(Press-News.org)
• New centre specifically focuses on using AI to improve society
• Current research is designed to improve transport, health and industry
• “There have been a lot of reports focusing on the negative use of AI...this is why the centre is so important now.”
Aston University researchers have marked the opening of a new centre which focuses on harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) to improve people’s lives.
The Aston Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research and Application (ACAIRA) has been set up to become a West Midlands hub for the use of AI to benefit of society.
Following its official opening, the academics leading it are looking to work with organisations and the public. Director Professor Anikó Ekárt said: “There have been a lot of reports focusing on the negative use of AI and subsequent fear of AI. This is why the centre is so important now, as we aim to achieve trustworthy, ethical and sustainable AI solutions for the future, by co-designing them with stakeholders.”
Deputy director Dr Ulysses Bernardet added: “We work with local, national and international institutions from academia, industry, and the public sector, expanding Aston University’s external reach in AI research and application.
“ACAIRA will benefit our students enormously by training them to become the next generation of AI practitioners and researchers equipped for future challenges.”
The centre is already involved in various projects that use AI to solve some of society’s challenges.
A collaboration with Legrand Care aims to extend and improve independent living conditions for older people by using AI to analyse data collected through home sensors which detect decline in wellbeing. This allows care professionals to change and improve individuals’ support plans whenever needed.
A project with engineering firm Lanemark aims to reduce the carbon footprint of industrial gas burners by exploring new, more sustainable fuel mixes.
Other projects include work with asbestos consultancy Thames Laboratories which will lead to reduced costs, emissions, enhanced productivity and improved resident satisfaction in social housing repairs and a partnership with transport safety consultancy Agilysis to produce an air quality prediction tool which uses live data to improve transport planning decisions.
The centre is part of the University’s College of Engineering and Physical Sciences and its official launch took place on the University campus on 29 February. The event included a talk by the chair of West Midlands AI and Future Tech Forum, Dr Chris Meah. He introduced the vision for AI within the West Midlands and the importance of bringing together academics, industry and the public.
Current research in sectors such as traffic management, social robotics, bioinformatics, health, and virtual humans was highlighted, followed by industry talks from companies Smart Transport Hub, Majestic, DRPG and Proximity Data Centres.
The centre’s academics work closely with West Midlands AI and Future Tech Forum and host the regular BrumAI Meetup.
END
Aston University research center to focus on using AI to improve lives
2024-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robot, can you say ‘cheese’?
2024-03-27
What would you do if you walked up to a robot with a human-like head and it smiled at you first? You’d likely smile back and perhaps feel the two of you were genuinely interacting. But how does a robot know how to do this? Or a better question, how does it know to get you to smile back?
While we’re getting accustomed to robots that are adept at verbal communication, thanks in part to advancements in large language models like ChatGPT, their nonverbal communication skills, especially facial expressions, have lagged far behind. Designing a robot that can not only make a wide range ...
Filters, coupled with Digital Health Program, reduced arsenic levels by nearly half in study participants in households relying on well water in American Indian Communities
2024-03-27
A community-led water-testing project made up of households that rely on private well water with high arsenic levels saw on average a 47 percent drop in participants’ urinary arsenic levels after filters were installed and a digital health program was implemented, according to a new study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Over the two-year study period, participating households received phone calls to encourage use of the filter and a reminder to replace the filter cartridge.
For the study—a ...
Oregon State dog-training program helps increase physical activity among kids with disabilities
2024-03-27
CORVALLIS, Ore. — By engaging regularly with their family dog and teaching it a series of tricks and commands, children with developmental disabilities experienced a significant increase in their daily physical activity, a new study from Oregon State University researchers found.
Children in the experimental group increased their moderate to vigorous physical activity by 17 minutes per day, while simultaneously reducing their sedentary time by nearly an hour per day.
“We often talk about physical activity as just fitness or exercise, but ...
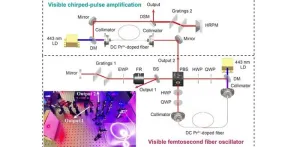
Unlocking visible femtosecond fiber oscillators: A breakthrough in laser science
2024-03-27
The emergence of ultrafast laser pulse generation, marking a significant milestone in laser science, has triggered incredible progress across a wide array of disciplines, encompassing industrial applications, energy technologies, life sciences, and beyond. Among the various laser platforms that have been developed, fiber femtosecond oscillators, esteemed for their compact design, outstanding performance, and cost-effectiveness, have become one of the mainstream technologies for femtosecond pulse generation. However, their operating wavelengths ...
Long-period oscillations control the Sun’s differential rotation
2024-03-27
The Sun’s differential rotation pattern has puzzled scientists for decades: while the poles rotate with a period of approximately 34 days, mid-latitudes rotate faster and the equatorial region requires only approximately 24 days for a full rotation. In addition, in past years advances in helioseismology, i.e. probing the solar interior with the help of solar acoustic waves, have established that this rotational profile is nearly constant throughout the entire convection zone. This layer of the Sun stretches ...
A combination of approved drugs enhances the delivery of anti-bacterial medications to treat tuberculosis
2024-03-27
BOSTON – Tuberculosis (TB) is often overlooked in developed countries such as the United States, but this bacterial infection remains one of the deadliest diseases globally and results in millions of deaths annually.
Deaths can occur even with treatment, sometimes because of drug resistance in TB bacteria and other times due to poor delivery of TB-targeting drugs to patients’ infected lung tissue.
To address the latter challenge, a team led by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in collaboration with scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and ...
Could AI play a role in locating damage to the brain after stroke?
2024-03-27
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 27, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Artificial intelligence (AI) may serve as a future tool for neurologists to help locate where in the brain a stroke occurred. In a new study, AI processed text from health histories and neurologic examinations to locate lesions in the brain. The study, which looked specifically at the large language model called generative pre-trained transformer 4 (GPT-4), is published in the March 27, 2024, online issue of Neurology® Clinical Practice, an official journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
A stroke can ...
High fat/low protein diets in rats during pregnancy and postnatally may cause altered glucose control and other "maladaptive" metabolic changes in their offspring
2024-03-27
High fat/low protein diets in rats during pregnancy and postnatally may cause altered glucose control and other "maladaptive" metabolic changes in their offspring
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299554
Article Title: Intrauterine and early-life malnutrition in rats disrupts the circadian rhythm programming of energy metabolites through adulthood
Author Countries: México
Funding: This research was partially supported by PD-LBAE-FC UNAM 2015-2019, DGAPA ...
Just 1 in 14 adults across 55 LMICs who have both hypertension and diabetes have both conditions under adequate control
2024-03-27
Just 1 in 14 adults across 55 LMICs who have both hypertension and diabetes have both conditions under adequate control, with only 20-30% of patients taking medications, indicating a lack of adequate healthcare in these settings.
======
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0003019
Article Title: Multiple cardiovascular risk factor care in 55 low- and middle-income countries: A cross-sectional analysis of nationally-representative, individual-level data from 280,783 adults
Author Countries: ...
Your emotional reaction to climate change may impact the policies you support
2024-03-27
Emotional reactions to climate change may lead to specific policy preferences, according to a study published March 27, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Teresa A. Myers of George Mason University and colleagues.
A politician, public speaker, or journalist may opt for an emotional appeal when communicating about climate change. Indeed, research shows that emotional investment can raise awareness of important issues and galvanize an otherwise apathetic public. However, existing research has not explored the unique links between specific ...