(Press-News.org) By 2030, the World Health Organization (WHO), the Global Fund and UNAIDS are hoping to end the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS epidemic. An international team of researchers led by Eric Arts, professor at the Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and Jamie Mann, senior lecturer at the University of Bristol (U.K.), has brought us another step closer to meeting this goal, by finding an effective and affordable targeted treatment strategy for an HIV cure.
In a first, the study published in the journal Emerging Microbes and Infections demonstrated the team’s patented therapeutic candidate, an HIV-virus-like-particle (HLP), is 100 times more effective than other candidate HIV cure therapeutics for people living with chronic HIV on combined antiretroviral therapy (cART). If successful in clinical trials, HLP could be used by millions of people living around the world to free them of HIV. This study was done using blood samples from people living with chronic HIV.
HLPs are dead HIV particles hosting a comprehensive set of HIV proteins that increase immune responses without infecting a person. When compared with other potential cure approaches, HLP is an affordable biotherapeutic and can be administered by intramuscular injection – similar to the seasonal flu vaccine.
“The development of this HIV cure was ten years in the making but with strong support from our collaborators in the U.S., Canada and Uganda, we have observed a striking ability of HLP to drive out the last remnants of HIV-1, which we hope will provide an affordable cure for all,” said Arts, who is a Canada Research Chair in HIV Pathogenesis and Viral Control. “To live HIV-free is a goal for the 39 million infected. It is also the priority of the UN and WHO to end the HIV pandemic by 2030.”
HIV is a retrovirus that attacks the body’s immune system and if left untreated, can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The virus weakens a person’s immune system by destroying CD4-T white blood cells, which are tasked with helping the immune system fight infections. Approximately 95 per cent of people living with HIV have chronic HIV – where the virus is slowly causing a slow destruction of the patients’ immune systems when they initiated lifelong cART.
While cART is effective at treating HIV, it has been unable to completely eliminate the virus from the body. This is because of the virus’ ability to create a “latent reservoir” – where it hides dormant inside of cells, safe from detection. Using blood samples from 32 participants living with chronic HIV from the U.S., Uganda and Canada, who were on stable cART for a median of approximately 13 years, researchers found that HLP was able to specifically target just the immune cells containing latent HIV reservoir and purge these cells of their HIV, a critical step towards an HIV-1 cure. An HIV cure is typically described as therapy and approach that eliminates all HIV without the need of continuous antiretroviral therapy.
“Over time, the virus grows more diverse within a single individual that is not on treatment which makes it more difficult to target,” said co-lead author Ryan Ho, master’s student in the department of microbiology and immunology. “This formulation we've crafted covers the theoretical diversity so it can reach the HIV-1 in all those people living with HIV.”
Minh Ha Ngo, lead author and postdoctoral scholar in the department of microbiology and immunology, says one concern expressed among people living with HIV for years is that continued use of cART could lead to the virus becoming unreachable and unable to be eliminated. The results of this study, by contrast, demonstrate that combining HLP with cART is still able to trigger the latent reservoir, even in chronic cases. If these dormant latent reservoirs can be awakened, then they can be eliminated from the body.
“Owing to its high mutation rate, HIV exhibits remarkable genetic diversity, resulting in different viral subtypes; some of which predominate in particular regions of the globe,” said Mann. “We were excited to see preliminary evidence that our HLP cure therapy reverses latency irrespective of the subtype of the individual's infection. Whilst this needs to be explored further, it hints at the global applicability of our approach.”
In the future, researchers plan to test HLP on a larger representative HIV cohort with subtype C infections, which includes people living in South Africa, Ethiopia, Vietnam and India. This would help determine if the treatment strategy is effective for most people living with acute and chronic HIV.
Current studies involve confirming a lack of toxicity in preparation for human clinical trials.
These studies will be made possible with the advanced Pathogen Research Centre at Schulich Medicine & Dentistry. This study was conducted in collaboration with University of Bristol, University of Toronto, Case Western Reserve University, Rakai Health Sciences Program, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and the U.S. National Institutes of Health.
The study was funded by the American Foundation for AIDS Research, and by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; part of the National Institutes of Health, and the Canada Research Chairs Program.
END
Researchers a step closer to a cure for HIV
New study shows virus-like particle can effectively ‘shock and kill’ latent HIV reservoir in those living with chronic HIV
2024-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AI predicts the taste and quality of beer
2024-03-26
Leuven (Belgium) 26 March 2024 - Belgian scientists have developed AI models that can predict how a particular beer will be rated by consumers, and what aroma compounds brewers can add to improve it. The research was published today in the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications and may revolutionize how the food and beverage industry develops new products.
Tricky to compare
Comparing and ranking flavor profiles of different beers is a challenge. There are a multitude of guides on the market describing ...
