(Press-News.org) Alyssa Ryan, an assistant professor of civil and architectural engineering and mechanics, in the University of Arizona College of Engineering, is leading a national study to identify disparities in traffic safety for all transportation users, including drivers, bicyclists and walkers.
"Transportation engineering is very focused on people and impacting society and how people interact with the world," said Ryan. "If you don't have transportation, you can't do anything."
With a $467,000 award from the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety and building on Ryan's previous research, the project aims to identify populations most at risk for crash injuries given factors such as location, race, sex, ethnicity and socioeconomic status.
"In our quest to ensure safe mobility for all communities," said Rebecca Steinbach, senior researcher at the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety, "we need a better understanding of the extent of disparities, contributing factors and countermeasures to mitigate disparities where they exist. The rigorous approach of this project will help identify meaningful solutions that can be applied by a variety of professionals to improve equity in traffic safety."
National resources, such as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act passed in 2021, are providing billions of dollars to states for equitable transportation improvements, and the researchers plan to take their findings and recommendations to officials in every state.
"We're really looking for trends, what is happening across the United States and who is getting into these crashes," said Ryan, also assistant director at the Center for Applied Transportation Sciences in the College of Engineering.
Ryan, in collaboration with Oregon State University professor David Hurwitz, will analyze massive datasets from the U.S. Census Bureau, National Emergency Medical Services Information System, Federal Highway Administration Highway Statistics and the Fatal Accident Reporting Systems to identify crash trends among different groups. This is the first time that data of such magnitude has been used to research traffic inequity on a national scale.
"This is an issue in society, but it presents itself in transportation in really compelling ways," said Hurwitz, the co-principal investigator who is a professor of transportation engineering and director of the Kiewit Center for Infrastructure and Transportation Research at OSU.
Hurwitz and Ryan, fellow University of Massachusetts Amherst alums, will split the data collection and analysis of four demographically diverse states, including Arizona and Oregon.
Historically, fatal crashes have been the preferred data source, said Ryan, and studies typically compared fatalities to race. In 2021, a Harvard study found that Black and Latino Americans were more likely to be killed in traffic than other racial or ethnic groups per mile traveled.
"But it's not enough data to really dive into what's happening," said Ryan. "In reality, the number of crashes we have every year in the U.S. alone is in the millions, so we're looking at the crashes themselves. It'll give us a much better perspective."
To help broaden the scope, this study combines layered national and state demographic data from sources such as the Census with injury and fatality data from Emergency Medical Services.
Tackling Tough History
Disparities have existed since the inception of the U.S. transportation system.
"These inequities are grounded in our history, and we need to do something about it," said Ryan.
"The interstate system that runs across the United States primarily went through neighborhoods and homes of people who were Black, people who were poor, Indigenous populations – destroying their communities and displacing them."
Further, regions with fewer resources for transportation infrastructure, including low-density, rural areas, often experience higher rates of serious crashes per capita. For instance, communities with less to spend on sidewalks next to roads tend to see more pedestrian-related crashes.
Ryan's previous crash data analysis also uncovered gender disparities.
"Female drivers were more likely to get injured in a crash, and they were more likely to walk away with certain injuries," she said.
Her 2020 study showed that no crash dummies with proportions characteristic of females had been used to date and concluded that women drivers' safety is overlooked in vehicle design and testing. The study found that female drivers are more likely than male drivers to experience a primary injury to the abdomen, chest and extremities.
Equity ≠ Equality
University of Arizona civil and architectural engineering and mechanics doctoral student Saquib Haroon, who is helping build machine learning models to distill the mountains of data and identify patterns, said the project makes an important distinction between social equity and equality.
Equality means everyone is treated similarly, he explained, whereas equity accepts that some individuals need to be provided with additional or different resources to be successful.
"We all need to understand that not everything in this world is going to be equal and focus on ensuring those who are disadvantaged receive adequate resources," he stressed.
END
Civil engineer looks to remedy inequities in traffic safety
With an award from the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety, University of Arizona assistant professor Alyssa Ryan leads a team to identify age-old transportation challenges in underserved populations
2024-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New research highlights effects of gentrification on urban wildlife populations across U.S. cities
2024-04-15
Chicago (April 15, 2024) – New research published on Monday, April 15 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) identifies how gentrified parts of a city have notably more urban wildlife than ungentrified parts of the same city, further limiting marginalized communities’ opportunity to connect with nature. The study, led by Lincoln Park Zoo’s Urban Wildlife Institute, analyzed data from 23 cities across the continental U.S., collected by partners of the Urban Wildlife Information Network ...
Vaccine breakthrough means no more chasing strains
2024-04-15
Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.
