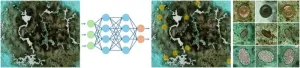
(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. – A team of computer scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst working on two different problems—how to quickly detect damaged buildings in crisis zones and how to accurately estimate the size of bird flocks—recently announced an AI framework that can do both. The framework, called DISCount, blends the speed and massive data-crunching power of artificial intelligence with the reliability of human analysis to quickly deliver reliable estimates that can quickly pinpoint and count specific features from very large collections of images. The research, published by the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, has been recognized by that association with an award for the best paper on AI for social impact.
“DISCount came together as two very different applications,” says Subhransu Maji, associate professor of information and computer sciences at UMass Amherst and one of the paper’s authors. “Through UMass Amherst’s Center for Data Science, we have been working with the Red Cross for years in helping them to build a computer vision tool that could accurately count buildings damaged during events like earthquakes or wars. At the same time, we were helping ornithologists at Colorado State University and the University of Oklahoma interested in using weather radar data to get accurate estimates of the size of bird flocks.”
Maji and his co-authors, lead author Gustavo Pérez, who completed this research as part of his doctoral training at UMass Amherst, and Dan Sheldon, associate professor of information and computer sciences at UMass Amherst, thought they could solve the damaged-buildings-and-bird-flock problems with computer vision, a type of AI that can scan enormous archives of images in search of something particular—a bird, a rubble pile—and count it.
But the team was running into the same roadblocks on each project: “the standard computer visions models were not accurate enough,” says Pérez. “We wanted to build automated tools that could be used by non-AI experts, but which could provide a higher degree of reliability.”
The answer, says Sheldon, was to fundamentally rethink the typical approaches to solving counting problems.
“Typically, you either have humans do time-intensive and accurate hand-counts of a very small data set, or you have computer vision run less-accurate automated counts of enormous data sets,” Sheldon says. “We thought: why not do both?”
DISCount is a framework that can work with any already existing AI computer vision model. It works by using the AI to analyze the very large data sets—say, all the images taken of a particular region in a decade—to determine which particular smaller set of data a human researcher should look at. This smaller set could, for example, be all the images from a few critical days that the computer vision model has determined best show the extent of building damage in that region. The human researcher could then hand-count the damaged buildings from the much smaller set of images and the algorithm will use them to extrapolate the number of buildings affected across the entire region. Finally, DISCount will estimate how accurate the human-derived estimate is.
“DISCount works significantly better than random sampling for the tasks we considered,” says Pérez. “And part of the beauty of our framework is that it is compatible with any computer-vision model, which lets the researcher select the best AI approach for their needs. Because it also gives a confidence interval, it gives researchers the ability to make informed judgments about how good their estimates are.”
“In retrospect, we had a relatively simple idea,” says Sheldon. “But that small mental shift—that we didn’t have to choose between human and artificial intelligence, has let us build a tool that is faster, more comprehensive, and more reliable than either approach alone.”
Contacts: Subhransu Maji, smaji@cs.umass.edu
Daegan Miller, drmiller@umass.edu
END
New computer vision tool wins prize for social impact
DISCount, created at UMass Amherst, derived from two very different needs: Counts of damaged buildings in crisis zones and bird flock sizes
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) and The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) launch BRIDGES 2.0 Research Initiative with support from the Foundation for Women’s Cancer (FWC).
2024-04-11
PRESS RELEASE
Chicago, IL and Philadelphia, PA, USA, April 11, 2024: The Society of Gynecologic Oncology (SGO) and The GOG Foundation, Inc. (GOG-F) Launch BRIDGES 2.0 Research Initiative with support from the Foundation for Women’s Cancer (FWC). After a successful inaugural year, the SGO and the GOG-F join forces to collaborate, and proudly announce the launch of an expanded two-year clinical trial education program supported by the FWC. This important career and clinical trial development initiative aims to cultivate the next generation of investigators in gynecologic oncology and will focus on clinical and translational research ...
Embryos in hungry mouse mums postpone development
2024-04-11
It’s challenging to sustain a pregnancy when food is short, or conditions are otherwise tough. That’s why many mammalian embryos can postpone their growth to get through periods of environmental stress and then re-enter development when conditions improve. This stalling of development is known as embryonic diapause, and understanding the mechanisms behind it might help improve infertility treatments, such as embryo freezing. Now, researchers at the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai, China, have discovered how nutrient depletion is sensed by embryos growing in hungry mouse mums to induce diapause. ...
