(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES – (3/26/24) - In a landmark move for biomedical progress, the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) today unveiled the launch of four pioneering startup companies. These ventures represent a strategic leap forward in TIBI's commitment to transforming healthcare through innovation. By harnessing the institute's groundbreaking research in biomaterials, micro-needles, organoids, tissue engineering, and advanced biosensing, these startups are poised to tackle some of the most pressing health challenges of our time.
Introducing the Future of Biomedical Solutions:
BioOptix: Revolutionizing ocular health, BioOptix is at the forefront of creating smart contact lenses capable of delivering medications for severe eye conditions, including glaucoma. These lenses are equipped with state-of-the-art monitoring and sensing technology, enabling precise treatment modulation directly to the eye.
Digital Immunology: At the intersection of technology and immunology, Digital Immunology is pioneering the use of cutting-edge biomaterials, high-throughput digital culture platforms, organoid technology, and artificial intelligence. This innovative approach accelerates the development of targeted immunotherapies and vaccines to combat cancer and a spectrum of other diseases.
OnVagus: Introducing a breakthrough in neural health, OnVagus is developing a non-invasive, wearable patch that disrupts harmful vagus nerve signaling associated with cancer-induced weight loss and muscle atrophy. This signaling contributes to one-third of all cancer fatalities. The OnVagus patch offers a drug-free alternative that holds promise for treating not only cancer-related symptoms but also obesity, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic diseases.
Surgi-Zipper: Redefining surgical recovery, Surgi-Zipper's innovative flexible patch provides a secure, leak-proof closure for air- or fluid-filled organs post-operation. Its unique biodegradable, double-layered design features a non-adhesive outer layer coupled with an inner layer that adheres to moist internal surfaces. The Surgi-Zipper is designed to remove tension from the surgical suture line in non-planar dynamic tissues and enhance healing, with potential applications extending to cardiovascular and pulmonary surgeries. The unique .chemical interactions between the adhesive layer and tissue allow ease of application and on-demand removal of the patch with laparoscopy or open surgery
Ali Khademhosseini, the esteemed Director and CEO of TIBI, expressed his enthusiasm: "The launch of these four startups marks a significant milestone in TIBI's journey towards bringing our advanced biomedical research to the forefront of medical application. We are thrilled to see our vision of rapid innovation translation come to life, offering tangible solutions that will improve health outcomes and patient care."
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation remains dedicated to its mission of pioneering breakthroughs in biomedical science and technology. With the establishment of these startups, TIBI is not just envisioning the future of medicine—it is actively creating it.
###
About the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation is accelerating the pace of translational research by supporting the world’s leading scientists with an open, entrepreneurial environment for bioengineering new materials, biological models, and advanced technologies to address critical challenges to the health of the planet and its people. The Institute’s worldwide collaborations with academic, clinical, and entrepreneurial partners provide a rich foundation for translating innovations to the real world.
PRESS CONTACT
Stewart Han, shan@terasaki.org, +1 818-836-4393
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
END
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation catalyzes healthcare revolution with launch of four cutting-edge startups
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Faux reefs for coastal protection
2024-03-26
Engineers have designed a modular artificial reef that can dissipate wave energy far better than natural coral reefs, according to a study. Sixty percent of the world’s coral reefs are under threat from rising ocean temperatures, overfishing, or coastal development. At the same time, climate change is leading to sea level rise, frequent high-tide flooding, and powerful storm surges. Artificial reefs can help protect coastal infrastructure from storms as well as provide habitat for marine organisms. Michael Triantafyllou and colleagues proposed and tested an architected cellular reef structure ...
Mount Sinai study calls for major changes in the way people with comorbidities are selected by physicians for lung cancer screening
2024-03-26
A Medicare policy requiring primary care providers (PCPs) to share in the decision-making with patients on whether to proceed with lung cancer screening is fraught with confusion and lack of evidence-based information, and may actually be undermining the purpose for which it was created, Mount Sinai researchers say.
In their study, published in Annals of Family Medicine, the team reported that the policy, enacted nearly 10 years ago to encourage the use of lung cancer screening, is in urgent need of new ...
