(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—New research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism finds a high prevalence of type D personality among people with hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. Between 10-15% of people with treated hypothyroidism experience persistent symptoms despite achieving normal thyroid hormone levels, and the underlying causes are unclear.
Type D personality, which is characterized by pessimism, worry, stress, negative emotions and social withdrawal, is sometimes associated with poor health status and symptom burden, but this association has not previously been studied in people with hypothyroidism.
The researchers of the current study surveyed over 3,500 people with self-reported, treated hypothyroidism and found over half of these people had type D personality. They asked questions to better understand their quality of life and why some patients were dissatisfied with their treatment outcomes.
“People with hypothyroidism and type D personality may experience more negative treatment outcomes than those without type D personality,” said study author Petros Perros, M.D., of Newcastle University in Newcastle upon Tyne, U.K. “We think that there are two likely interpretations, which may not be mutually exclusive - type D personality and hypothyroidism share similar underlying causes, or people with type D personality may perceive treatment outcomes more negatively.”
They confirmed some patients with hypothyroidism were dissatisfied with their care and experienced persistent unexplained symptoms. People with hypothyroidism who had type D personality had particularly high levels of anxiety, depression, dissatisfaction with treatment, persistent symptoms and poor quality of life.
“Further research is needed to confirm our findings and determine if it is possible to predict how newly diagnosed patients with hypothyroidism will respond to treatment based on personality traits. If so, studies could be designed specifically for such patients, to determine if interventions can improve outcomes,” Perros said.
Other study authors include: Endre Vezekenyi Nagy of the University of Debrecen in Debrecen, Hungary; Enrico Papini of Regina Apostolorum Hospital, Albano in Rome, Italy; Juan Abad-Madroñero and Alan J. Poots of Picker Institute Europe in Oxford, England; Peter Lakwijk of the Thyroid Federation International in Hoofddorp, Netherlands; Floortje Mols of Tilburg University in Tilburg, Netherlands; and Laszlo Hegedüs of Odense University Hospital in Odense, Denmark.
The study was funded by the Institut Biochimique SA (IBSA).
The manuscript, “Hypothyroidism and Type D Personality: Results From E-MPATHY, A Cross-Sectional International Online Patient Survey," was published online, ahead print.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
People with hypothyroidism and type D personality may be more likely to experience poor treatment outcomes
Researchers look to understand link between psychological and thyroid health
2024-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome in twins linked to novel genetic mutations
2024-04-09
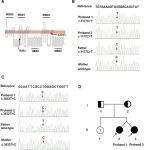
Researchers in China and Italy have made a significant breakthrough in understanding Dubin-Johnson syndrome (DJS), a rare inherited liver disorder. The team identified specific genetic mutations responsible for DJS in a pair of dizygotic twins, offering valuable insights into the cause of the disease and potentially improving diagnosis for patients with unclear symptoms.
DJS disrupts the liver's ability to eliminate waste products, leading to a buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment in the blood. This ...
Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 therapy in sinonasal mucosal melanoma: a 10-year experience at a single institution
2024-04-09
Background and objectives
Sinonasal mucosal melanoma (SNMM) is a rare aggressive malignancy that presents with dismal outcomes and a high metastatic propensity. The prognostic factors as well as therapeutic regimens remain largely unknown due to the rarity of SNMM. This study aimed to assess the characteristics of SNMM patients associated with a better prognosis.
Methods
We performed an observational cross-sectional study to investigate the prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) therapy in 12 SNNM patients who were diagnosed at our institution and treated with anti-PD-L1 ...
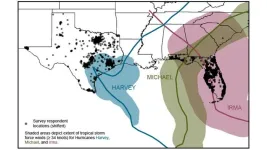
Floridians’ and Texans’ perceptions of hurricane risk
2024-04-09
Rapid climate change is prompting adaptation to threats such as tropical cyclones, wildfires, and droughts—but relatively trivial adaptation actions may lull people into inaccurate perceptions of their personal risk. Researchers from the University of California, Irvine; Stanford University; and the University of California, Los Angeles surveyed 2,774 Texas and Florida residents about tropical cyclones—also known in North America as hurricanes—five times between 2017 and 2022. The survey ...
