(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Leeds and Lancaster University in the UK have identified a new potential target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease – PDE4B.
Alzheimer's disease is the leading cause of dementia and disability in old age. As the number of people diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease is on the increase, new treatments are urgently needed to improve the quality of life for people living with the disease.
PDE4B is an enzyme inside cells that breaks down a molecule known as cyclic AMP, which regulates a range of cellular processes. Based on an Australian study that identified the PDE4B gene as a risk factor for developing Alzheimer's disease, the UK team investigated whether reducing PDE4B activity might protect against Alzheimer's disease pathology and be a useful treatment approach. To this end, they introduced a gene for reduced PDE4B activity into an Alzheimer's disease (AD) mouse model that develops amyloid plaques in the brain, a key pathological feature of the disease.
The researchers observed that AD mice showed memory deficits in maze tests, but memory was unimpaired in AD mice with genetically reduced PDE4B activity. Using functional brain imaging, the team found the metabolism of glucose, the main source of energy in the brain, was impaired in AD mice, like that seen in patients with the disease. However, AD mice with genetically reduced PDE4B activity showed healthy levels of glucose metabolism in the brain.
To understand the mechanisms involved, the researchers next looked at gene and protein expression levels in the brain. This identified increased inflammation in the brains of AD mice, like that seen in Alzheimer's disease patients, but inflammation was lower in AD mice with genetically reduced PDE4B activity. Similar effects were seen for a range of other proteins involved in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Overall, these data suggest that reducing PDE4B activity might be a useful approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, although more research is needed to validate the use of drugs that target the enzyme.
Dr Steven Clapcote, the lead researcher, from the University of Leeds, said, “Reducing the activity of the PDE4B enzyme had a profound protective effect on memory and glucose metabolism in the AD mouse model, despite these mice showing no decrease in the number of amyloid plaques in the brain. This raises the prospect that reducing PDE4B activity may protect against cognitive impairment not only in Alzheimer’s disease but also in other forms of dementia, such as Huntington’s disease.”
Dr Neil Dawson, a co-author of the paper, from Lancaster University, echoed these sentiments: “These results offer real hope for the development of new treatments that will benefit patients with Alzheimer’s disease in the future. It was intriguing to find that reducing PDE4B activity by just 27% could dramatically rescue memory, brain function and inflammation in the AD mice. The next stage is to test whether PDE4B inhibiting drugs have similar beneficial effects in the AD mouse model, to test their potential efficacy in Alzheimer’s disease.”
The research was published in the Nature Portfolio journal Neuropsychopharmacology and was supported by the Dunhill Medical Trust, BBSRC, Alzheimer’s Research UK, and the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey.
END
New treatment target identified for Alzheimer's disease
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discovery of amino acid unveils how light makes plants open
2024-03-26
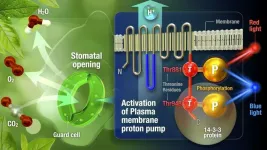
Scientists from Nagoya University have discovered a novel regulatory mechanism that controls the opening of stomata in plants, which is crucial for harnessing solar energy through photosynthesis. The team uncovered the role of phosphorylation at the 881st threonine residue (Thr881) of the plasma membrane proton pump in response to red and blue light in this process. This research opens up possibilities for manipulating plant physiology in specific ways, benefiting agriculture and the environment. The researchers reported their findings in Nature Communications.
“This phosphorylation event, ...
Crackdown on illicit drugs detects rise in ‘designer’ drug substitutes
2024-03-26
As authorities crack down on illicit drugs, University of South Australia experts have issued an alert on the use of the synthetic stimulant pentylone, as new research finds a 75% increase in detections across Australia.
In a new study as part of the Australian Criminal Intelligence Commission’s National Wastewater Drug Monitoring Program, researchers identified 20 different novel psychoactive substances (NPS) in wastewater treatment plants across Australia (between Feb 22-23) with pentylone detected at every collection site. Other NPS, eutylone and phenibut were also commonly detected.
Pentylone, (street name ‘bath salts’), ...
