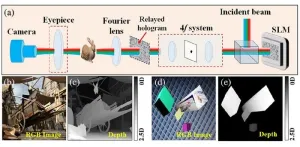
(Press-News.org) Holographic displays offer a promising avenue for achieving lifelike 3D reproductions with continuous depth sensation, holding potential applications in fields such as entertainment, medical imaging, and virtual reality. However, the conventional methods for generating computer-generated holograms (CGHs) rely on repetitive computations, leading to increased computational complexity and impracticality for real-time applications.
To tackle this issue, researchers from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology (China) have introduced a novel method for CGH generation that significantly reduces computational overhead while maintaining high-quality 3D visualization. As reported in Advanced Photonics Nexus, their approach leverages a split Lohmann lens-based diffraction model, enabling rapid synthesis of 3D holograms through a single-step backward propagation calculation. By incorporating a specially designed virtual digital phase modulation into the split Lohmann lens, their method achieves highly accurate reconstruction of 3D scenes with precise depth perception.
The significance of this research lies in its potential to revolutionize the creation of holographic displays by offering a practical solution for real-time CGH generation. Unlike traditional methods that suffer from computational bottlenecks, the proposed approach ensures consistent computation speed regardless of the depth sampling density, thereby enabling seamless integration into various applications requiring immersive 3D visualization.
To validate the effectiveness of their method, the researchers conducted both simulations and experiments, demonstrating its ability to generate realistic 3D holographic displays with accurate depth perception.
Overall, the study presents a promising advancement in the field of computer-generated holography, offering a practical solution for creating immersive 3D visualizations without the computational limitations of traditional methods. It helps pave the way for the widespread adoption of holographic displays in diverse industries and applications.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by C. Chang et al., “Split Lohmann computer holography: fast generation of 3D hologram in single-step diffraction calculation,” Adv. Photon. Nexus 3(3), 036001 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.APN.3.3.036001
END
Advancing real-time 3D holographic display: A breakthrough in computer-generated holography
An innovative method for real-time CGH generation leverages a split Lohmann lens-based diffraction model to significantly reduce computational overhead while maintaining high-quality 3D visualization
2024-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study shows renewable energy could work as power source at the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station
2024-04-08
A recent analysis shows that renewable energy could be a viable alternative to diesel fuel for science at the South Pole. The analysis deeply explores the feasibility of replacing part of the energy production at the South Pole with renewable sources.
For almost as long as humans have spent time in Antarctica, the continent has been a home for science. One of the research outposts located there is the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station. The science done there includes studies of climate change and cosmology.
Currently, ...
Cathie Biga is new American College of Cardiology president
2024-04-08
Cathie Biga, MSN, FACC, today became president of the American College of Cardiology and made history as the organization’s first non-physician president. She will serve a one-year term representing over 56,000 cardiovascular care team members around the world and leading the cardiovascular organization in its mission to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health for all.
“I’m excited to bring my own set of leadership skills and perspectives to the ACC as we kick off the first year of our new Strategic Plan and celebrate the College’s 75th ...
Data shows medical marijuana use decreased in states where recreational use became legal
2024-04-08
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 8 April 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, ...
Houston-area energy startup incubator wins phase 1 of DOE competition
2024-04-08
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Technology Transitions (OTT) selected Texas Innovates, a non-profit organization focused on hydrogen and carbon innovation and expansion in the greater Houston and Gulf Coast region, as one of 23 phase 1 winners of the Energy Program for Innovation Clusters (EPIC) Round 3 competition. Notably, Texas Innovates is the only Texas entity to advance to phase 2 of the competition.
“We have been working towards this day since we identified the need for energy hardware incubation in 2017 and were a finalist in 2019 for C40 Cities global competition to make Houston’s Velasco Incinerator ...
A pulse of innovation: AI at the service of heart research
2024-04-08
A Pulse of Innovation: AI at the Service of Heart Research
Columbia biomedical engineers use AI to build a transformative new tool to study and diagnose heart function
Understanding heart function and disease, as well as testing new drugs for heart conditions, has long been a complex and time-consuming task. A promising way to study disease and test new drugs is to use cellular and engineered tissue models in a dish, but existing methods to study heart cell contraction and calcium handling require a good deal of manual work, are prone to errors, and need expensive specialized equipment. There clearly is a critical medical ...
Targeting vulnerability in B-cell development leads to novel drug combination for leukemia
2024-04-08
Despite having an overall survival rate of 94%, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common childhood cancer, can prove challenging to treat, with survival among relapsed or resistant cases falling between 30-50%. Recent work by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists discovered which tumor cells resist treatment and why. This enabled the rational design of a combination therapy that better controlled high-risk subtypes of B-ALL in mouse models. The findings were published today in Cancer Cell.
