(Press-News.org) Common “hard” coastal defenses, like concrete sea walls, might struggle to keep up with increasing climate risks. A new study shows that combining them with nature-based solutions could, in some contexts, create defenses which are better able to adapt. Researchers reviewed 304 academic articles on the performance of coastal defenses around the world, including: natural environments; soft measures (which support or enrich nature); hard measures (such as concrete sea walls); and hybrids of the aforementioned. Soft and hybrid measures turned out to be more cost-effective than hard measures, and hybrid measures provided the highest hazard reduction overall in low-risk areas. Although their comparative performance during extreme events that pose a high risk is not clear due to lack of data, these results still support the careful inclusion of nature-based solutions to help protect, support and enrich coastal communities.
Japan’s dramatic natural coastline, with iconic views of Mount Fuji, wind-blown pines and rocky beaches, has been captured and admired in paintings and prints for hundreds of years. But take a walk by the ocean nowadays and it can be hard to find a stretch that retains its pristine natural seascape. By the early 1990s, a government survey found that around 40% of the coast had been altered with concrete sea walls, filled harbors, stacks of tetrapods and more, adding swaths of gray to the blue-green landscape. Sprawling coastal cities and towns have grown to house most of the population, so protecting homes and businesses from the dangers of tsunamis, typhoon swells and sea-level rise has become an ever-increasing challenge.
“Sea walls, dikes, dams and breakwaters, the so-called traditional hard measures, despite being the most popular coastal defenses globally and with proven track records, are facing challenges to keep pace with increasing climate risks”, explained Lam Thi Mai Huynh, a doctoral student from the graduate program in sustainability science at the University of Tokyo and lead author of a new study on coastal defenses. “These hard structures are expensive to build and require continuous upgrades and repairs as sea level rises and climatic hazards become stronger. Although they are good at mitigating certain coastal disaster risks, they can also cause significant disruption to coastal communities and have adverse environmental effects. Furthermore, they often significantly alter the seascape and sometimes alienate local communities from nature and the very environment we seek to protect.”
To better understand the performance and benefits of different hard and nature-based coastal defenses, an international team compared the results of 304 academic studies. Nature-based coastal defenses included: “natural” ecosystems, for example, existing mangroves and coral reefs; “soft” measures, which restore, rehabilitate, reforest or nourish natural ecosystems; and “hybrid” measures that combine both nature-based components and hard structures, such as placing concrete breakwaters in front of mangroves.
“By incorporating such natural components, we can create coastal defenses that reduce risk and also offer substantial environmental benefits. We believe that such strategies are very promising in many parts of the world, but they are also not a ‘fix-all’ solution,” said Professor Alexandros Gasparatos from the Institute for Future Initiatives at the University of Tokyo.
The researchers analyzed three key aspects of each type of defense: 1. risk reduction (how much the measure could reduce wave height and energy, and influence shoreline change); 2. climate change mitigation (including carbon storage and greenhouse gas emissions for nature-based measures); and 3. cost-effectiveness over a 20-year period.
“Our results indicate that among all coastal defense options in lower-risk areas, hybrid measures provide the highest risk reduction. Hybrid measures can harness the advantages of both hard and soft measures. They provide the immediacy of an engineered barrier while largely maintaining the ecological functionality of a permeable vegetated zone,” said Huynh. “All nature-based solutions are found to be effective in storing carbon, while both soft and hybrid measures are relatively more cost-effective than traditional hard measures over a 20-year period, though all have positive economic returns.”
These findings provide strong evidence for integrating and upscaling nature-based components into coastal defenses, but the team advised doing so with caution. “All types of coastal defenses have yet to be adequately tested through paired experiments in circumstances of extreme events and high-risk urgency,” warned Gasparatos. “Until there are many more such experiments focusing on this, we must caution against any universal assumptions about the comparative performance of coastal defense options, whether natural, soft or hybrid measures.”