A global map of how climate change is changing winegrowing regions
2024-03-26
Grapes grown to make wine are sensitive to climate conditions such as temperature and extreme drought. These effects are already visible worldwide on yields, the composition of grapes and the quality of wines, with already and soon-to-be-observed consequences on the geography of wine production. Understanding shifts in wine production potential due to climate change is a major scientific concern. Based on their expertise and a thorough analysis of the scientific literature — over 250 publications in the last 20 years – a research team has established a global map of evolving trends in the threats and potential benefits that climate change brings ...
SwRI’s Dr. Rohini Giles receives NASA Early Career Achievement Medal
2024-03-26
SAN ANTONIO — March 26, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute Senior Research Scientist Dr. Rohini Giles has received the NASA Early Career Achievement Medal. The medal recognizes unusual and significant performance supporting NASA’s mission during the first 10 years of their career. Giles was cited for “significant early career achievements in the analysis of Juno data to study Jovian Transient Luminous Events and the distribution of constituents in Jupiter’s atmosphere.”
“It’s ...
Sodium intake and cause-specific mortality among predominantly low-income Black and white residents
2024-03-26
About The Study: In this cohort study of 64,000 low-income Americans, nearly 80% of study participants consumed sodium exceeding the current recommended daily amount, which was associated with 10% to 30% of cardiovascular disease mortality. Public health programs targeted to reduce sodium intake among this underserved population may be beneficial.
Authors: Xiao-Ou Shu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3802)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Exclusive breastfeeding duration and risk of childhood cancers
2024-03-26
About The Study: In this cohort study including 309,000 Danish children, longer duration of exclusive breastfeeding was associated with reduced risk of childhood B-cell precursor-acute lymphoblastic leukemia, corroborating results of previous case-control investigations in this field. To inform future preemptive interventions, continued research should focus on the potential biologic mechanisms underlying the observed association.
Authors: Signe Holst Søegaard, Ph.D., of the Danish Cancer Society in Copenhagen, is the corresponding ...
Ancient DNA reveals origin of racial/ethnic disparity in a childhood cancer
2024-03-26
There are 40% more Hispanic/Latino kids diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) than white non-Hispanic/Latino children; actually, Hispanic/Latino individuals have the highest risk of ALL in the United States. However, the basis for this difference is not well understood. Researchers recently identified a genetic variant that accounts for the increased risk of B-cell ALL in Hispanic/Latino children, and using ancient DNA, they traced the mutation all the way back to the first migrants who ...
USC researchers find genetic variant contributing to disparities in childhood leukemia risk
2024-03-26
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood cancer, disproportionately affects children of Hispanic/Latino origin in the United States. They are 30-40% more likely to get ALL than non-Hispanic white children, but the exact genetic basis and cause of that increased risk are unknown.
Now, a study from the Keck School of Medicine of USC has revealed a key genetic variant contributing towards the increased risk, as well as details about the biological basis of ALL. The team used genetic fine-mapping analysis, a statistical method that allows researchers ...
Structural basis for the regulatory mechanism of mammalian mitochondrial respiratory chain megacomplex-I2III2IV2
2024-03-26
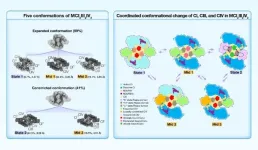
Mammalian mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes are the most important and complicated protein machinery in mitochondria. Although this system has been studied for more than a century, its composition and molecular mechanism are still largely unknown. Here, Yang’s group report the high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of porcine respiratory chain megacomplex-I2III2IV2 (MCI2III2IV2) in five different conformations, including State 1, State 2, Mid 1, Mid 2, and Mid 3. High-resolution cryo-EM imaging, combined with super-resolution gated stimulated emission depletion microscopy (gSTED), strongly supports ...
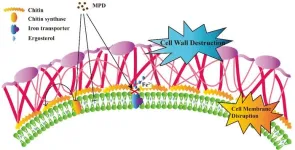
Antifungal activity of a maleimide derivative: Disruption of cell membranes and interference with iron ion homoeostasis
2024-03-26
This study is led by Prof. Ying Li (Xuzhou Medical University), Prof. Zuobin Zhu (Xuzhou Medical University), and Prof. Wenqiang Chang (Shandong University). A small molecule library consisting of 40 compounds, specifically N-substituted maleimide and its derivatives were initially screened in the study. Among them, twelve maleimides, each with a distinct N-protection group, were synthesized using ring-opening and ring-closing reactions involving various amines and maleic anhydride. Additionally, a set of twenty-eight ...
Addressing global energy needs with ideal electrocatalysts
2024-03-26
Researchers from the University of Tartu and the University of Copenhagen have proposed the theoretical description of an ideal electrocatalysis process, which, if implemented, could double the efficiency of energy conversion and storage devices.
As the world seeks sustainable solutions to meet escalating energy demands, a collaborative team of researchers from the Universities of Tartu and Copenhagen has proposed an innovative approach to overcome long-standing limitations in oxygen electrocatalysis. Oxygen electrocatalysis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Researchers a step closer to a cure for HIVNew study shows virus-like particle can effectively ‘shock and kill’ latent HIV reservoir in those living with chronic HIV