(Press-News.org) Leuven (Belgium) 26 March 2024 - Belgian scientists have developed AI models that can predict how a particular beer will be rated by consumers, and what aroma compounds brewers can add to improve it. The research was published today in the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications and may revolutionize how the food and beverage industry develops new products.
Tricky to compare
Comparing and ranking flavor profiles of different beers is a challenge. There are a multitude of guides on the market describing beverages with generic terms like ‘fruity’ and rating them based solely on one person’s taste. "This makes beer comparisons highly biased and makes it difficult to predict how a beer actually tastes,” says Kevin Verstrepen, professor at KU Leuven and director of the VIB-KU Leuven Center for Microbiology and the Leuven Institute for Beer Research.
I wanted to have a more neutral and scientific description for the different beers in the world. - Kevin Verstrepen
The team started chemically analyzing beers, carefully measuring the concentrations of hundreds of aroma compounds. Each beer was also evaluated on a set of 50 criteria by a trained panel of 15 people. “It was a truly Herculean effort. We began the project with less than 100 beers, and quickly realized this would not be enough to capture Belgium’s incredible beer diversity, so we ended up analyzing 250 beers,” remembers Dr. Miguel Roncoroni, who led the chemical analyses and tasting panel.
New insights with AI
It took the team 5 years, but once they had the chemical concentrations and detailed tasting reports for hundreds of different beers, they knew it would be possible to use AI to connect the two. One model could predict key aromas and the final appreciation score of a beer, without the need for human tasting. These outcomes, in turn, were used to further improve the taste of an existing commercial Belgian ale, by adding certain aromas predicted by the model to boost the beer’s quality. Sure enough, the modified beer indeed scored quite a bit better in blind tastings.
The flavor of beer is a complex mix of aroma compounds. It is impossible to predict how good a beer is by just measuring one or a few compounds. We really need the power of computers. - Michiel Schreurs
The study can be expanded to other food products, which may revolutionize how new foods are made.
Our biggest goal now is to make better alcohol-free beer. Using our model, we have already succeeded in creating a cocktail of natural aroma compounds that mimic the taste and smell of alcohol without the risk of a hangover. - Kevin Verstrepen
“However,” Michiel Scheurs adds jokingly, “we did celebrate the paper with the alcohol-containing variants!”.
END
AI predicts the taste and quality of beer
Revolutionizing the beverage industry and making better beer
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A global map of how climate change is changing winegrowing regions
2024-03-26
Grapes grown to make wine are sensitive to climate conditions such as temperature and extreme drought. These effects are already visible worldwide on yields, the composition of grapes and the quality of wines, with already and soon-to-be-observed consequences on the geography of wine production. Understanding shifts in wine production potential due to climate change is a major scientific concern. Based on their expertise and a thorough analysis of the scientific literature — over 250 publications in the last 20 years – a research team has established a global map of evolving trends in the threats and potential benefits that climate change brings ...
SwRI’s Dr. Rohini Giles receives NASA Early Career Achievement Medal
2024-03-26
SAN ANTONIO — March 26, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute Senior Research Scientist Dr. Rohini Giles has received the NASA Early Career Achievement Medal. The medal recognizes unusual and significant performance supporting NASA’s mission during the first 10 years of their career. Giles was cited for “significant early career achievements in the analysis of Juno data to study Jovian Transient Luminous Events and the distribution of constituents in Jupiter’s atmosphere.”
“It’s ...
Sodium intake and cause-specific mortality among predominantly low-income Black and white residents
2024-03-26
About The Study: In this cohort study of 64,000 low-income Americans, nearly 80% of study participants consumed sodium exceeding the current recommended daily amount, which was associated with 10% to 30% of cardiovascular disease mortality. Public health programs targeted to reduce sodium intake among this underserved population may be beneficial.
Authors: Xiao-Ou Shu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3802)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Exclusive breastfeeding duration and risk of childhood cancers
2024-03-26
About The Study: In this cohort study including 309,000 Danish children, longer duration of exclusive breastfeeding was associated with reduced risk of childhood B-cell precursor-acute lymphoblastic leukemia, corroborating results of previous case-control investigations in this field. To inform future preemptive interventions, continued research should focus on the potential biologic mechanisms underlying the observed association.
