(Press-News.org) Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, along with stroke, are among the top three neurodegenerative disorders, characterized by the malfunction and progressive degeneration of neurons, the nerve cells. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these neurological disorders and developing therapies requires labeling technologies that can visualize neuronal changes not only in normal conditions but also in disease states.
A research team led by Dr. Kim Yun Kyung from the Brain Science Institute at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with Professor Chang Young-Tae's team from Pohang University of Science and Technology, has announced the development of a next-generation neuron labeling technology called NeuM. NeuM (Neuronal Membrane-selective) selectively labels neuronal membranes, visualizing neuronal structures and allowing real-time monitoring of neuronal changes.
Neurons continuously modify their structure and function to transmit information from sensory organs to the brain, regulating thoughts, memories, and behaviors. Therefore, to overcome degenerative neurological diseases, it is essential to develop techniques that selectively label living neurons for real-time monitoring. However, current gene-based and antibody-based labeling technologies, commonly used to observe neurons, suffer from low accuracy and difficulty in long-term tracking due to their dependence on specific gene expression or proteins.
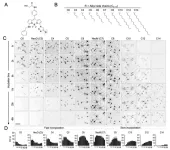
NeuM, developed by the research team through molecular design of neuronal cells, possesses excellent binding affinity to neuronal membranes, enabling long-term tracking and high-resolution imaging of neurons. The fluorescent probes within NeuM bind to neuronal membranes utilizing the activity of living cells, emitting fluorescent signals upon excitation by specific wavelengths of light. This visualization of neuronal membranes allows for detailed observation of neuronal terminal structures and high-resolution monitoring of neuronal differentiation and interactions.
NeuM, as the first technology to stain cell membranes through endocytosis in living neurons, exhibits selective reactivity towards living cells, excluding dead cells without internalization. Moreover, the research team has succeeded in extending the observation time of neurons from a mere 6 hours to up to 72 hours, enabling the capture of dynamic changes in living neurons over an extended period in response to environmental changes.
NeuM is expected to provide insights into research and therapy development for degenerative neurological diseases, for which there are currently no cures. These diseases, including Alzheimer's, result from neuronal damage due to the production of toxic proteins such as amyloid and the influx of inflammatory substances. NeuM's precise observation of neuronal changes can effectively facilitate the evaluation of candidate therapeutic compounds.
Dr. Kim stated, "NeuM, developed this time, can distinguish aging and degenerating neurons, becoming a crucial tool in elucidating the mechanisms of degenerative brain disorders and developing treatments." He further added, "In the future, we plan to refine NeuM for even more precise analysis of neurons by designing fluorescence wavelengths to distinguish colors such as green and red."
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-ho) through KIST's major projects and the Dementia Overcoming Project (RS-2023-00261784). The research results have been published in the latest issue of the international academic journal "Angewandte Chemie."
END
Key to unlocking the secret of degenerative brain disorders found
Development of 'NeuM', a neuron labeling technology enabling detailed observation of neuronal structure. Successful monitoring of neuronal changes for up to 72 hours.
2024-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Understanding the link between family physician characteristics and COVID-19 vaccination gaps
2024-04-08
New research examining the characteristics of physicians with the largest share of patients unvaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 may help increase vaccination rates going forward. The study, published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230816, found that family physicians in Ontario with the largest percentage of unvaccinated patients generally served patients living in marginalized neighbourhoods and had less support in their practices.
Researchers analyzed linked data on 9060 family physicians with more than 10 million enrolled patients ...
Ontario’s proposed plan to broaden alcohol sales will harm people
2024-04-08
The Ontario government’s plans to broaden alcohol sales to privately operated stores in the province could lead to higher consumption rates and related harms, write commentary authors in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240069.
“These changes will result in a 289% increase in the number of alcohol stores in Ontario (n = 2935 in March 2023, per the Liquor Control Board of Ontario), will likely reduce the price of alcohol, and will represent the biggest shift in decades with respect to how alcohol is sold in Canada,” write Drs. Norman Giesbrecht, Centre for Addiction and ...
Researchers identify an economic solution to Canada's opioid crisis
2024-04-08
Nasal-administered naloxone is more cost-effective and could help reduce the number of opioid-related fatalities compared to the current publicly funded intermuscular version, a new study has found.
Since 2016, Canada's opioid crisis has worsened, with over 40,000 opioid-related deaths, or about 22 deaths per day. Most of these accidental deaths (88 per cent) occur in British Columbia, Alberta and Ontario.
An effective way to help prevent opioid-related deaths is through community pharmacy-based naloxone programs. Currently, ...
Cancer stage compared with mortality as end points in randomized clinical trials of cancer screening
2024-04-08
About The Study: In this systematic review and meta-analysis that included 41 randomized clinical trials of cancer screening, incidence of late-stage cancer may be a suitable alternative end point to cancer-specific mortality for some cancer types, but is not suitable for others. These results have implications for clinical trials of multicancer screening tests.
