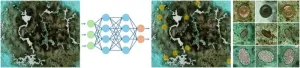
(Press-News.org) Image-based artificial intelligence spots parasitic worm infections in children's stool samples, particularly light intensity infections that may be missed by manual microscopy.
#####
Article URL: http://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0012041
Article Title: Diagnosis of soil-transmitted helminth infections with digital mobile microscopy and artificial intelligence in a resource-limited setting
Author Countries: Finland, Kenya, Sweden
Funding: This research was financially supported by The Erling-Persson Foundation (grant number 2021 0110) JL, Vetenskapsrådet (grant number 2021-04811) JL, Finska Läkaresällskapet r.f. JL, Medicinska Understödsföreningen Liv och Hälsa rf JL and Wilhelm och Else Stockmanns stiftelse JL. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Image-based artificial intelligence spots parasitic worm infections in children's stool samples
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists use wearable technology to detect stress levels during sleep
2024-04-11
What if changes in a person’s stress levels could be detected while they sleep using wearable devices? A new study by University of Vermont researchers published today in PLOS Digital Health is the first to find changes in perceived stress levels reflected in sleep data—an important step towards identifying biomarkers that may help flag individuals in need of support.
Given how critical sleep is to physical and mental health, the research team suspected signals might exist in sleep data, says Laura Bloomfield, a research assistant professor of mathematics and statistics and lead author of the study. “Changes in stress are visible.”
When parsing baseline sleep ...
Beautiful nebula, violent history: Clash of stars solves stellar mystery
2024-04-11
When astronomers looked at a stellar pair at the heart of a stunning cloud of gas and dust, they were in for a surprise. Star pairs are typically very similar, like twins, but in HD 148937, one star appears younger and, unlike the other, is magnetic. New data from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) suggest there were originally three stars in the system, until two of them clashed and merged. This violent event created the surrounding cloud and forever altered the system’s fate.
“When doing background reading, ...
A magnetic massive star was produced by a stellar merger
2024-04-11
Shedding light on why some massive stars have magnetic fields even though these stars’ interiors layers don’t undergo convection, researchers report observational evidence that magnetic fields form in some such stars through stellar mergers. The magnetic fields of low-mass stars, like the Sun, are produced by a dynamo generated in the convective layers of the star’s interior. Massive stars – those 8 or more solar masses at formation – do not have the convective interiors required to sustain magnetic fields in ...
Thin oil films enable stable oil and water mixtures sans surfactant
2024-04-11
Thin oil films absorbed onto the surface of water droplets lead to anomalously stable, surfactant-free oil and water mixtures, according to a new study. The findings demonstrate a mechanism for stabilizing water droplets in a water-oil emulsification without the need for a surfactant, which could have important technological applications, including the creation of very pure and controlled materials. Oil and water cannot form homogenous mixtures. Instead, when combined, droplets of one fluid will disperse inside the other, forming ...
*FREE* Growing tribal clean energy in the US
2024-04-11
New US federal legislation sets aside nearly $14 billion for 574 federally recognized indigenous nations and villages, which can be used to support tribal climate responsiveness and energy sovereignty. In a Policy Forum, Kimberly Yazzie and colleagues present a roadmap for designing, implementing, and funding projects and people to accelerate the renewable energy transition while also benefiting the indigenous entities involved. According to the authors, this opportunity positions indigenous communities to develop their economies and energy projects ...
The nitroplast revealed: a nitrogen-fixing organelle in a marine alga
2024-04-11
A nitrogen-fixing bacterial endosymbiont of marine algae is evolving into a nitrogen-fixing organelle, or nitroplast, according to a new study, thereby expanding a function that was thought to be exclusively carried out by prokaryotic cells to eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are remarkably complex and contain various organelles, which are specialized structures within a living cell that have specific biological functions. Two organelles, mitochondria and chloroplasts, play a key role in energy metabolism and ...
First step to untangle DNA: supercoiled DNA captures gyrase like a lasso ropes cattle
2024-04-11
Picture in your mind a traditional “landline” telephone with a coiled cord connecting the handset to the phone. The coiled telephone cord and the DNA double helix that stores the genetic material in every cell in the body have one thing in common; they both supercoil, or coil about themselves, and tangle in ways that can be difficult to undo. In the case of DNA, if this overwinding is not dealt with, essential processes such as copying DNA and cell division grind to a halt. Fortunately, cells have an ingenious solution to carefully regulate DNA supercoiling.
In this study published in the journal Science, researchers ...
Brainless memory makes the spinal cord smarter than previously thought
2024-04-11
Aya Takeoka at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan and colleagues have discovered the neural circuitry in the spinal cord that allows brain-independent motor learning. Published in Science on April 11, the study found two critical groups of spinal cord neurons, one necessary for new adaptive learning, and another for recalling adaptations once they have been learned. The findings could help scientists develop ways to assist motor recovery after spinal cord injury.
Scientists have known for some time that motor output from the spinal cord can be adjusted through practice ...
Study reveals giant store of global soil carbon
2024-04-11
Soil carbon usually refers only to the organic matter component of soils, known as soil organic carbon (SOC). However, soil carbon also has an inorganic component, known as soil inorganic carbon (SIC). Solid SIC, often calcium carbonate, tends to accumulate more in arid regions with infertile soils, which has led many to believe it is not important.
In a study published in Science, researchers led by Prof. HUANG Yuanyuan from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Prof. ZHANG Ganlin from the Institute of Soil Science of CAS, together ...
Wired to learn and remember
2024-04-11
Leuven (Belgium), 11 April 2024 — The role of the spinal cord is often simplified to that of a simple relay station, carrying messages between the brain and the body. However, the spinal cord can actually learn and remember movements on its own. A team of researchers at the Leuven-based Neuro-Electronics Research Flanders (NERF) details how two different neuronal populations enable the spinal cord to adapt and recall learned behavior in a way that is completely independent of the brain. These remarkable ...