(Press-News.org) University of Cincinnati researchers will present abstracts at the American Academy of Neurology annual meeting 2024, April 13-18 in Denver, Colorado.
Two-component treatment leads to improvement for patients
Late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD) is a rare, inherited genetic disease caused by the accumulation of glycogen, the body’s stored form of glucose, in muscles and other organs. Left untreated, the muscle weakness it causes can lead to the loss of the ability to walk and breathing impairment.
A research team led by UC’s Hani Kushlaf, MD, looked at the effect of a two-component enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) of drugs cipaglucosidase and miglustat (cipa+mig) compared to a single ERT drug, alglucosidase alfa (alg) and a placebo. UC researchers participated in the Phase 3 trials that led to the Food and Drug Administration approval of both ERT regimens.
“The research question was to look at the magnitude and practical significance of the effect of cip+mig versus alg using patient data from the PROPEL trial on outcomes that included motor function, pulmonary function, muscle strength, biomarkers and patient- and physician-reported quality of life,” said Kushlaf, associate professor and director of Neuromuscular Research and the Neuromuscular Disorders Division in UC’s Department of Neurology & Rehabilitation Medicine in the College of Medicine.
Patients who switched to the dual ERT regimen experienced improvement or stability across the measured outcomes with no worsening of outcomes. Those who remained on the single ERT drug plus placebo experienced worsening or stability across the measured outcomes.
“This analysis highlights the potential of cipaglucosidase+miglustat to become an important treatment option for patients with LOPD, including patients already on enzyme replacement therapy,” Kushlaf said.
This research was sponsored by Amicus Therapeutics, Inc.
Research team learns more about events following immunotherapy treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), an immunotherapy that activates the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells, has revolutionized cancer treatment. But while boosting anti-tumor immunity, the treatments may cause severe neurological-immune related adverse events.
“These neurological-immune-related adverse events include meningitis, encephalitis, demyelinating diseases, vasculitis, neuropathy, neuromuscular junction disorders and myopathy,” said Luca Marsili, MD, PhD, movement disorder fellow in the Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation Medicine in the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine.
Marsili said the frequency of these adverse events, and the best way to manage them, is still largely unknown.
A team led by Marsili and Alberto Espay, MD, reviewed reported neurological-immune-related adverse events in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors at UC from 2011-2023. They found the adverse events are rare, affecting 28 patients out of 1,677 treated, or 1.66%.
The adverse events were most often associated with melanoma treatment with pembrolizumab, a common immunotherapy treatment.
“The adverse events were most expressed as peripheral neuropathies and encephalitis, manifesting early during treatment within a mean of 2.3 months after ICI initiation,” Marsili said. “Most ICIs, 68%, were discontinued, and in only 10.7% of cases they were restarted without complications.”
Moving forward, the team said further research is needed to determine clinical susceptibility factors and appropriate timing of restarting ICI treatment after discontinuing due to an adverse event. They are also planning to do more detailed demographic and clinical comparisons of the 28 patients identified to have adverse events to see if there are any predictive factors like tumor type, age, sex or ethnicity.
“This study is part of a broader project in collaboration with the University of Udine in Italy and with the Department of Internal Medicine at UC,” Marsili said. “We would like to gather a high number of participants to assess incidence/prevalence of these adverse events and also to raise awareness among neurologists on how to treat/manage them.”
Safe, effective treatment for Parkinson’s
Alberto Espay, MD, will present findings recently published in the Lancet Neurology journal that found Parkinson’s disease medication delivered through an infusion pump is safe and effective at reducing symptoms for longer periods of time.
Parkinson’s symptoms such as tremors, slowness and stiffness are caused by low levels of dopamine in the body. For decades, doctors have treated Parkinson’s by giving patients levodopa, the inactive substance in the brain that once converted makes dopamine.
“Levodopa is a replacement strategy. We all make levodopa, but Parkinson's patients make less of it,” said Espay, co-principal investigator of the trial, the James J. and Joan A. Gardner Family Center for Parkinson’s Disease Research Endowed Chair in UC’s Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation Medicine and a physician at the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute.
Levodopa is most commonly administered orally, but this trial tested continuous, 24-hour levodopa delivery through a subcutaneous infusion pump. A total of 381 patients with Parkinson’s disease in 16 countries enrolled in the trial and were randomized to receive levodopa through the infusion pump or through traditional oral medication.
The researchers found levodopa delivered through the infusion pump was safe and led to almost two hours a day (1.72) of additional “on time,” or the time when the medication is working and symptoms are lessened, compared to taking levodopa orally.
“Once approved, this will become an important treatment strategy to consider for patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing motor fluctuations not adequately controlled with medication,” he said. “Future studies will need to determine the durability of the long-term benefits and whether any safety issues could emerge, as well as how it might compare with deep brain stimulation.”
UC research being presented at AAN includes:
Kushlaf presenting “Effect Size Analysis of Cipaglucosidase Alfa Plus Miglustat Versus Alglucosidase Alfa in ERT-experienced Adults with Late-onset Pompe Disease in PROPEL.”
Marsili and Espay presenting “Neurological Immune-related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Single-center Retrospective Study.”
Espay presenting “Efficacy of ND0612, a 24-hour Subcutaneous Levodopa/Carbidopa Infusion for People with Parkinson’s Disease Experiencing Motor Fluctuations: Subgroup-analyses from a Randomized, Controlled Phase 3 Study.”
Stacie Demel, DO, PhD, a physician-researcher at the UC Gardner Neuroscience Institute and associate professor of clinical neurology and rehabilitation medicine in UC’s College of Medicine, presenting “Methylation Patterns Differ Between ICH Cases and Controls.”
