(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study showed that a non-invasive imaging test can help identify patients with coronary artery blockage or narrowing who need a revascularization procedure. The findings were published as a Special Report in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Doctors use coronary CT angiography (CTA) to diagnose narrowed or blocked arteries in the heart. A CTA exam receives a score from mild (0-1) to moderate (2-3) to severe (4-5). Patients with scores above 3 typically require medical treatments and can potentially benefit from stents or surgeries (revascularization) to restore blood flow to the heart.
“CTA tells you the degree to which a vessel is blocked,” said Mangun Kaur Randhawa, M.D., a post-doctoral research fellow in the Department of Radiology at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston. “But the degree of blockage doesn't always reliably predict the amount of blood flow in the vessel.”
Doctors have traditionally relied on an invasive procedure known as invasive coronary angiography to image vessels and more recently have added other invasive tests like fractional flow reserve (FFR) to identify and assess significant blockages in the vessels. CT-FFR is a relatively new alternative that non-invasively models a patient’s coronary blood flow using CTA images of the heart, AI algorithms and/or computational fluid dynamics.
To assess the impact of the selective use of CT-FFR on clinical outcomes, Dr. Randhawa’s research team conducted a retrospective study of patients who underwent coronary CTA at MGH between August 2020 and August 2021.
During the study period, 3,098 patients underwent coronary CTA. Of these, 113 coronary bypass grafting patients were excluded. Of the remaining 2,985 patients, 292 (9.7%) were referred for CT-FFR analysis, and eight of these exams were excluded, leaving a final study group of 284.
As expected, most referrals to CT-FFR were patients with scores of 3 or above. CT-FFR was requested in the majority (73.5 %) of patients with a score of 3 (moderate narrowing/blockage).
“In patients with moderate narrowing or blockage of the arteries, there can be ambiguity about who would benefit from invasive testing and revascularization procedures,” Dr. Randhawa said. “CT-FFR helps us identify and select those patients who are most likely to benefit.”
Out of the 284 patients, 160 (56.3%) had a negative CT-FFR result of > 0.80, 88 patients (30.9%) had a clearly positive (abnormal) result of ≤ 0.75, and the remaining 36 patients (12.6%) had a borderline result between 0.76-0.80.
Patients with significant narrowing/blockages on coronary CTA who underwent CT-FFR had lower rates of invasive coronary angiography (25.5% vs. 74.5%) and subsequent percutaneous coronary intervention (21.1% vs. 78.9%) than patients who were not referred for a CT-FFR.
“CT-FFR helps us identify patients who would most benefit from undergoing invasive procedures and to defer stenting or surgical treatment in patients who likely won’t,” said senior author Brian B. Ghoshhajra, M.D., M.B.A., associate chair for operations and academic chief of cardiovascular imaging at MGH. “CT-FFR makes the CT ‘better’, but we found that the benefits were highest when used selectively.”
Dr. Ghoshhajra added that their CT-FFR analysis was successful in the large majority of patients, regardless of challenging factors such as elevated or irregular heart rates and obesity.
“When you objectively measure coronary artery flow with CT-FFR, you induce fewer patients to be further investigated and treated, because you tend to treat not just what the eyeball sees, but what the physiology supports,” he said.
The researchers said the study results demonstrate the utility of CT-FFR in clinical practice, when used selectively, highlighting its potential to reduce the frequency of invasive procedures in patients with significant coronary artery narrowing or blockages without compromising safety.
###
“Selective Use of CT Fractional Flow at a Large Academic Medical Center: Insights from Clinical Implementation after 1 Year of Practice.” Collaborating with Drs. Randhawa and Ghoshhajra were Angelo K. Takigami, M.D., Vikas Thondapu, M.D., Ph.D., Praveen G. Ranganath, M.D., Eric Zhang, M.D., Anushri Parakh, M.D., Reece J. Goiffon, M.D., Ph.D., Vinit Baliyan, M.D., Borek Foldyna, M.D., Michael T. Lu, M.D., Albree Tower-Rader, M.D., Nandini M. Meyersohn, M.D., and Sandeep Hedgire, M.D.
Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging is edited by Suhny Abbara, M.D., University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/cardiothoracic)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research, and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on cardiac imaging, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
Many people are familiar with the principle of electronic excitation from their physics lessons: electrons in atoms or molecules absorb energy, typically from light, and rise to a higher energy level. This can have various consequences – in photovoltaic technology, the phenomenon ensures that electricity can be generated from sunlight.