While acknowledging the limits imposed by the lack of available research on extreme and high-risk situations, Huynh and Gasparatos still believe that this study supports the idea of investing in nature-based solutions for coastal defense in lower-risk areas. Research like this has important implications for policymakers, coastal planners and communities looking to make evidence-based decisions.
“I firmly believe that we must think more carefully about the design and function of these barriers in this era of ever-accelerating climate change,” said Huynh. “Not only can nature-based solutions contribute to risk reduction and climate mitigation in many areas, but they can also help reconnect people with nature and support biodiversity. Greening our coastlines can create spaces which enhance quality of life, foster community well-being and inspire environmental stewardship.”
#####
Paper Title:
Lam T.M. Huynh, Jie Su, Quanli Wang, Lindsay C. Stringer, Adam D. Switzer, Alexandros Gasparatos. Meta-analysis shows hybrid engineering-natural coastal defences perform best for climate adaptation and mitigation. Nature Communications. April 9th 2024. Doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46970-w
Funding:
L.H acknowledges the support of Grant-in-Aid Research Fellowship for young Scientist offered by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (23KJ0544). A.G is supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research A offered by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (22H00567). A.D.S. is supported by the Singapore Ministry of Education Academic Research Fund (MOE2019-T3-1-004 and MOET32022-0006).
Useful Links
Graduate Program in Sustainability Science - Global Leadership Initiative: https://www.sustainability.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences: https://www.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Institute for Future Initiatives: https://ifi.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Gasparatos Lab: https://www.gasparatos-lab.org/
Research Contact:
Lam Thi Mai Huynh
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo
5-1-5 Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa City 277- 8563, Japan.
Email: lam.huynh@s.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Professor Alexandros Gasparatos
Institute for Future Initiatives (IFI), The University of Tokyo
Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033
Email: gasparatos@ifi.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact:
Mrs. Nicola Burghall
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on X (formally Twitter) at @UTokyo_News_en.
END
A natural touch for coastal defense
Hybrid solutions which combine nature with common “hard” coastal protection measures may offer more benefits in lower-risk areas
2024-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Remote work cuts car travel and emissions, but hurts public transit ridership
2024-04-09
Remote work could cut hundreds of millions of tons of carbon emissions from car travel – but at the cost of billions lost in public transit revenues, according to a new study.
Using the latest data on remote work and transportation behavior since the pandemic upended work arrangements, researchers at the University of Florida, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Peking University revealed how cities could meet their sustainability goals by promoting remote work.
The researchers found that a 10% increase in remote workers could lead ...
Better battery manufacturing: Robotic lab vets new reaction design strategy
2024-04-09
Images // Video
New chemistries for batteries, semiconductors and more could be easier to manufacture, thanks to a new approach to making chemically complex materials that researchers at the University of Michigan and Samsung's Advanced Materials Lab have demonstrated.
Their new recipes use unconventional ingredients to make battery materials with fewer impurities, requiring fewer costly refinement steps and increasing their economic viability.
"Over the past two decades, many battery materials with enhanced capacity, charging speed and stability ...
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) shown to reduce severity of certain mental illnesses
2024-04-09
Researchers have found that Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT), where an electric current is passed through the brain, can reduce the severity of mental illnesses.
ECT is a safe and effective treatment for some mental illnesses including severe/psychotic depression, postnatal psychosis and mania.[1],[2] Patients are placed under general anaesthetic and the brain is stimulated with short electric pulses.[3] This causes a brief seizure which lasts for less than two minutes.[3]
The use of ECT across Scotland was assessed over an 11-year period from 2009 to 2019 using data from the Scottish Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) Audit Network (SEAN). The Scotland-wide ...
Lonely children more likely to experience psychosis, new study finds
2024-04-09
A new study suggests that children who felt lonely for more than 6 months before the age of 12 are more likely to experience an episode of psychosis than children who did not, with women more affected than men.
