(Press-News.org) One of the features of the deaf community is that it is highly diverse. As well as including people of different ages and genders, the members of the community do not all share the same type of deafness or form of communication. Firstly, the time of onset of deafness and the degree of hearing loss vary greatly. And secondly, not everybody uses sign and oral language in the same way. All these aspects have a bearing on the well-being of deaf people. However, few studies specifically analyse the effect of each one.
The PhD thesis, defended by Amaia Jauregi-Orbe at the Faculty of Education - Bilbao, makes a significant contribution to the scientific literature. So far there has been no record of any other research of this magnitude analysing all these factors and exploring their relationship with so many variables, thus allowing psychosocial well-being (self-concept, self-esteem, perception of social support and loneliness, etc.) to be measured. “I set out to make a general diagnosis designed to contribute towards approaching the reality of deaf people and making it visible. The work provides data with the potential to enrich the academic debate,” she said.
One of the pieces of evidence revealed by the study is that women have higher levels of personal growth than men. This is a fact that has surprised the researcher herself, given that her initial hypothesis suggested the opposite. Jauregi believes that this may be due to the fact that “the associative fabric of the deaf community offers women empowerment tools that allow them to strengthen their capacities and autonomy”.
Moreover, the study also identified significant differences linked to age. People under 30 have higher self-esteem, greater perceived social support and greater personal growth than people in older age groups. “The reasons behind this need to be explored now. I believe that one of the important variables may be the fact that they have received an inclusive education,” she explained.
In relation to this hypothesis, the results of the thesis indicate that prelingually deaf people (those who lost their hearing before acquiring oral language) who were educated in mainstream schools have higher self-esteem than those who were educated in special schools. Another remarkable result linked to the educational context is that well-being varies depending on the level of education achieved. The group of people with a university education have a higher level of self-esteem, personal growth and social well-being than the group that achieved primary education or lower.
According to the conclusions of the thesis, other factors, such as linguistic-cultural or occupational factors, for example, do not seem to have a direct bearing on the psychosocial well-being of deaf people. However, the researcher considers that the data could be read differently if the intersectionality of the variables were analysed: “To gain a better understanding of the reality, studies need to be carried out in the future to explore the correlation between the different factors.”
Large sample and adapted assessment instruments
The research design and procedure are two of the strong points in the research, as all the challenges involved in research into deaf people have been addressed. The results of the PhD thesis were obtained after analysing the responses of 166 deaf adults of different sexes, ages, types of deafness and linguistic and cultural characteristics. It was ensured that the group of participants was representative of the diversity of the deaf community and that the evaluation instruments were adapted to the heterogeneous needs of the participants.
Additional information
Amaia Jauregi-Orbe wrote up her PhD thesis in the Department of Evolutionary Psychology and Education; her supervisors were Dr Elena Bernarás-Iturrioz and Dr Joana Jaureguizar-Alboniga-Mayor of the UPV/EHU. Amaia Jauregi is currently a tenured lecturer in the Department of Educational Psychology at the Begoñako Andra Mari University Teacher Training College. Her line of research focuses on the educational response to students with special educational needs and high abilities, as well as on the psychosocial well-being of deaf people.
END
Among deaf people, women have higher levels of personal growth
A PhD thesis on the well-being of deaf people also concludes that age or educational background are determining factors
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Severe hurricanes boost influx of juveniles and gene flow in a coral reef sponge
2024-03-26
Named for its ropy-looking long branches, Aplysina cauliformis, a coral reef sponge, provides a critical 3D habitat for marine organisms and helps to stabilize the foundation of coral reefs. However, these upright branching sponges are highly susceptible to breaking during storms, which increases sponge fragmentation and contributes to population clonality and inbreeding.
Many sponges can survive severe damage and undergo frequent fragmentation, which is considered a mechanism for asexual reproduction. While fragmentation is a commonly utilized reproductive strategy in rope sponges, they also can reproduce sexually by producing larvae. How and whether they recolonize following ...
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation catalyzes healthcare revolution with launch of four cutting-edge startups
2024-03-26
LOS ANGELES – (3/26/24) - In a landmark move for biomedical progress, the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI) today unveiled the launch of four pioneering startup companies. These ventures represent a strategic leap forward in TIBI's commitment to transforming healthcare through innovation. By harnessing the institute's groundbreaking research in biomaterials, micro-needles, organoids, tissue engineering, and advanced biosensing, these startups are poised to tackle some of the most pressing health challenges ...
