(Press-News.org) A new paper in Nicotine & Tobacco Research, published by Oxford University Press, finds that smokers who switch to electronic cigarettes are now more likely to stop smoking regular cigarettes. In the past, smokers who began using electronic cigarettes mostly continued smoking.
Electronic nicotine delivery systems first emerged on the U.S. market in 2007. The first e-cigarettes resembled conventional cigarettes (in appearance) and used fixed low-voltage batteries. Beginning in 2016, manufacturers introduced e-liquids containing nicotine salt formulations. These new e-cigarettes became widely available. These nicotine salts are lower in pH than freebase formulations, which allow manufacturers to increase nicotine concentration while avoiding harshness and bitterness.
Past population-level research provided conflicting findings on whether vaping helps people who smoke combustible cigarettes to quit smoking. Some research suggests improved cigarette quitting-related outcomes with e-cigarette use, while other research suggests the opposite. Inconsistent findings may be due to differences in the samples and measures considered, differences in the analytic approaches of researchers used, the rapidly changing product environment, or policy contexts.
The researchers here examined differences in real-world trends in population-level cigarette discontinuation rates from 2013 to 2021, comparing U.S. adults who smoked combustible cigarettes and used e-cigarettes with U.S. adults who smoked combustible cigarettes and did not use e-cigarettes.
Using data from among adults (ages 21+) in the Population Assessment of Tobacco and Health (PATH) Study, a national longitudinal study of tobacco use from people from all over the United States, the researchers found that between 2013 and 2016, rates of discontinuing cigarette smoking among adults in the U.S. population were statistically indistinguishable between those who used e-cigarettes and those who did not. Cigarette discontinuation rates were 15.5% for those who used e-cigarettes and 15.6% for those who did not.
But the quit rates changed in subsequent years; the researchers here found that between 2018 and 2021 only 20% of smokers who did not use e-cigarettes stopped smoking combustible cigarettes, but some 30.9% of smokers who used e-cigarettes stopped smoking combustible cigarettes.
The paper notes that the full study period spanned a time in the United States when the e-cigarette marketplace was expanding; salt-based nicotine formulations gained market share in 2016 and vaping products became available with increased nicotine yields over time. This was also a period in which state and federal governments restricted tobacco in various ways, including increasing the tobacco-purchase age to 21 and restricting flavored e-cigarettes.
“Our findings here suggest that the times have changed when it comes to vaping and smoking cessation for adults in the US,” notes study first author, Karin Kasza, an assistant professor of oncology in the Department of Health Behavior at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center in Buffalo, NY. “While our study doesn’t give the answers as to why vaping is associated with cigarette quitting in the population today when it wasn’t associated with quitting years ago, design changes leading to e-cigarettes that deliver nicotine more effectively should be investigated. This work underscores the importance of using the most recent data to inform public health decisions.”
The paper, “Divergence in cigarette discontinuation rates by use of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS): Longitudinal findings from the U.S. PATH Study Waves 1-6,” is available (at midnight on April 3rd) at https://doi.org/10.1093/ntr/ntae027.
Direct correspondence to:
Karin Kasza
Department of Health Behavior
Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
665 Elm St
Buffalo, NY 14203
karin.kasza@roswellpark.org
To request a copy of the study, please contact:
Daniel Luzer
daniel.luzer@oup.com
END
E-cigarette users now more likely to quit traditional cigarettes
2024-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chatbot guides women through post-prison challenges
2024-04-03
Most women leaving prison face profound disadvantages and rarely have access to the resources needed to settle back into the community. Seemingly simple tasks such as obtaining replacement identification documents or opening a bank account become tangled in complexities.
Now researchers at the University of South Australia are co-designing a chatbot to help formerly incarcerated women re-establish their lives on the outside, and reduce the risk of them returning to prison.
Led by a team of UniSA researchers in collaboration with advocacy group Seeds of Affinity, the tech-based solution aims to help women access trusted ...
Doctors on front line of tackling childhood obesity but more training and resources needed
2024-04-03
Doctors are feeling unable to tackle growing problem of childhood obesity due to a lack of training and capacity according to new research.
In a paper published in the British Journal of General Practice, researchers from the University of Birmingham conducted in-depth interviews with healthcare professionals (HCPs) to understand their experiences of supporting families to tackle childhood obesity.
One participant in the study said:
“I had one mum and her child was overweight, but she was a young parent and she actually didn’t know how to cook the dinners and, yeah… we spent a lot of time with her giving her ...