Every year, researchers try to predict the four influenza strains that are most likely to be prevalent during the upcoming flu season. And every year, people line up to get their updated vaccine, hoping the researchers formulated the shot correctly.
The same is true of COVID vaccines, which have been reformulated to target sub-variants of the most prevalent strains ...
Epilepsy drug prevents brain tumors in mice with NF1
2024-04-15
A drug used to treat children with epilepsy prevents brain tumor formation and growth in two mouse models of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. NF1 is a genetic condition that causes tumors to grow on nerves throughout the body, including the optic nerves, which connect the eyes to the brain.
The findings lay the groundwork for a clinical trial to assess whether the drug, lamotrigine, can prevent or delay brain tumors in children with NF1. The study is online in the journal Neuro-Oncology.
“Based on these data, the Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium is considering launching a first-of-its-kind ...
Study uses thermodynamics to describe expansion of the Universe
2024-04-15
The idea that the Universe is expanding dates from almost a century ago. It was first put forward by Belgian cosmologist Georges Lemaître (1894-1966) in 1927 and confirmed observationally by American astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) two years later. Hubble observed that the redshift in the electromagnetic spectrum of the light received from celestial objects was directly proportional to their distance from Earth, which meant that bodies farther away from Earth were moving away faster and the universe must be expanding.
A surprising new ingredient was added to the model in 1998 when observations of ...
New mechanism uncovered in early stages of Alzheimer's disease
2024-04-15
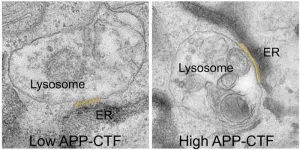
Leuven (Belgium), 16 April 2024 – Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains one of the most challenging and prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. In a new study published in Developmental Cell, researchers from the lab of Wim Annaert (VIB-KU Leuven) have identified a novel mechanism potentially connected to the early stages of AD. They demonstrated that a fragment of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), called APP-CTF, disrupts communication between cellular compartments crucial for calcium storage and waste disposal, which ...
Elite coaches leaving home as Western countries seek sport success
2024-04-15
Nations battling for Olympic success in a global sporting ‘arms race’ has led to elite coaches migrating to Western countries as they bid to escape antiquated and restrictive coaching regimes in their home countries, reveals a new study funded by the International Olympic Committee’s Olympic Studies Centre.
National teams pursuing Olympic gold medals are increasingly recruiting foreign elite coaches from the leading countries, as they try to close the gap between themselves and the top medal-winners in particular ...
Millions of gamers advance biomedical research
2024-04-15
Leveraging gamers and video game technology can dramatically boost scientific research according to a new study published today in Nature Biotechnology.
4.5 million gamers around the world have advanced medical science by helping to reconstruct microbial evolutionary histories using a minigame included inside the critically and commercially successful video game, Borderlands 3. Their playing has led to a significantly refined estimate of the relationships of microbes in the human gut. The results of this collaboration will both substantially advance our knowledge of the microbiome ...
Global North energy outsourcing demands more attention
2024-04-15
Manufacturing nations in the Global North are stockpiling energy and emission problems by outsourcing energy-intensive industrial processes to countries in the Global South, a new study reveals.
Global North countries use their advantages in capital and technology to grab a large amount of energy through outsourcing - creating a ‘false decoupling’ of energy consumption from economic growth.
But backward production technologies in the Global South tend to result in more energy consumption per unit of output – leading to greater carbon emissions ...
Mayo researchers invented a new class of AI to improve cancer research and treatments
2024-04-15
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Mayo Clinic researchers recently invented a new class of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms called hypothesis-driven AI that are a significant departure from traditional AI models which learn solely from data.
In a review published in Cancers, the researchers note that this emerging class of AI offers an innovative way to use massive datasets to help discover the complex causes of diseases such as cancer and improve treatment strategies.
"This fosters a new era in designing targeted and informed AI algorithms to solve scientific questions, ...
Machine learning could help reveal undiscovered particles within data from the Large Hadron Collider
2024-04-15
Scientists used a neural network, a type of brain-inspired machine learning algorithm, to sift through large volumes of particle collision data.
Particle physicists are tasked with mining this massive and growing store of collision data for evidence of undiscovered particles. In particular, they’re searching for particles not included in the Standard Model of particle physics, our current understanding of the universe’s makeup that scientists suspect is incomplete.
As part of the ATLAS collaboration, scientists ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
[Press-News.org] Civil engineer looks to remedy inequities in traffic safetyWith an award from the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety, University of Arizona assistant professor Alyssa Ryan leads a team to identify age-old transportation challenges in underserved populations