santa Barbara suggests less extreme measures could help address California’s water issues. Researchers combined remote sensing, big data and machine ...
Humans pass more viruses to other animals than we catch from them
2024-03-25
Humans pass on more viruses to domestic and wild animals than we catch from them, according to a major new analysis of viral genomes by UCL researchers.
For the new paper published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, the team analysed all publicly available viral genome sequences, to reconstruct where viruses have jumped from one host to infect another vertebrate species.
Most emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases are caused by viruses circulating in animals. When these viruses cross over from animals into humans, a process known as zoonosis, they can cause disease outbreaks, epidemics and pandemics such as Ebola, flu or Covid-19. Given the enormous impact ...
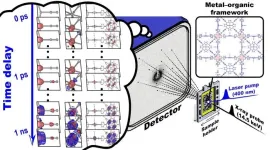
Filming ultrafast molecular motions in single crystal
2024-03-25
Understanding the behavior of matter is crucial for advancing scientific fields like biology, chemistry, and materials science. X-ray crystallography has been instrumental in this pursuit, allowing scientists to determine molecular structures with precision. In traditional X-ray crystallography experiments, a single crystal is exposed to X-rays multiple times to obtain diffraction signals. This poses a problem, where the sample has its structure altered or damaged by X-ray exposure.
In recent years, advances in technology have allowed for the development of “time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography” (TR-SFX). In serial ...
Better phosphorus use can ensure its stocks last more than 500 years and boost global food production - new evidence shows
2024-03-25
More efficient use of phosphorus could see limited stocks of the important fertiliser last more than 500 years and boost global food production to feed growing populations.
But these benefits will only happen if countries are less wasteful with how they use phosphorus, a study published today in Nature Food shows.
Around 30-40 per cent of farm soils have over-applications of phosphorus, with European and North American countries over-applying the most.
The global population is due to hit nearly 10 billion by 2050 and it is estimated that to feed ...
New all-liquid iron flow battery for grid energy storage
2024-03-25
RICHLAND, Wash.— A commonplace chemical used in water treatment facilities has been repurposed for large-scale energy storage in a new battery design by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. The design provides a pathway to a safe, economical, water-based, flow battery made with Earth-abundant materials. It provides another pathway in the quest to incorporate intermittent energy sources such as wind and solar energy into the nation’s electric grid.
The researchers report ...
Gene discovery offers new hope for people living with chronic skin disease
2024-03-25
Scientists from The Australian National University (ANU) have discovered a gene mutation is responsible for causing psoriasis – a chronic inflammatory skin disease that causes patients to develop red, scaly and itchy patches across their body.
According to ANU researcher Dr Chelisa Cardinez, if two copies of this mutated gene (known as IKBKB) are present, patients with psoriasis may go on to develop psoriatic arthritis, leaving them with joint pain, stiffness and swelling. Thanks to the world-first discovery from ANU, scientists now know what causes the progression from a skin-only disease to a skin and joint disease.
It’s hoped the findings will lead ...
What factors contribute to differences in cervical cancer screening in rural and urban community health centers?
2024-03-25
In the United States, community health centers (CHCs) mainly serve historically marginalized populations. New research reveals that both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, females receiving care at rural CHCs were less likely to be up to date with cervical cancer screening than those in urban CHCs. Factors associated with these differences included the proportion of patients with limited English proficiency and low income, as well as area-level unemployment and primary care physician density. The findings are ...
2 in 3 parents say their adolescent or teen worries about how sick days may impact grades
2024-03-25
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Many parents struggle deciding whether their middle or high school aged child should stay home from school if they don’t feel well, a new national poll suggests.
Among top factors: how their adolescent or teen is behaving due to symptoms and if they can get through a school day, the risk that they’re contagious and whether the student will miss a test, presentation or after school activity.
One in five parents also consider if their child needs a mental health day, according to the University of Michigan ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Honey bees at risk for colony collapse from longer, warmer fall seasonsCold storage for colonies could help mitigate climate change effects