“We found a new explanation of B-ALL ...
People make more patient decisions when shown the benefits first
2024-04-08
Key takeways
UCLA psychologists asked experiment participants to choose to receive $40 in seven days or $60 in 30 days, for example, under a variety of time constraints.
The experiment showed that people tend to make more impulsive decisions if they think about time delays first, and more patient decisions if they think about the greater reward associated with waiting longer.
The findings could be applied where people are being encouraged to make life choices that will benefit them in the long run, such as eating healthier, exercising or saving for retirement, by emphasizing the future large rewards and deemphasizing ...
New diagnostic tool achieves accuracy of PCR tests with faster and simpler nanopore system
2024-04-08
EMBARGOED UNTIL APRIL 8, 2024 AT 3:00 PM U.S. ET/ 12:00 PM PT
Over the past four years, many of us have become accustomed to a swab up the nose to test for COVID-19, using at-home rapid antigen tests or the more accurate clinic-provided PCR tests with a longer processing time. Now a new diagnostic tool developed by UC Santa Cruz Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Holger Schmidt and his collaborators can test for SARS-CoV-2 and Zika virus with the same or better accuracy as high-precision PCR tests in a matter of hours.
In a new paper in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Schmidt ...
Pregnancy accelerates biological aging in a healthy, young adult population
2024-04-08
Pregnancy may carry a cost, reports a new study from the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health. The research, carried out among 1735 young people in the Philippines, shows that women who reported having been pregnant looked biologically older than women who had never been pregnant, and women who had been pregnant more often looked biologically older than those who reported fewer pregnancies. Notably, the number of pregnancies fathered was not associated with biological aging among same-aged cohort ...
Different means to the same end: How a worm protects its chromosomes
2024-04-08
University of Michigan researchers have discovered that a worm commonly used in the study of biology uses a set of proteins unlike those seen in other studied organisms to protect the ends of its DNA.
In mammals, shelterin is a complex of proteins that "shelters" the ends of our chromosomes from unraveling or fusing together. Keeping chromosomes from fusing together is an important job: chromosomes carry our body's DNA. If chromosome ends fuse, or if they fuse with other chromosomes, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists show how to predict world’s deadly scorpion hotspots
ASU researchers to lead AAAS panel on water insecurity in the United States
ASU professor Anne Stone to present at AAAS Conference in Phoenix on ancient origins of modern disease
Proposals for exploring viruses and skin as the next experimental quantum frontiers share US$30,000 science award
ASU researchers showcase scalable tech solutions for older adults living alone with cognitive decline at AAAS 2026
Scientists identify smooth regional trends in fruit fly survival strategies
Antipathy toward snakes? Your parents likely talked you into that at an early age
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for Feb. 2026
Online exposure to medical misinformation concentrated among older adults
Telehealth improves access to genetic services for adult survivors of childhood cancers
Outdated mortality benchmarks risk missing early signs of famine and delay recognizing mass starvation
Newly discovered bacterium converts carbon dioxide into chemicals using electricity
Flipping and reversing mini-proteins could improve disease treatment
Scientists reveal major hidden source of atmospheric nitrogen pollution in fragile lake basin
Biochar emerges as a powerful tool for soil carbon neutrality and climate mitigation
Tiny cell messengers show big promise for safer protein and gene delivery
AMS releases statement regarding the decision to rescind EPA’s 2009 Endangerment Finding
Parents’ alcohol and drug use influences their children’s consumption, research shows
Modular assembly of chiral nitrogen-bridged rings achieved by palladium-catalyzed diastereoselective and enantioselective cascade cyclization reactions
Promoting civic engagement
AMS Science Preview: Hurricane slowdown, school snow days
Deforestation in the Amazon raises the surface temperature by 3 °C during the dry season
Model more accurately maps the impact of frost on corn crops
How did humans develop sharp vision? Lab-grown retinas show likely answer
Sour grapes? Taste, experience of sour foods depends on individual consumer
At AAAS, professor Krystal Tsosie argues the future of science must be Indigenous-led
From the lab to the living room: Decoding Parkinson’s patients movements in the real world
Research advances in porous materials, as highlighted in the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Sally C. Morton, executive vice president of ASU Knowledge Enterprise, presents a bold and practical framework for moving research from discovery to real-world impact
Biochemical parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy versus individuals with diabetes alone, non-diabetic nephropathy, and healthy controls
[Press-News.org] Advancing real-time 3D holographic display: A breakthrough in computer-generated holographyAn innovative method for real-time CGH generation leverages a split Lohmann lens-based diffraction model to significantly reduce computational overhead while maintaining high-quality 3D visualization