Authors: Hilary A. Robbins, Ph.D., M.H.S., M.S.P.H., of the International Agency for Research on Cancer in Lyon, France, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.5814)
Editor’s ...
$2.3 trillion wasted globally in failed digital transformation programs – costly and complex business strategies are ‘not necessary’
2024-04-08
Strategies implemented by firms are too ambitious and wide-ranging, according to a specialist, with their poor design and structure preventing digital transformation success.
Firms seeking to harness new digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, must approach this organizational change in an entirely new way to avoid contributing to the $2.3 trillion wasted on unsuccessful projects globally so far.
This is the message of digital transformation expert Brian Harkin, author of Evolving from Digital Transformation to Digital Acceleration Using The Galapagos Framework, which helps business leaders understand how their approach to digital change ...
Frequently need to pee? App-based therapy can help, finds research
2024-04-08
Combining pelvic floor exercises with behavioral therapy could be more effective than current medical treatments at helping men with frequent urges to urinate, new research in men has found.
The initial results from the Bladder Emptying Disorder Therapy (BEST) Trial are presented today [Monday 8 April 2024] at the European Association of Urology Congress in Paris. They reveal that an app-based therapy leads to significant improvements in the lower urinary tract symptoms that many millions of men experience – hesitancy, straining, frequent urges to urinate and emptying the bladder effectively. Full results ...
Boreal forest and tundra regions worst hit over next 500 years of climate change, study shows
2024-04-08
The boreal forest, covering much of Canada and Alaska, and the treeless shrublands to the north of the forest region, may be among the worst impacted by climate change over the next 500 years, according to a new study.
The study, led by researchers at the White Rose universities of York and Leeds, as well as Oxford and Montreal, and ETH, Switzerland, ran a widely-used climate model with different atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide to assess the impact climate change could have on the ...
Telephone-based guideline-directed medical therapy optimization in Navajo nation
2024-04-07
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial including 103 American Indian patients, a telephone-based strategy of remote initiation and titration for outpatients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction led to improved rates of guideline-directed medical therapy at 30 days compared with usual care. This low-cost strategy could be expanded to other rural settings where access to care is limited.
Authors: Lauren A. Eberly, M.D., M.P.H., of the Indian Health Service in Gallup, New Mexico, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
AACR: Novel immunotherapies show promise for patients with kidney cancer and for solid organ transplant recipients with skin cancer
2024-04-07
ABSTRACTS: CT002, CT003
SAN DIEGO ― Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center presented encouraging findings today from two clinical trials in a plenary session highlighting advances in novel immunotherapy approaches at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2024. The studies describe the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy in patients with advanced kidney cancer and an oncolytic immunotherapy for patients with skin cancer following organ transplants. Information on all MD Anderson AACR Annual Meeting content can be found at MDAnderson.org/AACR.
Novel allogenic ...
New Phase 1 data from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center shows an investigational cancer vaccine may elicit lasting immune response in patients with pancreatic cancer
2024-04-07
New data presented today by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) researchers show an experimental approach to treating pancreatic cancer with the messenger RNA (mRNA)-based therapeutic cancer vaccine candidate, autogene cevumeran, continues to show potential to stimulate an immune response that may reduce the risk of the disease returning after surgery. New results from a phase 1 clinical trial show that the cancer vaccine candidate activated immune cells that persisted in the body for up to three years after treatment in certain patients. In addition, a vaccine-induced immune ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
Study: Anxiety, gloom often accompany intellectual deficits
Massage Therapy Foundation awards $300,000 research grant to the University of Denver
Gastrointestinal toxicity linked to targeted cancer therapies in the United States
Countdown to the Bial Award in Biomedicine 2025
Blood marker from dementia research could help track aging across the animal world
Birds change altitude to survive epic journeys across deserts and seas
Here's why you need a backup for the map on your phone
ACS Central Science | Researchers from Insilico Medicine and Lilly publish foundational vision for fully autonomous “Prompt-to-Drug” pharmaceutical R&D
Increasing the number of coronary interventions in patients with acute myocardial infarction does not appear to reduce death rates
Tackling uplift resistance in tall infrastructures sustainably
Novel wireless origami-inspired smart cushioning device for safer logistics
Hidden genetic mismatch, which triples the risk of a life-threatening immune attack after cord blood transplantation
Physical function is a crucial predictor of survival after heart failure
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
Sleep loss linked to higher atrial fibrillation risk in working-age adults
[Press-News.org] Key to unlocking the secret of degenerative brain disorders foundDevelopment of 'NeuM', a neuron labeling technology enabling detailed observation of neuronal structure. Successful monitoring of neuronal changes for up to 72 hours.