(Press-News.org) Liver disease is a major health concern, causing millions of deaths worldwide each year. One serious complication is liver fibrosis, scarring that can lead to liver failure. There is currently no effective treatment, but new research suggests promise for exosomes, tiny sacs released by cells.
Non-parenchymal cells like hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), Kupffer cells (KCs), and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) play a key role in fibrosis development. These cells are involved in inflammation, scar formation, and tissue repair. Understanding their function is vital for new therapies.
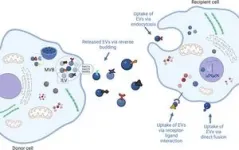
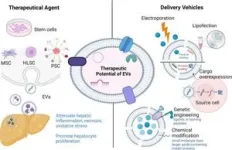
Exosomes are emerging as potential treatments for liver fibrosis. Derived from various cell sources, they can be engineered to target specific non-parenchymal cells. This targeted approach offers several advantages.
Exosomes can deliver drugs directly to cells involved in fibrosis, reducing side effects on healthy tissue. They can efficiently carry therapeutic cargo like drugs, RNA molecules, and signalling molecules. Additionally, exosomes can be modified to target specific cell types within the liver.
Current research explores exosomes in several ways. Exosomes from stem cells or engineered with antifibrotic molecules can inhibit HSC activation and collagen production. Exosomes can also modulate KCs, promoting their anti-inflammatory phenotype to break down scar tissue. Moreover, exosomes may help repair LSEC fenestrae, pores essential for nutrient exchange and waste removal.
Exosome therapy offers a promising, innovative approach to treating liver fibrosis. While further research is needed to fully understand their potential, exosomes represent a significant step forward in this fight. Standardised protocols for exosome production, storage, and clinical use are crucial. Exploring exosome applications and targeting strategies is essential to ensure their safety and efficacy as therapeutic agents or delivery vehicles for liver fibrosis treatment.
Overall, exosomes hold great promise as a novel therapy for liver fibrosis, offering opportunities for targeted treatment and improved patient outcomes. However, it is important to note that no exosome therapy for liver fibrosis has reached clinical trials yet. Continued research and development are essential to advance our understanding and use of exosomes in liver fibrosis therapy.
See the article:
Liu Y, Wang L. Extracellular vesicles targeting non-parenchymal cells: the therapeutical effect on liver fibrosis. eGastroenterology2024;2:e100040. doi:10.1136/
egastro-2023-100040
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
Flexible solar cells have many potential applications in aerospace and flexible electronics, but low energy conversion efficiency has limited their practical use. A new manufacturing method has increased the power efficiency of flexible solar cells made from perovskite, a class of compounds with a specific crystalline structure that facilitates the conversion of solar energy into electricity.
Current flexible perovskite solar cells (FPSCs) suffer from lower power conversion efficiency than ...
A new image from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration— which includes scientists from the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA)— has uncovered strong and organized magnetic fields spiraling from the edge of the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*). Seen in polarized light for the first time, this new view of the monster lurking at the heart of the Milky Way Galaxy has revealed a magnetic field structure strikingly similar to that of the black hole at the center of the M87 galaxy, suggesting that strong magnetic fields may be common to all black holes. This similarity also hints toward a hidden ...
People with specific genetic traits and those who have anxiety or depression have a significantly higher heart attack risk during periods of social or political stress than at other times, according to a new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session. Researchers said the findings suggest opportunities to identify those at elevated risk and perhaps even prevent cardiac events.
Doctors have long noticed that heart attacks tend to spike around certain times, such as the winter holidays, but the reasons ...
Young adults who were prescribed stimulant medications for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were significantly more likely to develop cardiomyopathy (weakened heart muscle) compared with those who were not prescribed stimulants, in a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session.
The study found that people prescribed stimulants such as Adderall and Ritalin were 17% more likely to have cardiomyopathy at one year and 57% more likely to have cardiomyopathy at eight years compared with those who were not taking these medications. Cardiomyopathy involves structural ...
Sleeping fewer than seven hours is associated with a higher risk of developing high blood pressure over time, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Annual Scientific Session.
While the association between sleep patterns and high blood pressure has been reported, evidence about the nature of this relationship has been inconsistent, according to researchers. The current analysis pools data from 16 studies conducted between January 2000 and May 2023, evaluating hypertension incidence in 1,044,035 people from six countries who did not have a prior history of high blood pressure over a median follow-up of five years (follow-up ranged from 2.4 to 18 years). ...
Many new drugs inhibit the processes that cancer cells need to divide rapidly. So as to inhibit the cancer as a whole. But cancer cells have all sorts of workarounds to get around that effect. As a result, the tumor becomes unresponsive to treatment.
That's why researcher Matheus dos Santos Dias is taking a completely different approach. He had to convince some colleagues before he could start working on this quite surprising idea. After all, you're not going to give cancer cells a boost, are you? "We're going against the prevailing view that you can only fight cancer cells by inhibiting them," he knows. "But we had strong evidence that it also works if you overstimulate ...
This unusual, subterranean mammal with extreme longevity shows genetic adaptations to low oxygen environments which could offer opportunities for advancing other areas of physiological and medical research in humans, including the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
New research from Queen Mary University of London led by Dr Dunja Aksentijevic in the Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry has revealed that that the genome of the naked mole-rat contains specific adaptations that allow them to survive in low-oxygen, and even no oxygen environments ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Understanding the structure of proteins is critical for demystifying their functions and developing drugs that target them. To that end, a team of researchers at Brown University has developed a way of using machine learning to rapidly predict multiple protein configurations to advance understanding of protein dynamics and functions.
A study describing the approach was published in Nature Communications on Wednesday, March 27.
The authors say the technique is accurate, fast, cost-effective and has the potential to revolutionize drug discovery ...
The researchers had previously identified a ‘weak spot’ in the brain, which is a specific network of higher-order regions that not only develop later during adolescence, but also show earlier degeneration in old age. They showed that this brain network is also particularly vulnerable to schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease.
In this new study, published in Nature Communications, they investigated the genetic and modifiable influences on these fragile brain regions by looking at the brain scans of 40,000 UK Biobank participants aged over 45.
The researchers examined 161 risk factors for dementia, and ranked their impact on this vulnerable ...
Leuven, Antwerp, and London, 27 March – Microglia are specialized immune cells in the brain. While they normally protect our brains, they can also contribute to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's. The exact mechanism behind this contribution is not yet fully understood due to the complexities involved in studying them in human brain samples. Now, a research team led by Prof. Bart De Strooper (UK-DRI@UCL and VIB-KU Leuven) and Prof. Renzo Mancuso (VIB-UAntwerp) made a xenotransplantation model – mice with stem-cell-derived human microglia in their brains to observe how human microglia respond to the disease environment. Their findings, published ...