(Press-News.org)
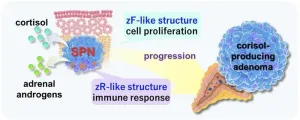
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers from Kyushu University's Faculty of Medical Sciences report on new insights into the mechanisms of how adrenal gland tumors are formed. The team identified a new type of tumor cell population that they termed 'steroids-producing nodules' or SPNs, that exhibits the unique characteristic of producing two different hormones. Specific structures in SPNs were found to lead to cortisol-producing adenomas, or CPAs, noncancerous tumors that produce excessive cortisol.
Their findings, published in eBioMedicine, provide clues into the formation and maintenance of the human adrenal cortex, which can lead to better treatments in diseases linked to its dysfunction.
Nobody likes the feeling of being under stress, your heart rate rises, your muscles tense, and your body starts twitching with energy. One of the key chemical compounds behind this is cortisol, known colloquially as the 'stress hormone.' Cortisol is a family of steroid hormones known as 'adrenal steroid hormones' and are produced within the small glands above the kidneys called the adrenal cortex.
The adrenal cortex is critical in producing the vital hormones regulating everything from your sleep-wake cycle, blood pressure, and even sexual development. Naturally, disruptions in the adrenal gland have been linked to a wide range of diseases.
"For example, tumors that can develop in the adrenal cortex can lead to the production of excessive amounts of certain hormones. One type of tumor we study are cortisol-producing adenomas, or CPAs, which are noncancerous tumors that produce excessive cortisol," explains Research Fellow Tazuru Fukumoto, the first author of the study. "While researchers have found several genetic mutations linked to CPA, how exactly these tumors develop remained unclear."
The human adrenal cortex is made of three layers, with each layer producing specific hormones: the zona glomerulosa that produce aldosterone, zona fasciculata (zF) that produce cortisol, and the zona reticularis (zR) that produce adrenal androgens.
The team began by collecting tissue samples from patients with adrenal tumors and conducted histopathologic tests along with the latest genetic analysis. They found structures that exhibited a unique two-layered zF and zR-like structure, producing both cortisol and adrenal androgens.
"We called these structures steroids-producing nodules, or SPNs. SPNs had mutations in the gene GNAS, that is known to cause CPAs. Further analyses showed that the zF-like quality enhanced cell proliferation, but the zR-like structure had a tumor suppressive effect. We also found that this zF-like structure was the main cause for the development of CPAs" continues Fukumoto. "In summary, when cells of the adrenal cortex acquire the GNAS gene mutation, they develop into SPNs, wherein their zF-like structure contributes to them becoming CPAs."
The team hopes their findings can lead to better understanding and treatment of adrenocortical tumors and the diseases they are linked to.
"Steroid based drugs are vital in the treatment of many diseases including autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, and allergic diseases like asthma. However, long-term use will atrophy of the adrenal cortex," concludes Professor Yoshihiro Ogawa who led the study. "We hope our results will advance our understanding of the layered structure of the adrenal cortex and can lead to the prevention and treatment of adrenal cortex atrophy in the future."
###
For more information about this research, see "Steroids-producing nodules: a two-layered adrenocortical nodular structure as a precursor lesion of cortisol-producing adenoma," Tazuru Fukumoto, Hironobu Umakoshi, Norifusa Iwahashi, Tatsuki Ogasawara, Maki Yokomoto-Umakoshi, Hiroki Kaneko, Masamichi Fujita, Naohiro Uchida, Hiroshi Nakao, Namiko Kawamura, Yayoi Matsuda, Ryuichi Sakamoto, Takashi Miyazawa, Masahide Seki, Masatoshi Eto, Yoshinao Oda, Yutaka Suzuki, Seishi Ogawa, and Yoshihiro Ogawa eBioMedicine, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105087
About Kyushu University
Kyushu University is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its founding in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U's world-class research centers cover a wide range of study areas and research fields, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences. Its multiple campuses—including one of the largest in Japan—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu that is frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as Japan's gateway to Asia. Through its Vision 2030, Kyushu U will 'Drive Social Change with Integrative Knowledge.' Its synergistic application of knowledge will encompass all of academia and solve issues in society while innovating new systems for a better future.
END
· AI responses to common patient questions were on par or exceeded answers from professional societies
· Goal also to reduce clinician workload and burnout
· More than 60% of cancer patients require radiation oncology treatment
CHICAGO --- Cancer patients about to undergo radiation oncology treatment have lots of questions. Could ChatGPT be the best way to get answers?