Galaxies get more chaotic as they age
2024-04-03
Galaxies start life with their stars rotating in an orderly pattern but in some the motion of stars in more random. Until now, scientists have been uncertain about what causes this – possibly the surrounding environment or the mass of the galaxy itself.
A new study, published in a paper today in MNRAS (Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society), has found that the most important factor is neither of these things. It shows the tendency of the stars to have random motion is driven mostly by the age of the galaxy – things just get messy over time.
“When we did the analysis, we found that age, consistently, whichever way we slice or dice it, is always the most ...
Sandia pumps $140B into the economy through technology development
2024-04-03
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — To say that the technology and products Sandia National Laboratories researchers have helped imagine, innovate and industrialize have had a massive impact on the country would be an understatement.
Two studies commissioned by Sandia and the National Nuclear Security Administration show Sandia’s work has had an overall economic impact of $140 billion since the year 2000. That’s a significant figure, especially considering it spans just 20 years, less than a third of Sandia’s 75-year existence.
“I am very proud of how Sandia excels in fulfilling its technology transfer mission to deliver economic impact to the U.S.,” ...
Even moderate alcohol usage during pregnancy linked to birth abnormalities, UNM researchers find
2024-04-03
University of New Mexico researchers have found that even low to moderate alcohol use by pregnant patients may contribute to subtle changes in their babies’ prenatal development, including lower birth length and a shorter duration of gestation.
In a new paper published in the journal Alcohol Clinical & Experimental Research, a team led by Ludmila Bakhireva, MD, PhD, MPH, professor and assistant dean for Clinical and Translational Research in the UNM College of Pharmacy, also reported some sex-related differences in the effects of drinking during pregnancy on the developing ...
Sylvester physician co-authors global plan to combat prostate cancer
2024-04-03
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL APRIL 4, 2024, at 6:30 pm EDT) – Annual prostate cancer cases worldwide are projected to double by the year 2040, and annual deaths are projected to increase by 85% to almost 700,000 over the same timeframe – mainly among men in low- and middle-income countries. A commissioned report published online in The Lancet on April 4 highlights the future landscape of prostate cancer and seeks to guide cancer experts worldwide on how to manage the massive influx of prostate cancer patients projected over the next two decades.
Brandon Mahal, M.D., radiation oncologist and ...
Last chance to record archaic Greek language ‘heading for extinction’
2024-04-03
A new data crowdsourcing platform aims to preserve the sound of Romeyka, an endangered millennia-old variety of Greek. Experts consider the language to be a linguistic goldmine and a living bridge to the ancient world.
The initiative, led by Professor Ioanna Sitaridou from the University of Cambridge, contributes to the UN’s International Decade of Indigenous Languages (2022-32), which aims ‘to draw global attention on the critical situation of many indigenous languages and to mobilise stakeholders and resources for their preservation, revitalization and promotion.’
Romeyka is thought to have only a couple of thousand ...
Chicks prove vision and touch linked at birth
2024-04-03
Newly hatched chicks raised in darkness and allowed to touch either a smooth or bumpy cube for 24 hours instantly recognised the object with their vision upon first exposure to light.
This suggests chicks can link touch and vision without any prior experience combining these senses, challenging the long-held belief that such integration requires learning.
The discovery implies a pre-wired ability in the brain for cross-modal perception, potentially redefining our understanding of animal cognition and sensory processing.
In a study published in Biology Letters, researchers at Queen Mary University of London have cracked ...
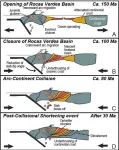
Researchers propose new step in tectonic squeeze that turns seafloor into mountains
2024-04-03
Scientists use tiny minerals called zircons as geologic timekeepers. Often no bigger than a grain of sand, these crystals record chemical signatures of the geological environment where they formed. In a new study led by scientists at The University of Texas at Austin, researchers used them to describe what could be an overlooked step in a fundamental tectonic process that raises seafloors into mountains.
In a study published in the journal Geology, the researchers describe zircons from the Andes mountains of Patagonia. Although the zircons formed when tectonic plates were colliding, they have a chemical signature associated ...
Gut bacteria that strongly influence obesity are different in men and women, study finds
2024-04-03
Novel approach finds gut microbiota that are highly predictive of BMI, waist circumference, and fat mass are different in men and women
And might change the chemical makeup (metabolome) of the gut in ways that affect the metabolism of different bioactive molecules that influence metabolic disease development
Interventions to help prevent obesity-favourable microbiome may need to be different in men and women
*This is an early press release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2024) Venice 12-15 May. Please credit the Congress if using this material*
New research being presented at this year’s European ...