Psychosis refers to a collection of symptoms that affect a person’s mind, where there has been some loss of contact with reality.[1] During an episode of psychosis, a person may have difficulty recognising what is real and what is not.[1] Symptoms of psychosis include hallucinations, delusions and confused thoughts.[2] In some instances, psychosis may be a symptom of other mental health conditions, such as schizophrenia, ...
HKUST and Tsinghua researchers develop mechanism of electrical 180° switching of Néel vector
2024-04-09
A collaborated research team led by The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and Tsinghua University has theoretically proposed a new mechanism of electrical 180° switching of Néel vector and experimentally realized it in antiferromagnetic materials with spin-splitting band structure featuring the C-paired spin-valley locking, also named as altermagnet. The team also demonstrated the material's capability to manipulate Néel vector, paving the way for the manufacturing ...
Military veterans say extremism was preceded by negative service experiences
2024-04-09
Interviews with military veterans who expressed support for extremist groups or related beliefs on a prior survey show that many experienced a significant negative event during their military service, according to a new RAND report.
Researchers found that these veterans also often faced difficulties transitioning to civilian life and sometimes shared their beliefs with a wider social network.
RAND researchers conducted 21 interviews with veterans who had indicated support for one or more extremist groups or related beliefs to understand possible drivers and patterns of extremism among veterans. That support ...
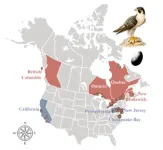
Peregrine falcons expose lasting harms of flame retardant use
2024-04-09
Peregrine falcon populations across North America are heavily contaminated with harmful flame retardants–including those that have been phased out for years–according to a new study published in Environmental Science & Technology. Flame retardants are chemicals added to furniture, electronics, and other everyday products to meet flammability standards, though they often do not work as intended. They also migrate out of products they are added to and end up in wildlife and people and many are linked to serious health and environmental harms.
“Our ...
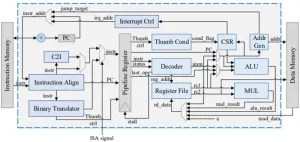
RVAM16: A low-cost multiple-ISA processor based on RISC-V and ARM thumb
2024-04-09
The increasing demand in the embedded field has led to the emergence of several impressive Instruction Set Architectures (ISAs). However, when processors migrate from one ISA to another, software compatibility issues are unavoidable. Despite the availability of software binary translation systems for ensuring software compatibility, these systems have limitations (e.g. performance and power) in low-cost embedded systems. To solve the problems, a research team led by Professor Libo HUANG published their new research on 18 Mar 2024 in ...
Will the convergence of light and matter in Janus particles transcend performance limitations in the optical display industry?
2024-04-09
A research team consisting of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Hyeongwoo Lee, an integrated PhD student, from the Department of Physics at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has pioneered an innovative technique in ultra-high-resolution spectroscopy. Their breakthrough marks the world's first instance of electrically controlling polaritons—hybridized light-matter particles—at room temperature.
Polaritons are "half-light half-matter" hybrid particles, having both the characteristics of photons—particles of light—and those of solid matter. Their unique characteristics exhibit properties distinct from both traditional ...
A gene mutation associated with a rare neurological disorder and increased susceptibility to viral infections may be treatable with oleic acid
2024-04-09
A mutation in a protein regulating natural killer (NK) cells’ function is at the root of immune deficiency in some people with a rare genetic condition characterized by cognitive and developmental delay, seizures, and other manifestations, new UCLA-led research suggests.
The researchers found that loss or mutations in a gene called MEF2C disrupted the ability of NK cells to take up chemical compounds called lipids that are used to fuel crucial functions such as tumor cell killing and creating inflammatory molecules. They found that people with the rare neurological syndrome called (MCHS) who have the mutation in this gene are particularly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
[Press-News.org] A natural touch for coastal defenseHybrid solutions which combine nature with common “hard” coastal protection measures may offer more benefits in lower-risk areas