A new Northwestern Medicine study tested a specially designed ChatGPT to see if it could successfully provide answers to patients’ common questions about radiation oncology. Patients may be too overwhelmed to address all their concerns during a clinical visit ...
About The Study: In this study of 9,740 surveillance colonoscopies among 9,601 adults ages 70 to 85 with prior colorectal adenoma, colorectal cancer detection was rare regardless of prior adenoma finding, whereas the advanced neoplasia yield was 12% overall. Yields were higher among those with a prior advanced adenoma than among those with prior nonadvanced adenoma and did not increase significantly with age. These findings can help inform whether to continue surveillance colonoscopy in older adults.
Authors: Jeffrey K. Lee, M.D., M.P.H., of Kaiser Permanente Northern California in Oakland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
About The Study: High levels of glucose and triglycerides and low levels of high-density lipoprotein were associated with future risk of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders in this study of more than 200,000 participants. These findings may support closer follow-up of individuals with metabolic dysregulations for the prevention and diagnosis of psychiatric disorders.
Authors: Charilaos Chourpiliadis, M.D., of the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, is the corresponding ...
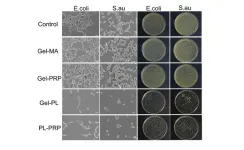
WASHINGTON, April 2, 2024 – Hydrogels are popular for use in skin ailments and tissue engineering. These polymer-based biocompatible materials are useful for their abilities to retain water, deliver drugs into wounds, and biodegrade. However, they are complicated to manufacture and not very resilient to external forces like rubbing against clothing, sheets, or wound dressings. They are also not inherently able to battle bacterial infections, so they are often infused with antimicrobial drugs or metal ions, which can ...
The human body uses adhesion to hold itself together. For example, a tendon attaches muscle to bone, while connective tissue attaches muscle to skin.
Hydrogel-based soft materials are based on these biomimetic mechanical behaviors, which makes them a revolutionary design of biomedical implants, human-machine interfaces, and bio-inspired soft robots. However, there are limitations to overcome before they are able to fully replace commonly used hard materials.
Qihan Liu, assistant professor of mechanical and materials ...
Changes in the gut microbiome have been implicated in a range of diseases including type 2 diabetes, obesity, and inflammatory bowel disease. Now, a team of researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard along with Massachusetts General Hospital has found that microbes in the gut may affect cardiovascular disease as well. In a study published in Cell, the team has identified specific species of bacteria that consume cholesterol in the gut and may help lower cholesterol and heart disease risk in people.
Members of Ramnik Xavier’s lab, Broad’s Metabolomics Platform, and ...
Cells within the intestines perform various roles including nutrient absorption, sensing, and maintaining homeostasis. Certain chronic disorders are distinctly characterized by gut inflammation, which disrupts intestinal cells and can lead to a remodeling of the gut and the introduction of new immune cells. To better understand the types of cells and their positioning within the intestines, researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, in collaboration with investigators ...
If you want to spread a message about climate change and global warming, you need to adapt the message according to your intended audience and what you want to achieve.
Researchers have now developed an app to help people who want to spread their message on climate issues to ensure they generate the most support possible – be they researchers, politicians, various decision makers or legislators.
Huge survey involving 63 countries
59,000 people participated in surveys as part of the work on creating the app, and Norway was among ...
Today the University of Phoenix Career Institute® released its 2024 Career Optimism Index®, a comprehensive study examining the state of American workers' career trajectories and sentiments about the future of their job and career opportunities. This year's Index, the fourth consecutive year it has been fielded, reveals that workers and employers are facing a critical moment of talent stagnation in the workplace.
More than half (53%) of Americans report feeling easily replaceable in their job position and 64% of workers say their company does not offer opportunities ...
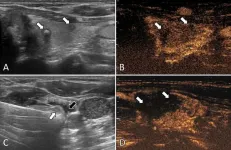
OAK BROOK, Ill. – In a 10-center study, microwave ablation offered progression free survival rates and fewer complications than surgery in the treatment of a form of thyroid cancer known as papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), according to research published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The most common type of thyroid cancer, PTC often presents with multifocality, meaning that two or more bumps or nodules (papillae) are found within the thyroid gland. The occurrence of multifocality within PTC cases is notably frequent, ranging between approximately ...