Smart maneuver: Epstein-Barr virus hijacks host genome boosting nasopharyngeal carcinoma
2024-03-26
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (or NPC) is a rare type of cancer affecting the epithelial tissue of the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nasal cavity. Among the three main subtypes of NPC, non-keratinizing undifferentiated squamous carcinoma is endemic to the regions of Southern China and Southeast Asia, with a strong association with Epstein-Barr virus (or EBV) infection. EBV, also known as human tumor virus, is a double-stranded DNA virus that is associated with various cancers, such as Burkitt lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma, and gastric cancer. EBV genomes mostly survive autonomously as episomes or extrachromosomal ...
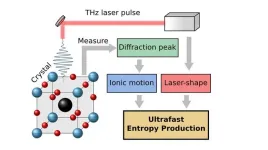
New method to measure entropy production on the nanoscale
2024-03-26
Entropy, the amount of molecular disorder, is produced in several systems but cannot be measured directly. An equation developed by researchers at Chalmers University of Technology and Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, now sheds new light on how entropy is produced on a very short time scale in laser excited materials.
“New computational models give us new research opportunities. Extending thermodynamics for ultrashort excitations will provide novel insights into how materials function on the nanoscale,” says Matthias Geilhufe, Assistant Professor ...
Scientists on the hunt for evidence of quantum gravity’s existence at the South Pole
2024-03-26
Scientists on the hunt for evidence of quantum gravity’s existence at the South Pole
University of Copenhagen team contributes to an Antarctic large-scale experiment striving to find out if gravity also exists at the quantum level. An extraordinary particle able to travel undisturbed through space seems to hold the answer.
Several thousand sensors distributed over a square kilometer near the South Pole are tasked with answering one of the large outstanding questions in physics: does quantum gravity exist? ...
New roadmap to prevent pandemics centers on protecting biodiversity
2024-03-26
ITHACA, N.Y. – An international team of 25 scientists has proposed a roadmap for how to prevent the next pandemic by conserving natural areas and promoting biodiversity, thereby providing animals with enough food, safe havens and distance to limit contact and the transfer of pathogens to humans.
Pandemics begin when disease-harboring animals, such as bats, come in close proximity with people, livestock or other animals and pass on new pathogens. Viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, Nipah, Hendra and possibly Ebola have all fatally spilled over from bats to humans, ...
New maps help decision-makers factor albedo into tree-planting decisions
2024-03-26
Arlington, VA – As efforts to restore tree cover accelerate to help avoid runaway climate change, a new study highlights how restoring tree cover can, in some locations, heat up the Earth rather than cool it by affecting how much sunlight the surface reflects (i.e. “the albedo").
This new study by researchers at Clark University in the United States alongside scientists from The Nature Conservancy (TNC) and ETH-Zurich, published today in the journal Nature Communications, provides a global analysis of where restoration of tree cover is most effective at cooling the global climate system, considering ...
The construction of visual attention highlighted at the neuronal level
2024-03-26
In a world inundated with a constant stream of new information—notifications, ads, emails, news—we often struggle to prevent our attention from being constantly hijacked by external events. But is it truly within our power to filter and select our perceptions? And why do we find ourselves so easily distracted?
“Exogenous attention, the cognitive process that allows a salient visual stimulus to impose itself on us, is automatic. When a colleague walks past our desk, our attention is diverted from our computer screen despite ourselves,” explains Tal Seidel Malkinson (University of Lorraine), ...
Spielberg was right: Triceratops teamed up
2024-03-26
Actually, the team from Naturalis Biodiversity Center in the Netherlands was looking for a Tyrannosaurus, that summer of 2013 in Wyoming. Instead, they found a Triceratops: the famous dinosaur with the three horns and the large neck frill. And then they found another one. And another one. And more. The dig turned into a project that would last for more than ten years.
All in all, they dug up 1200 bones and bone fragments, of at least five individuals. A team of professional and volunteer paleontologists ...
Young adults with migraine, other nontraditional risk factors may have higher stroke risk
2024-03-26
Research Highlights:
Nontraditional risk factors for stroke were significantly associated with the development of strokes in adults younger than ages 35 to 45.
Migraine was the most important nontraditional risk factor for stroke among both men and women, according to the study of adults in Colorado.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Tuesday, March 26, 2024
DALLAS, March 26, 2024 — Adults younger than 35- to 45-years old may have a higher risk of developing a stroke from nontraditional risk factors ...