(Press-News.org) CORVALLIS, Ore. — By engaging regularly with their family dog and teaching it a series of tricks and commands, children with developmental disabilities experienced a significant increase in their daily physical activity, a new study from Oregon State University researchers found.
Children in the experimental group increased their moderate to vigorous physical activity by 17 minutes per day, while simultaneously reducing their sedentary time by nearly an hour per day.
“We often talk about physical activity as just fitness or exercise, but really, it’s about moving and being active on a daily basis,” said study co-author Megan MacDonald, head of OSU’s School of Exercise, Sport, and Health Sciences in the College of Health. “It’s getting out with your dog, playing, having fun.”
Previous research has found that more than 80% of American children are not getting the recommended amount of physical activity — at least 60 minutes per day of moderate to vigorous activity, per the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services — and that overall physical activity declines progressively with age.
Studies have also shown that children with developmental disabilities are significantly less physically active than their peers without disabilities.
“In my opinion, the biggest barrier is just access: access to physical activity from your home, from your community and often from your school. Those are the places we know kids are getting physical activity,” MacDonald said. “But if we want to engage in a sport or activity that’s not inclusive, or that has concerns about adding someone with a disability, that’s an issue. If we have schools that aren’t engaging in inclusive or adaptive physical education — which they are legally required to do — that’s an issue.”
For the current study, published today, MacDonald teamed up with Monique Udell from OSU’s College of Agricultural Sciences. As director of the Human-Animal Interaction Laboratory, Udell’s research includes animal training, human-animal bonding and mutually beneficial interactions.
The team started in 2017 with 45 child-dog pairs, where each child was identified by parents as having some form of developmental disability. The canine participants included a wide range of breeds, ages and previous training experience.
The study revolved around the “Do As I Do” training intervention, in which participants are essentially playing a game of “Simon Says” with their dogs. Pairs in the experimental group received 10 hour-long one-on-one sessions with a dog trainer where they learned about dog body language and behavior, and taught their dogs multiple commands, including the “Do it” command that tells the dog to mimic the behavior their owner has just demonstrated.
“Not all kids got to the final protocol, but what was kind of amazing was that everyone progressed,” MacDonald said. “At the end we had a little showcase, and everyone was able to show something new they could do with their dog.”
Participants assigned to the “active control” group engaged in a dog-walking program for the same amount of time as the Do As I Do program, while kids in the “waitlist control” group did not participate in any guided physical activity with their dogs.
All children were fitted with accelerometers to record their physical activity levels before and after the program. In the end, 14 kids had enough accelerometer data to be included in the results.
Compared with the waitlist control group, children in the Do As I Do training group increased their moderate to vigorous physical activity time by 17.3 minutes per day, and decreased their sedentary time by 58 minutes per day. The group also increased their time spent in light activity by about 40 minutes per day.
An increase of 17 minutes daily amounts to almost 30% of the total recommended time (60 minutes) kids spend in moderate to vigorous physical activity.
“It’s very hard to get significant differences in physical activity; it’s a behavioral thing,” MacDonald said. “So we’re pretty excited about these results.”
And kids are receiving more than just physical benefits, she said. In teaching them to recognize and respond to dogs’ body language, the program also helps kids gain more awareness of nonverbal cues from the people around them.
Training with their family dog also helps build responsibility, independence and a sense of ownership — while, perhaps, giving the parents who are usually responsible for 100% of dog care a much-needed break, MacDonald said.
“It’s one of the coolest studies I’ve worked on,” she said.
OSU co-authors on the study also included Saethra Darling, Duo Jiang, John Schuna and Shelby Wanser.
The team is already working on a similar study with pet cats, and has been doing outreach in the Pacific Northwest with dog trainers, who have shown a lot of interest in becoming involved, MacDonald said.
END
Oregon State dog-training program helps increase physical activity among kids with disabilities
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
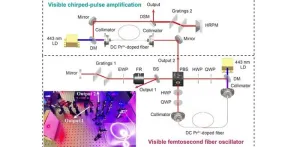
Unlocking visible femtosecond fiber oscillators: A breakthrough in laser science
2024-03-27
The emergence of ultrafast laser pulse generation, marking a significant milestone in laser science, has triggered incredible progress across a wide array of disciplines, encompassing industrial applications, energy technologies, life sciences, and beyond. Among the various laser platforms that have been developed, fiber femtosecond oscillators, esteemed for their compact design, outstanding performance, and cost-effectiveness, have become one of the mainstream technologies for femtosecond pulse generation. However, their operating wavelengths ...