Measuring electronic excitation according to scientific standards and investigating how excited electrons influence each other is a real challenge: “Electronic excitation and the subsequent processes take place extremely quickly, many things happen simultaneously“, explains Tobias Brixner, Chair of Physical Chemistry ...
The maritime profession is among the world’s oldest professions, and today’s shipping is based on long and proud traditions. Professional pride and commitment are often deeply ingrained in seafarers, and for many, the job is more of a way of life. New technologies will bring about major changes in the work of bridge officers, who have the ultimate responsibility on board Norwegian vessels.
Strong doubts about safety
“Bridge officers rely on automated systems that are already found on board, such as advanced autopilot systems. However, there is strong scepticism, almost mistrust, that increased automation and autonomous ...
People who use willpower to overcome temptations and achieve their goals are perceived as more trustworthy than those who use strategies that involve external incentives or deterrents – such as swear jars or internet-blocking apps – according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“The knowledge that people can use external commitment strategies to overcome self-control problems has existed in some form for thousands of years. Since at least the time of Homer and Odysseus, the focus has primarily been on the efficacy of these strategies for the person choosing to engage ...
CLEVELAND—A recent study by Case Western Reserve University used national data from U.S. military veterans with diabetes to validate and modify a widely accepted model used to predict the risk of heart failure in diabetic patients.
The model, called the WATCH-DM score, is used to predict the likelihood of heart failure in diabetes patients within five years.
But because it overlooks the influence of social determinants of health‚ such as housing, food and a patient’s neighborhood, the researchers used a social deprivation index (SDI), a multi-component summary score, to adjust the WATCH-DM score.
The SDI, introduced by the Robert ...
RESTON, Va. — A new set of maps that document the movements of ungulates was published today in the fourth volume of the Ungulate Migrations of the Western United States. The maps in this collaborative U.S. Geological Survey report series reveal the migration routes and critical ranges used by ungulates, or hooved mammals, in the western U.S., furthering scientists’ understanding of the geography of big game migrations.
The new volume, “Ungulate Migrations of the Western United States: Volume 4,” documents 33 mule deer, ...
Can Jos Malda crack the code of cartilage?
In our aging society, healing joint problems is becoming increasingly important. To do this, cartilage damage must become repairable. But so far it has proven impossible to recreate the intricate internal structure of cartilage. Professor Jos Malda has now received an ERC Advanced grant of €2.5 million to crack that code.
Bringing biology and technology together
Throughout his career, Jos Malda has been concerned with the interface between biology and technology. It took him from studying Bioprocess Engineering in Wageningen to ...
A recent Mayo Clinic study published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association investigated lucid episodes in people living with later stages of dementia, providing insights into how these occurrences reveal themselves.
The findings showed that 75% of people having lucid episodes were reported to have Alzheimer’s Disease as opposed to other forms of dementia.
Researchers define lucid episodes as unexpected, spontaneous, meaningful and relevant communication from a ...
11 April, Prague, Czech Republic—Glen Kelley’s journey as a heart transplant recipient came full circle today in Prague, as he addressed attendees of the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), including members of his own care teams.
As a high school senior outside of Peoria, Illinois, Kelley was diagnosed with stage-4 Hodgkin’s lymphoma and underwent eight months of chemotherapy and radiation. After 10 months in remission, the ...
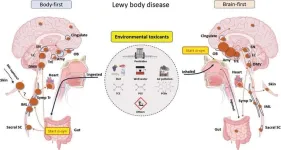
The nose or the gut? For the past two decades, the scientific community has debated the wellspring of the toxic proteins at the source of Parkinson’s disease. In 2003, a German pathologist, Heiko Braak, MD, first proposed that the disease begins outside the brain. More recently, Per Borghammer, MD, with Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues argue that the disease is the result of processes that start in either the brain’s smell center (brain-first) or the body’s intestinal tract (body-first).
A new hypothesis paper appearing in the Journal of Parkinson’s ...
Professor Jill Walker Rettberg, Co-Director of the Centre for Digital Narrative at the University of Bergen, is awarded an ERC Advanced Grant for the project AI STORIES. The grant consists of 2.5 million Euro over 5 years. This is Rettberg's second ERC Grant.
“The AI STORIES project builds on the premise that storytelling is central to human culture, with narratives shaping our understanding of the world. We will study artificial intelligence and how it creates new narratives,” says Rettberg.
Generative AI has been dubbed ...