Scripps Research study reveals new approach for combatting “resting” bacteria
2024-04-11
LA JOLLA, CA—Most disease-causing bacteria are known for their speed: In mere minutes, they can double their population, quickly making a person sick. But just as dangerous as this rapid growth can be a bacterium’s resting state, which helps the pathogen evade antibiotics and contributes to severe chronic infections in the lungs and blood, within wounds, and on the surfaces of medical devices.
Now, Scripps Research scientists have discovered how long chains of molecules called polyphosphates (polyP) are needed for bacteria to slow down movements within cells and let them enter this resting ...
UT Health San Antonio appoints Anthony Francis as associate vice president for innovation and development
2024-04-11
SAN ANTONIO, April 10, 2024 – The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has appointed Anthony Francis, a renowned leader in translating research to market opportunity, as associate vice president for innovation and development in the Office of the Vice President for Research.
He joins the institution from the University of California San Francisco, where he was executive director of the Office of Technology Management and Advancement. Francis is credited with transforming ...
Study finds increased anxiety and PTSD among people who remained in Ukraine
2024-04-11
Researchers from the International Blast Injury Research Network at the University of Southampton conducted a survey to understand how the mental health of displaced Ukrainians has been affected by the ongoing war. Their findings, published in PLOS Global Public Health, describe high levels of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and generalized anxiety among both refugees and people displaced within Ukraine.
Since the Russian invasion of Ukraine began in February 2022, at least 13 million people have been displaced from their homes. Both exposure ...
Image-based artificial intelligence spots parasitic worm infections in children's stool samples
2024-04-11
Image-based artificial intelligence spots parasitic worm infections in children's stool samples, particularly light intensity infections that may be missed by manual microscopy.
#####
Article URL: http://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0012041
Article Title: Diagnosis of soil-transmitted helminth infections with digital mobile microscopy and artificial intelligence in a resource-limited setting
Author Countries: Finland, Kenya, Sweden
Funding: This research was financially supported by The Erling-Persson Foundation (grant number 2021 0110) JL, Vetenskapsrådet (grant number 2021-04811) JL, Finska Läkaresällskapet ...
Scientists use wearable technology to detect stress levels during sleep
2024-04-11
What if changes in a person’s stress levels could be detected while they sleep using wearable devices? A new study by University of Vermont researchers published today in PLOS Digital Health is the first to find changes in perceived stress levels reflected in sleep data—an important step towards identifying biomarkers that may help flag individuals in need of support.
Given how critical sleep is to physical and mental health, the research team suspected signals might exist in sleep data, says Laura Bloomfield, a research assistant professor of mathematics and statistics and lead author of the study. “Changes in stress are visible.”
When parsing baseline sleep ...
Beautiful nebula, violent history: Clash of stars solves stellar mystery
2024-04-11
When astronomers looked at a stellar pair at the heart of a stunning cloud of gas and dust, they were in for a surprise. Star pairs are typically very similar, like twins, but in HD 148937, one star appears younger and, unlike the other, is magnetic. New data from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) suggest there were originally three stars in the system, until two of them clashed and merged. This violent event created the surrounding cloud and forever altered the system’s fate.
“When doing background reading, ...
A magnetic massive star was produced by a stellar merger
2024-04-11
Shedding light on why some massive stars have magnetic fields even though these stars’ interiors layers don’t undergo convection, researchers report observational evidence that magnetic fields form in some such stars through stellar mergers. The magnetic fields of low-mass stars, like the Sun, are produced by a dynamo generated in the convective layers of the star’s interior. Massive stars – those 8 or more solar masses at formation – do not have the convective interiors required to sustain magnetic fields in ...
Thin oil films enable stable oil and water mixtures sans surfactant
2024-04-11
Thin oil films absorbed onto the surface of water droplets lead to anomalously stable, surfactant-free oil and water mixtures, according to a new study. The findings demonstrate a mechanism for stabilizing water droplets in a water-oil emulsification without the need for a surfactant, which could have important technological applications, including the creation of very pure and controlled materials. Oil and water cannot form homogenous mixtures. Instead, when combined, droplets of one fluid will disperse inside the other, forming ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] New computer vision tool wins prize for social impactDISCount, created at UMass Amherst, derived from two very different needs: Counts of damaged buildings in crisis zones and bird flock sizes