Faux reefs for coastal protection
2024-03-26
Engineers have designed a modular artificial reef that can dissipate wave energy far better than natural coral reefs, according to a study. Sixty percent of the world’s coral reefs are under threat from rising ocean temperatures, overfishing, or coastal development. At the same time, climate change is leading to sea level rise, frequent high-tide flooding, and powerful storm surges. Artificial reefs can help protect coastal infrastructure from storms as well as provide habitat for marine organisms. Michael Triantafyllou and colleagues proposed and tested an architected cellular reef structure ...
Mount Sinai study calls for major changes in the way people with comorbidities are selected by physicians for lung cancer screening
2024-03-26
A Medicare policy requiring primary care providers (PCPs) to share in the decision-making with patients on whether to proceed with lung cancer screening is fraught with confusion and lack of evidence-based information, and may actually be undermining the purpose for which it was created, Mount Sinai researchers say.
In their study, published in Annals of Family Medicine, the team reported that the policy, enacted nearly 10 years ago to encourage the use of lung cancer screening, is in urgent need of new ...
Smart maneuver: Epstein-Barr virus hijacks host genome boosting nasopharyngeal carcinoma
2024-03-26
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (or NPC) is a rare type of cancer affecting the epithelial tissue of the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nasal cavity. Among the three main subtypes of NPC, non-keratinizing undifferentiated squamous carcinoma is endemic to the regions of Southern China and Southeast Asia, with a strong association with Epstein-Barr virus (or EBV) infection. EBV, also known as human tumor virus, is a double-stranded DNA virus that is associated with various cancers, such as Burkitt lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma, and gastric cancer. EBV genomes mostly survive autonomously as episomes or extrachromosomal ...
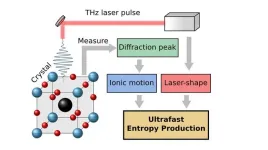
New method to measure entropy production on the nanoscale
2024-03-26
Entropy, the amount of molecular disorder, is produced in several systems but cannot be measured directly. An equation developed by researchers at Chalmers University of Technology and Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, now sheds new light on how entropy is produced on a very short time scale in laser excited materials.
“New computational models give us new research opportunities. Extending thermodynamics for ultrashort excitations will provide novel insights into how materials function on the nanoscale,” says Matthias Geilhufe, Assistant Professor ...
Scientists on the hunt for evidence of quantum gravity’s existence at the South Pole
2024-03-26
Scientists on the hunt for evidence of quantum gravity’s existence at the South Pole
University of Copenhagen team contributes to an Antarctic large-scale experiment striving to find out if gravity also exists at the quantum level. An extraordinary particle able to travel undisturbed through space seems to hold the answer.
Several thousand sensors distributed over a square kilometer near the South Pole are tasked with answering one of the large outstanding questions in physics: does quantum gravity exist? ...
New roadmap to prevent pandemics centers on protecting biodiversity
2024-03-26
ITHACA, N.Y. – An international team of 25 scientists has proposed a roadmap for how to prevent the next pandemic by conserving natural areas and promoting biodiversity, thereby providing animals with enough food, safe havens and distance to limit contact and the transfer of pathogens to humans.
Pandemics begin when disease-harboring animals, such as bats, come in close proximity with people, livestock or other animals and pass on new pathogens. Viruses such as SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1, Nipah, Hendra and possibly Ebola have all fatally spilled over from bats to humans, ...
New maps help decision-makers factor albedo into tree-planting decisions
2024-03-26
Arlington, VA – As efforts to restore tree cover accelerate to help avoid runaway climate change, a new study highlights how restoring tree cover can, in some locations, heat up the Earth rather than cool it by affecting how much sunlight the surface reflects (i.e. “the albedo").
This new study by researchers at Clark University in the United States alongside scientists from The Nature Conservancy (TNC) and ETH-Zurich, published today in the journal Nature Communications, provides a global analysis of where restoration of tree cover is most effective at cooling the global climate system, considering ...
The construction of visual attention highlighted at the neuronal level
2024-03-26
In a world inundated with a constant stream of new information—notifications, ads, emails, news—we often struggle to prevent our attention from being constantly hijacked by external events. But is it truly within our power to filter and select our perceptions? And why do we find ourselves so easily distracted?
“Exogenous attention, the cognitive process that allows a salient visual stimulus to impose itself on us, is automatic. When a colleague walks past our desk, our attention is diverted from our computer screen despite ourselves,” explains Tal Seidel Malkinson (University of Lorraine), ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Among deaf people, women have higher levels of personal growthA PhD thesis on the well-being of deaf people also concludes that age or educational background are determining factors