(Press-News.org) Leiden - also known as the ‘City of Keys’ and the 'City of Discoveries' - was aptly chosen to host the third Empowering Biodiversity Research (EBR III) conference. The two-day conference - this time focusing on the utilisation of biodiversity data as a vehicle for biodiversity research to reach to Policy - was held in a no less fitting locality: the Naturalis Biodiversity Center.
On 25th and 26th March 2024, the delegates got the chance to learn more about the latest discoveries, trends and innovations from scientists, as well as various stakeholders, including representatives of policy-making bodies, research institutions and infrastructures. The conference also ran a poster session and a Biodiversity Informatics market, where scientists, research teams, project consortia, and providers of biodiversity research-related services and tools could showcase their work and meet like-minded professionals.
BiCIKL stops at the Naturalis Biodiversity Center
The famous for its bicycle friendliness country also made a suitable stop for BiCIKL (an acronym for the Biodiversity Community Integrated Knowledge Library): a project funded under the European Commission’s Horizon 2020 programme that aimed at triggering a culture change in the way users access, (re)use, publish and share biodiversity data. To do this, the BiCIKL consortium set off on a 3-year journey to build on the existing biodiversity data infrastructures, workflows, standards and the linkages between them.
Many of the people who have been involved in the project over the last three years could be seen all around the beautiful venue. Above all, Naturalis is itself one of the partnering institutions at BiCIKL. Then, on Tuesday, on behalf of the BiCIKL consortium and the project’s coordinator: the scientific publisher and technology innovator: Pensoft, Iva Boyadzhieva presented the work done within the project one month ahead of its official conclusion at the end of April.
As she talked about the way the BiCIKL consortium took to traverse obstacles to wider use and adoption of FAIR and linked biodiversity data, she focused on BiCIKL’s main outcome: the Biodiversity Knowledge Hub (BKH).
Intended to act as a knowledge broker for users who wish to navigate and access sources of open and FAIR biodiversity data, guidelines, tools and services, in practicality, the BKH is a one-stop portal for understanding the complex but increasingly interconnected landscape of biodiversity research infrastructures in Europe and beyond. It collates information, guidelines, recommendations and best practices in usage of FAIR and linked biodiversity data, as well as a continuously expanded catalogue of compliant relevant services and tools.
At the core of the BKH is the FAIR Data Place (FDP), where users can familiarise themselves with each of the participating biodiversity infrastructures and network organisations, and also learn about the specific services they provide. There, anyone can explore various biodiversity data tools and services by browsing by their main data type, e.g. specimens, sequences, taxon names, literature.
While the project might be coming to an end, she pointed out, the BKH is here to stay as a navigation system in a universe of interconnected biodiversity research infrastructures. To do this, not only will the partners continue to maintain it, but it will also remain open to any research infrastructure that wishes to feature its own tools and services compliant with the linked and FAIR data requirements set by the BiCIKL consortium.
What else was on at the EBR III?
Indisputably, the ‘hot’ topics at the EBR III were the novel technologies for remote and non-invasive, yet efficient biomonitoring; the utilisation of data and other input sourced by citizen scientists; as well as leveraging different types and sources of biodiversity data, in order to better inform decision-makers, but also future-proof the scientific knowledge we have collected and generated to date.
***
Amongst the other Horizon Europe projects presented at the EBR III conference was B-Cubed (Biodiversity Building Blocks for policy). On Monday, the project’s coordinator Dr Quentin Groom (Meise Botanic Garden) familiarised the conference participants with the project, which aims to standardise access to biodiversity data, in order to empower policymakers to proactively address the impacts of biodiversity change.
***
MAMBO: another Horizon Europe project where Pensoft has been contributing with expertise in science communication, dissemination and exploitation, was also an active participant at the event. An acronym for Modern Approaches to the Monitoring of BiOdiversity, MAMBO had its own session on Tuesday morning, where Dr Vincent Kalkman (Naturalis Biodiversity Center), Dr France Gerard (UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology) and Prof. Toke Høye (Aarhus University) each took to the stage to demonstrate how modern technology developed within the project is to improve biodiversity and habitat monitoring. Learn more about MAMBO and Pensoft’s involvement in this blog post.
***
The EBR III conference also saw a presentation - albeit remote - from Prof. Dr. Florian Leese (Dean at the University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany, and Editor-in-Chief at the Metabarcoding and Metagenomics journal), where he talked about the promise, but also the challenges for DNA-based methods to empower biodiversity monitoring.
Amongst the key tasks here, he pointed out, are the alignment of DNA-based methods with the Global Biodiversity Framework; central push and funding for standards and guidance; publication of data in portals that adhere to the best data practices and rules; and the mobilisation of existing resources such as the meteorological ones.
He also made a reference to the Forum Paper “Introducing guidelines for publishing DNA-derived occurrence data through biodiversity data platforms” by R. Henrik Nilsson et al., where the international team provided a brief rationale and an overview of guidelines targeting the principles and approaches of exposing DNA-derived occurrence data in the context of broader biodiversity data. In the study, published in the Metabarcoding and Metagenomics journal in 2022, they also introduced a living version of these guidelines, which continues to encourage feedback and interaction as new techniques and best practices emerge.
***
You can find the programme and the slides presentations on the conference website. Highlights from the conference are also accessible from X via the conference hashtag: #EBR2024.
Don’t forget to also explore the Biodiversity Knowledge Hub for yourself at: https://biodiversityknowledgehub.eu/ and watch the introduction video.