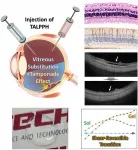
Treatment for blindness-causing retinal detachment using viscous seaweed
2024-03-26
It’s taboo to consume seaweed soup before exams in Korea since it can lead to failing the exam. The belief is rooted in the idea that the slippery nature of seaweed may cause people to slip and falter during the test. The slick surface of seaweeds such as seaweed and kelp is attributed to alginate, a mucilaginous substance. Notably, an intriguing study exploring the use of alginate for the treatment of retinal detachment has been recently published.
A collaborative effort between Professor Hyung Joon Cha from the Department of Chemical Engineering and the School of Convergence Science and Technology and Dr. Geunho Choi from ...
More needs to be done for depressed stroke survivors as incidence climbs
2024-03-26
Researchers say more needs to be done for depressed stroke survivors as new findings show 60% of stroke survivors would experience depression within 18 years, a much higher estimation than previous studies.
This compares to 22% of the general population experiencing depression in the same time frame.
The King’s College London study, published today in The Lancet Regional Health – Europe, also found 90% of cases of depression occurred within five years of surviving a stroke, indicating a key time for healthcare intervention.
The findings, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research, looks at incidence of mild ...
Research lights up process for turning CO2 into sustainable fuel
2024-03-26
Researchers have successfully transformed CO2 into methanol by shining sunlight on single atoms of copper deposited on a light-activated material, a discovery that paves the way for creating new green fuels.
An international team of researchers from the University of Nottingham's School of Chemistry, University of Birmingham, University of Queensland and University of Ulm have designed a material, made up of copper anchored on nanocrystalline carbon nitride. The copper atoms are nested ...
Essays on democracy draw attention to critical threats, explore safeguards ahead of Jan. 6
2024-03-25
Following the events of Jan. 6, 2021 — when a violent mob stormed the U.S. Capitol building in an effort to interrupt the certification process of the 2020 presidential election — experts began to question how to protect the next presidential election from a similar threat. To that end, University of Notre Dame political scientists have partnered with preeminent scholars of democracy from across the country to produce a set of recommendations to strengthen and safeguard democracy in America.
The University’s Rooney Center for the Study of American Democracy established the January 6th, ...
New surfactant could improve lung treatments for premature babies
2024-03-25
Scientists have developed a new lung surfactant that is produced synthetically rather than relying on the use of animal tissues. With further development, the formulation could provide a cheaper and more readily available alternative to Infasurf, a medication used to prevent and treat respiratory distress in premature babies.
Surfactants are substances that decrease surface tension where liquids interface with other liquids, gases or solids. In addition to their use in medicines, they are found in a wide range of products including detergents, cosmetics, motor oils and adhesives.
Suzanne Farver Lukjan, a lecturer in chemistry ...
Researchers uncover key biomolecule involved in whooping cough infection
2024-03-25
Researchers have identified a new complex-carbohydrate biomolecule, or glycan, that plays a key role in the nasal colonization of the Bordetella bacteria responsible for whooping cough. The discovery could make it possible to create a new drug or vaccine that interferes with the glycan to greatly reduce or even stop ongoing Bordetella transmission.
Bordetella pertussis is the cause of the respiratory infection pertussis, which is widely known as whooping cough. Today’s pertussis vaccines keep people from getting severely sick, but they don’t eliminate the bacteria because it excels at colonizing, ...
Study links long-term consumption of reused deep-fried oil with increased neurodegeneration
2024-03-25
A new study found higher levels of neurodegeneration in rats that consumed reused deep fried cooking oils and their offspring compared to rats on a normal diet. Deep frying, which involves completely submerging food in hot oil, is a common method of food preparation around the world.
Results from the study also suggest that the increased neurodegeneration is tied to the oil’s effects on the bidirectional communication network between the liver, gut and brain. The liver–gut–brain axis plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological functions, and its dysregulation has been ...
Study suggests statins could help fight gum disease
2024-03-25
Could taking statins benefit your mouth in addition to your arteries? A new study conducted in cell cultures showed that cholesterol-lowering drugs help to dampen the inflammation associated with periodontal disease by altering the behavior of macrophages, a type of immune cell.
Statins are the most common type of prescription medication in the United States today, taken by over 40 million Americans to lower cholesterol. The study suggests these drugs improve gum health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Subramanya Pandruvada, an assistant professor in the College ...