Long-period oscillations control the Sun’s differential rotation
2024-03-27
The Sun’s differential rotation pattern has puzzled scientists for decades: while the poles rotate with a period of approximately 34 days, mid-latitudes rotate faster and the equatorial region requires only approximately 24 days for a full rotation. In addition, in past years advances in helioseismology, i.e. probing the solar interior with the help of solar acoustic waves, have established that this rotational profile is nearly constant throughout the entire convection zone. This layer of the Sun stretches ...
A combination of approved drugs enhances the delivery of anti-bacterial medications to treat tuberculosis
2024-03-27
BOSTON – Tuberculosis (TB) is often overlooked in developed countries such as the United States, but this bacterial infection remains one of the deadliest diseases globally and results in millions of deaths annually.
Deaths can occur even with treatment, sometimes because of drug resistance in TB bacteria and other times due to poor delivery of TB-targeting drugs to patients’ infected lung tissue.
To address the latter challenge, a team led by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in collaboration with scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and ...
Could AI play a role in locating damage to the brain after stroke?
2024-03-27
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 27, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Artificial intelligence (AI) may serve as a future tool for neurologists to help locate where in the brain a stroke occurred. In a new study, AI processed text from health histories and neurologic examinations to locate lesions in the brain. The study, which looked specifically at the large language model called generative pre-trained transformer 4 (GPT-4), is published in the March 27, 2024, online issue of Neurology® Clinical Practice, an official journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
A stroke can ...
High fat/low protein diets in rats during pregnancy and postnatally may cause altered glucose control and other "maladaptive" metabolic changes in their offspring
2024-03-27
High fat/low protein diets in rats during pregnancy and postnatally may cause altered glucose control and other "maladaptive" metabolic changes in their offspring
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299554
Article Title: Intrauterine and early-life malnutrition in rats disrupts the circadian rhythm programming of energy metabolites through adulthood
Author Countries: México
Funding: This research was partially supported by PD-LBAE-FC UNAM 2015-2019, DGAPA ...
Just 1 in 14 adults across 55 LMICs who have both hypertension and diabetes have both conditions under adequate control
2024-03-27
Just 1 in 14 adults across 55 LMICs who have both hypertension and diabetes have both conditions under adequate control, with only 20-30% of patients taking medications, indicating a lack of adequate healthcare in these settings.
======
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0003019
Article Title: Multiple cardiovascular risk factor care in 55 low- and middle-income countries: A cross-sectional analysis of nationally-representative, individual-level data from 280,783 adults
Author Countries: ...
Your emotional reaction to climate change may impact the policies you support
2024-03-27
Emotional reactions to climate change may lead to specific policy preferences, according to a study published March 27, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Teresa A. Myers of George Mason University and colleagues.
A politician, public speaker, or journalist may opt for an emotional appeal when communicating about climate change. Indeed, research shows that emotional investment can raise awareness of important issues and galvanize an otherwise apathetic public. However, existing research has not explored the unique links between specific ...
Persistent hiccups in a far-off galaxy draw astronomers to new black hole behavior
2024-03-27
At the heart of a far-off galaxy, a supermassive black hole appears to have had a case of the hiccups.
Astronomers from MIT, Italy, the Czech Republic, and elsewhere have found that a previously quiet black hole, which sits at the center of a galaxy about 800 million light years away, has suddenly erupted, giving off plumes of gas every 8.5 days before settling back to its normal, quiet state.
The periodic hiccups are a new behavior that has not been observed in black ...
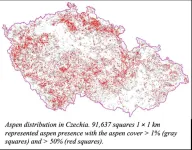
Europe’s forgotten forests could be 21st century ‘biodiversity hot spots’
2024-03-27
An overlooked and long-neglected type of forest has vast capacity to rebound, enhancing species diversity and resilience to climate change, according to an international team of forest scientists.
According to new research, published today in the peer-reviewed science journal PLOS ONE, there is ample habitat for the Eurasian aspen, and these environments will continue to be suitable for this “keystone species” as the global climate warms.
“The Eurasian aspen, and aspen species globally, are home to vast populations of other dependent plants and animals,” said the study’s lead author, Antonin Kusbach, an applied ecologist at Mendel University in ...
Combining epigenetic cancer medications may have benefit for colorectal cancers and other tumor types
2024-03-27
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (March 27, 2024) — A pair of medications that make malignant cells act as if they have a virus could hold new promise for treating colorectal cancers and other solid tumors, reports a study published today in Science Advances.
The preclinical research, led by Van Andel Institute scientists, determined how low doses of a DNMT inhibitor sensitize cancer cells to an EZH2 inhibitor, resulting in a one-two punch that combats cancer cells better than either drug alone.
The findings are the foundation for an upcoming Phase I clinical trial to evaluate this combination ...