Virtue in Japan: perception differences among educational specialists and general public
2024-04-09
Virtue is a normative concept comprising a set of moral and social codes acceptable to society. Historically, in the West, especially in ancient Greek and Christian belief systems, virtue was viewed as "excellence" aspirational to all human beings. In contrast, the East, especially in a Confucian belief system, viewed it similarly but being aspirational to only select individuals, such as rulers. However, the rise of modern values and sociopolitical overhauls almost pushed the concept of ...
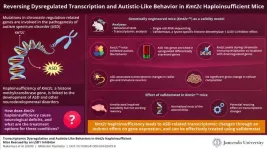
New study uncovers how altered gene expression can induce autism
2024-04-09
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) encompasses neurodevelopmental conditions where patients display repetitive behavior and impaired sociality. Genetic factors have been shown to influence the development of ASD. Additionally, recent studies have shown that the genes involved in chromatin modification and gene transcription are involved in the pathogenesis of ASD. Among the many genes implicated in this process, the gene KMT2C (lysine methyltransferase 2c), which codes for a catalytic unit of H3K4 (histone H3 lysine 4) methyltransferase complex, has been identified to be associated with the development ...
Targeting RAS proteins may prevent relapse in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
2024-04-09
Relapses in a common form of leukemia may be preventable following new research which has identified how the cancer develops resistance to first line treatments.
New research published in iScience by researchers from the University of Birmingham, the Institute of Cancer Research (ICR), Newcastle University, the Princess Maxima Centre of Pediatric oncology and the University of Virginia identified changes in a mutated form of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) samples from patients who relapsed after receiving FLT3 inhibitor treatment.
The team found that the resistant cancer had up-regulated multiple other signalling pathways to overcome the drug’s action, and ...
What’s quieter than a fish? A school of them
2024-04-09
Swimming in schools makes fish surprisingly stealthy underwater, with a group able to sound like a single fish.
The new findings by Johns Hopkins University engineers working with a high-tech simulation of schooling mackerel, offers new insight into why fish swim in schools and promise for the design and operation of much quieter submarines and autonomous undersea vehicles.
“It’s widely known that swimming in groups provides fish with added protection from predators, but we questioned whether it also contributes to reducing their noise,” said senior author Rajat Mittal. “Our results suggest that the substantial decrease in ...
Growth mindset messages can close grade gap for first-generation students
2024-04-09
PULLMAN, Wash. – Just two emails, at the right time with the right message, can make a big difference for students who are the first in their families to go to college.
A recent Washington State University study highlighted the power of an instructors’ growth mindset -- the belief that abilities are not innate but can be improved. Researchers found that when first-generation students in an introductory science course received growth mindset emails after their initial exams, they did better in the whole course than a control group.
On average the students raised their final grade by about a third of a letter grade, such as moving ...
After being insulted, writing down your feelings on paper then getting rid of it reduces anger
2024-04-09
A research group in Japan has discovered that writing down one's reaction to a negative incident on a piece of paper and then shredding it or throwing it away reduces feelings of anger.
“We expected that our method would suppress anger to some extent,” lead researcher Nobuyuki Kawai said. “However, we were amazed that anger was eliminated almost entirely.”
This research is important because controlling anger at home and in the workplace can reduce negative consequences in our jobs and personal lives. Unfortunately, ...
A natural touch for coastal defense
2024-04-09
Common “hard” coastal defenses, like concrete sea walls, might struggle to keep up with increasing climate risks. A new study shows that combining them with nature-based solutions could, in some contexts, create defenses which are better able to adapt. Researchers reviewed 304 academic articles on the performance of coastal defenses around the world, including: natural environments; soft measures (which support or enrich nature); hard measures (such as concrete sea walls); and hybrids of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] People with hypothyroidism and type D personality may be more likely to experience poor treatment outcomesResearchers look to understand link between psychological and thyroid health