END
A BiCIKL ride to the Empowering Biodiversity Research conference for a report on a 3-year endeavor towards FAIR biodiversity data
2024-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Visiting white parts of town make some Black kids feel less safe
2024-04-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Some Black youth feel less safe when they visit predominantly white areas of their city, a new study in Columbus has found.
And it was those Black kids who spent the most time in white-dominated areas who felt less safe, said Christopher Browning, lead author of the study and professor of sociology at The Ohio State University.
“Familiarity with white neighborhoods doesn’t make Black kids feel more comfortable and safer. In fact, familiarity seems to reveal ...
Deforestation harms biodiversity of the Amazon’s perfume-loving orchid bees
2024-04-10
LAWRENCE — A survey of orchid bees in the Brazilian Amazon state of Rondônia, carried out in the 1990s, is shedding new light the impact of deforestation on the scent-collecting pollinators, which some view as bellwethers of biodiversity in the neotropics.
The findings, from a researcher at the University of Kansas, are published today in the peer-reviewed journal Biological Conservation.
“This study on orchid bees was an add-on to previous research on stingless bees. Orchid bees are so easy to collect, so we added them to ...
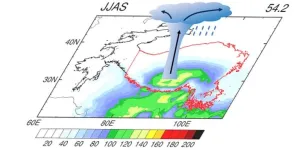
Long-term satellite observations show climatological characteristics of isolated deep convection over the Tibetan Plateau
2024-04-10
The Tibetan Plateau is a prevalent region for deep convection owing to its unique thermodynamic forcing. Deep convection can exist as isolated deep convection (IDC), which is small in size, or mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), which are convective storms organized into larger and longer-lived systems. Most previous research has focused on MCSs over the Tibetan Plateau, but less so on IDC systems (hereafter, IDCs).
Dr. Ying Na from Wuxi University, and Dr. Chaofan Li from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, examined the climatological features of IDCs by using high-resolution satellite observations in June to September ...
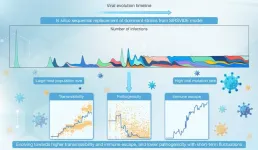
Modeling viral evolution: A novel SIRSVIDE framework with application to SARS-CoV-2 dynamics
2024-04-10
Understanding the mutation and evolution of viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2) is crucial for effective public health management and response. Traditional epidemiological models often assume that viral transmissibility and pathogenicity remain constant during disease transmission, ignoring the fact that viruses continuously evolve through natural selection and random mutations. This simplification limits the accuracy of these models in predicting epidemic trends, especially when facing rapidly mutating viruses.
To overcome these limitations, ...
New data: UTSA economic development institute added $2.6 billion to Texas’ economy
2024-04-10
SAN ANTONIO, TEXAS — The Valdez Institute for Economic Development (VIED) at UTSA generated an overall direct economic impact of $2.6 billion for the Texas economy in 2023, according to the organization’s 2023 annual report, which was released Tuesday.
The latest figure represents the work of the institute’s portfolio of time-tested economic development strategies and new innovations that enabled business owners and entrepreneurs to start and grow their small businesses.
During the 2023 fiscal year, the institute:
Served 41,231 business ...
Waterproof ‘e-glove’ could help scuba divers communicate
2024-04-10
When scuba divers need to say “I’m okay” or “Shark!” to their dive partners, they use hand signals to communicate visually. But sometimes these movements are difficult to see. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have constructed a waterproof “e-glove” that wirelessly transmits hand gestures made underwater to a computer that translates them into messages. The new technology could someday help divers communicate better with each other and with boat crews on the surface.
E-gloves — gloves fitted ...
BioOne presents 2024 BioOne Ambassador Award to five early career scientists
2024-04-10
BioOne proudly announces the 2024 recipients of the BioOne Ambassador Award. Now in its seventh year, this prestigious award recognizes early-career researchers in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences who demonstrate creative approaches to science communication thereby fostering greater science literacy and aiding in the understanding of the natural world. BioOne Ambassadors are nominated by BioOne publishing partners, and each winning author will receive a $1,000 award and have their work promoted through BioOne’s multiple channels.
This year’s honorees are:
Dr. Elis Fisk – Draw and Learn: A Bighorn Sheep Mystery; nominated by The Wildlife ...
Thinking outside the doctor’s office: Poll looks at older adults’ use of urgent care, retail clinics and more
2024-04-10
When today’s older adults were growing up, urgent care centers and clinics inside retail stores didn’t exist. But most of them have now embraced these non-traditional sites for getting medical care, a new national poll finds.
In the past two years, 60% of people age 50 to 80 have visited an urgent care clinic, or a clinic based in a retail store, workplace or vehicle, according to new findings from the University of Michigan National Poll on Healthy Aging.
Urgent care clinics were the most ...
New mechanism discovered for the life-threatening arrhythmias in Andersen-Tawil syndrome
2024-04-10
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) has made a breakthrough discovery in the understanding of cardiac arrhythmias by unraveling the complexities of Andersen-Tawil syndrome (ATS), an extremely rare inherited cardiac disorder. Led by Dr. José Jalife, head of the CNIC Cardiac Arrhythmia Group, the study demonstrates that a specific genetic mutation (C122Y) in the Kir2.1 potassium channel alters the function not only of Kir2.1 but also of the main cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5, thus establishing a direct link with the life-threatening arrhythmias associated with ATS1.
The study, published in the journal Circulation Research, reveals that ...
Study suggests racial discrimination during midlife associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology later in life
2024-04-10
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – April 10, 2024 – Racial discrimination experienced during midlife is associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to a new study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the University of Georgia.
The findings appear online today in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We know that Black Americans are at an elevated risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias compared to non-Hispanic ...