Authors: Signe Holst Søegaard, Ph.D., of the Danish Cancer Society in Copenhagen, is the corresponding ...
Ancient DNA reveals origin of racial/ethnic disparity in a childhood cancer
2024-03-26
There are 40% more Hispanic/Latino kids diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) than white non-Hispanic/Latino children; actually, Hispanic/Latino individuals have the highest risk of ALL in the United States. However, the basis for this difference is not well understood. Researchers recently identified a genetic variant that accounts for the increased risk of B-cell ALL in Hispanic/Latino children, and using ancient DNA, they traced the mutation all the way back to the first migrants who ...
USC researchers find genetic variant contributing to disparities in childhood leukemia risk
2024-03-26
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood cancer, disproportionately affects children of Hispanic/Latino origin in the United States. They are 30-40% more likely to get ALL than non-Hispanic white children, but the exact genetic basis and cause of that increased risk are unknown.
Now, a study from the Keck School of Medicine of USC has revealed a key genetic variant contributing towards the increased risk, as well as details about the biological basis of ALL. The team used genetic fine-mapping analysis, a statistical method that allows researchers ...
Structural basis for the regulatory mechanism of mammalian mitochondrial respiratory chain megacomplex-I2III2IV2
2024-03-26
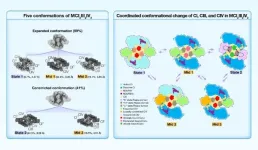
Mammalian mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes are the most important and complicated protein machinery in mitochondria. Although this system has been studied for more than a century, its composition and molecular mechanism are still largely unknown. Here, Yang’s group report the high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of porcine respiratory chain megacomplex-I2III2IV2 (MCI2III2IV2) in five different conformations, including State 1, State 2, Mid 1, Mid 2, and Mid 3. High-resolution cryo-EM imaging, combined with super-resolution gated stimulated emission depletion microscopy (gSTED), strongly supports ...
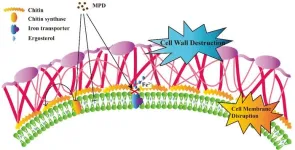
Antifungal activity of a maleimide derivative: Disruption of cell membranes and interference with iron ion homoeostasis
2024-03-26
This study is led by Prof. Ying Li (Xuzhou Medical University), Prof. Zuobin Zhu (Xuzhou Medical University), and Prof. Wenqiang Chang (Shandong University). A small molecule library consisting of 40 compounds, specifically N-substituted maleimide and its derivatives were initially screened in the study. Among them, twelve maleimides, each with a distinct N-protection group, were synthesized using ring-opening and ring-closing reactions involving various amines and maleic anhydride. Additionally, a set of twenty-eight ...
Addressing global energy needs with ideal electrocatalysts
2024-03-26
Researchers from the University of Tartu and the University of Copenhagen have proposed the theoretical description of an ideal electrocatalysis process, which, if implemented, could double the efficiency of energy conversion and storage devices.
As the world seeks sustainable solutions to meet escalating energy demands, a collaborative team of researchers from the Universities of Tartu and Copenhagen has proposed an innovative approach to overcome long-standing limitations in oxygen electrocatalysis. Oxygen electrocatalysis ...
Researchers identify new way to inhibit immune cells that drive allergic asthma
2024-03-26
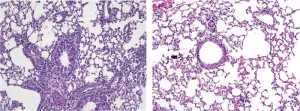
Researchers at the Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, have discovered that a protein called Piezo1 prevents a type of immune cell in the lung from becoming hyperactivated by allergens. The study, to be published March 26 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that switching on Piezo1 could represent a new therapeutic approach to reducing lung inflammation and treating allergic asthma.
Type 2 innate lymphoid cells (also known as ILC2s) are a type of immune cell that resides in the lungs, skin, and other tissues of the body. ILC2s in the lungs become activated in the presence of allergens and produce ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] AI predicts the taste and quality of beerRevolutionizing the beverage industry and making better beer