Yang Yu, MD, UC medical resident/fellow, presenting “Multiple Sclerosis in a Patient with Friedreich's Ataxia.”
Rhonna Shatz, DO, adjunct associate professor, division director for behavioral neurology, and the Bob and Sandy Heimann Endowed Chair in Research and Education in Alzheimer’s Disease in the UC College of Medicine, presenting “Identifying a Relationship Between Executive Dysfunction, Poor Sleep Hygiene/Sleep Apnea, and Ventriculomegaly in Cancer-related Cognitive Impairment (CRCI)” END
University of Cincinnati experts present at national neurology conference
2024-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bonobos are more aggressive than previously thought
2024-04-12
Chimpanzees and bonobos are often thought to reflect two different sides of human nature—the conflict-ready chimpanzee versus the peaceful bonobo—but a new study publishing April 12 in the journal Current Biology shows that, within their own communities, male bonobos are more frequently aggressive than male chimpanzees. For both species, more aggressive males had more mating opportunities.
“Chimpanzees and bonobos use aggression in different ways for specific reasons,” says anthropologist and lead author Maud Mouginot of Boston University. “The idea is not to invalidate the ...
How seaweed became multicellular
2024-04-12
A deep dive into macroalgae genetics has uncovered the genetic underpinnings that enabled macroalgae, or “seaweed,” to evolve multicellularity. Three lineages of macroalgae developed multicellularity independently and during very different time periods by acquiring genes that enable cell adhesion, extracellular matrix formation, and cell differentiation, researchers report April 12 in the journal Molecular Plant. Surprisingly, many of these multicellular-enabling genes had viral origins. The study, which increased the total number of sequenced macroalgal genomes from 14 to 124, is the first to investigate ...
Melanomas resist drugs by ‘breaking’ genes
2024-04-12
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. With global incidence rates rising, new, more effective treatments are necessary to alleviate the health burden of the disease. Important advances in recent years include doctors using genetic tests to look for specific mutations they can target for more personalised, effective treatment.
Around 1 in 2 melanoma patients will have mutations in the BRAF gene. This gene normally makes a protein which helps control cell growth, but mutations can cause the cells to grow and divide uncontrollably instead, happening in many different types of cancer including ...
Africa’s iconic flamingos threatened by rising lake levels, study shows
2024-04-12
It is one of the world’s most spectacular sights – huge flocks or “flamboyances” of flamingos around East Africa’s lakes – as seen in the film Out of Africa or David Attenborough’s A Perfect Planet.
But new research led by King’s College London has revealed how the lesser flamingo is at danger of being flushed out of its historic feeding grounds, with serious consequences for the future of the species.
For the first time satellite earth observation data has been used to study all the key flamingo feeding lakes in Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania over two decades and it identified how rising ...
Vaccination timeliness among US children ages 0-19 months
2024-04-12
About The Study: In this study of National Immunization Survey–Child data, improvements in vaccination timeliness were observed from the 2011 to the 2021 survey. However, widening disparities by socioeconomic indicators signal that increased efforts to facilitate timely vaccination among children in lower-income families are needed.
Authors: Sophia R. Newcomer, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of Montana, Missoula, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
Changes in permanent contraception procedures among young adults following the Dobbs decision
2024-04-12
About The Study: Researchers observed an abrupt increase in permanent contraception procedures among adults ages 18 to 30 following Dobbs. The increase in procedures for female patients was double that for male patients. These patterns offer insights into the gendered dynamics of permanent contraceptive use and may reflect the disproportionate health, social, and economic consequences of compulsory pregnancy on women and people with the capacity to become pregnant.
Authors: Jacqueline E. Ellison, Ph.D., of the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Semaglutide vs endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty for weight loss
2024-04-12
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is cost saving compared with semaglutide in the treatment of class II obesity. On price threshold analyses, a 3-fold decrease in the price of semaglutide is needed to achieve nondominance.
Authors: Christopher C. Thompson, M.D., M.Sc., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.6221)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
First national study of Dobbs ruling’s effect on permanent contraception among young adults
2024-04-12
The first study to evaluate the effect of the Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization ruling on permanent contraception procedures among young adults nationwide was published today in a JAMA Health Forum research letter.
The study, authored by policy researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health and Boston University, underscores how the 2022 U.S. Supreme Court ruling changed preferences for permanent contraception among people ages 18 to 30, who are more likely to have abortions and are also more likely to experience sterilization regret compared to people over 30.
The study is also the first to assess how the Dobbs ruling ...
One of the largest male infertility genetic studies improves molecular diagnostics and personalized management of andrology patients
2024-04-12
Approximately one in seven couples face difficulties conceiving a child naturally. Half of these cases are due to male infertility – either caused by the complete absence or low number of mature sperm. In today’s clinical practice, over half of these cases remain unexplained, hindering optimal counselling, treatment, and prevention of potential comorbidities. Known genetic factors account for ~10% of male infertility; however, it is believed that a large portion of unexplained cases of spermatogenic failure are caused by genetic defects that ...
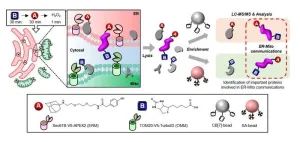
Decoding the language of cells: Unveiling the proteins behind cellular organelle communication
2024-04-12
In cellular biology, unraveling the complexities of cellular function at the molecular level remains a paramount endeavor. Significant scientific focus has been placed on understanding the interactions at organelle contact sites, especially between mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). These sites are critical hubs for the exchange of essential biomolecules, such as lipids and calcium, which are vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Disruptions in this inter-organelle communication are implicated in the onset ...