(Press-News.org) Chicago (April 15, 2024) – New research published on Monday, April 15 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) identifies how gentrified parts of a city have notably more urban wildlife than ungentrified parts of the same city, further limiting marginalized communities’ opportunity to connect with nature. The study, led by Lincoln Park Zoo’s Urban Wildlife Institute, analyzed data from 23 cities across the continental U.S., collected by partners of the Urban Wildlife Information Network (UWIN), a collective of scientists, ecologists, and educators dedicated to understanding biodiversity and mitigating human-wildlife conflict in cities.
Gentrification, defined by Merriam-Webster as “the process whereby the character of a poor urban area is changed by wealthier people moving in, improving housing, and attracting new businesses, typically displacing current inhabitants in the process,” has been shown to result in inequitable access to urban nature across city populations. In this most recent study from UWI, not only do the results illustrate how the effects of gentrification are felt by animals, but they also provide further evidence of how nature is chronically inaccessible to marginalized urban communities. The study found that, on average, the number of different species living in a gentrified part of a city is 13% higher than in a compositionally comparable ungentrified part of the same city. This means that gentrified neighborhoods can support one to two more species on average, and therefore humans living in these areas have greater exposure to urban wildlife without having to actively seek it out.
“When asking ‘in a city, who does and does not have easy access to nature?,’ we found that gentrification, which changes the demographic composition of people in neighborhoods, has consequences that extend to other species we share cities with. This leaves marginalized communities without meaningful access to nature, which is a problem,” said Mason Fidino, Ph.D., Quantitative Ecologist at Lincoln Park Zoo and lead author on the study. “My hope is that these results can be used to advocate for updated land development and management practices that prioritize social equity and access to nature spaces for all urban communities.”
As part of the study, UWIN partners placed motion-detecting wildlife cameras at a total of 999 sites in cities across the country, weaving together a national network to monitor biodiversity between 2019 and 2021. The analysis looked at 21 mammal species across 11 families, including various squirrels, deer, foxes, bobcats, beavers, and more. A data set of this magnitude provides an unprecedented overview of North American mammal distributions across a wide array of urban landscapes from Los Angeles to Boston.
In east coast cities, the study found that gentrification has the greatest effect on alpha diversity, or total number of different species. In west coast cities, however, gentrification had a greater effect on beta diversity, or differences in the composition of species present, between gentrified and non-gentrified parts of cities. This is particularly notable because certain kinds of urban wildlife, like songbirds or rabbits, are generally considered more desirable than other kinds, like rats or mice. So even in west coast cities that have similar richness of wildlife across gentrified and ungentrified areas, the impact of urban wildlife on human quality of life can still vary greatly based on the types of animals present in both areas.
The study found that gentrification is not the only human-made factor impacting urban wildlife, though. Impervious cover, such as concrete, asphalt, and compacted soil, has an even greater effect on non-human animals living in cities. This means that a highly developed gentrified area, such as a downtown neighborhood, will still have less urban wildlife than an ungentrified neighborhood with less impervious cover.
While impervious cover has the most direct impact on animal diversity in urban areas, gentrification can and does lessen the negative effect of impervious cover on mammals. Gentrification often introduces green infrastructure to neighborhoods, like parks and gardens, which provide a respite from urban life for many species big and small. This study ultimately provides further evidence that urban nature is not as accessible to marginalized human populations, emphasizing the need for cities to prioritize environmental equity in planning and development.
This study was made possible through collaboration with UWIN partners including:
Arizona
Arizona State University College of Integrative Sciences and Arts
Arizona State University School of Life Sciences
Arkansas
Arkansas Game & Fish Commission
Hendrix College Biology & Health Sciences Department
California
Arroyos & Foothills Conservancy
California State University Long Beach Department of Biological Sciences
Conservation Society of California
Oakland Zoo
Occidental College Department of Biology
University of California Berkeley Department of Environmental Science
Canada
University of Toronto Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
Colorado
Playa Lakes Joint Venture
University of Colorado Denver Department of Integrative Biology
Georgia
University of Georgia Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources
Illinois
DePaul University Department of Biological Sciences
Lincoln Park Zoo
University of Illinois Prairie Research Institute
Indiana
Butler University Center for Urban Ecology and Sustainability
Butler University Department of Biological Sciences
Iowa
University of Iowa Department of Geographical and Sustainable Studies
Maryland
Wildlife Habitat Council
Massachusetts
Boston University Department of Earth and Environment
Bridgewater State University Department of Biological Sciences
Lesley University Department of Natural Sciences and Mathematics
Mississippi
Mississippi State University
Missouri
University of Health Sciences and Pharmacy
Washington University Tyson Research Center
Oregon
Portland State University Honors College
Texas
Memorial Park Conservancy
University of Houston Department of Biology and Biochemistry
Utah
Sageland Collaborative
University of Utah Science Research Initiative
Utah’s Hogle Zoo
Washington
Seattle University Department of Biology
Woodland Park Zoo
Wisconsin
University of Wisconsin-Madison Department of Forest and Wildlife Ecology
Since 2010, the Urban Wildlife Institute at Lincoln Park Zoo has been pioneering the study of interactions between urban development and the natural ecosystem to develop scientific standards for minimizing conflict between them. In 2017, UWI launched the Urban Wildlife Information Network, an alliance of ecologists and educators all over the world using shared methods to collect data on how wildlife adapt to and use cities.
Read the full paper Gentrification drives patterns of alpha and beta diversity in cities, 2023-18596R, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
END
New research highlights effects of gentrification on urban wildlife populations across U.S. cities
Data sheds light on how marginalized urban communities are further limited in their access to nature
2024-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vaccine breakthrough means no more chasing strains
2024-04-15
Scientists at UC Riverside have demonstrated a new, RNA-based vaccine strategy that is effective against any strain of a virus and can be used safely even by babies or the immunocompromised.
Every year, researchers try to predict the four influenza strains that are most likely to be prevalent during the upcoming flu season. And every year, people line up to get their updated vaccine, hoping the researchers formulated the shot correctly.
The same is true of COVID vaccines, which have been reformulated to target sub-variants of the most prevalent strains ...
Epilepsy drug prevents brain tumors in mice with NF1
2024-04-15
A drug used to treat children with epilepsy prevents brain tumor formation and growth in two mouse models of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. NF1 is a genetic condition that causes tumors to grow on nerves throughout the body, including the optic nerves, which connect the eyes to the brain.
The findings lay the groundwork for a clinical trial to assess whether the drug, lamotrigine, can prevent or delay brain tumors in children with NF1. The study is online in the journal Neuro-Oncology.
“Based on these data, the Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium is considering launching a first-of-its-kind ...
Study uses thermodynamics to describe expansion of the Universe
2024-04-15
The idea that the Universe is expanding dates from almost a century ago. It was first put forward by Belgian cosmologist Georges Lemaître (1894-1966) in 1927 and confirmed observationally by American astronomer Edwin Hubble (1889-1953) two years later. Hubble observed that the redshift in the electromagnetic spectrum of the light received from celestial objects was directly proportional to their distance from Earth, which meant that bodies farther away from Earth were moving away faster and the universe must be expanding.
A surprising new ingredient was added to the model in 1998 when observations of ...
New mechanism uncovered in early stages of Alzheimer's disease
2024-04-15
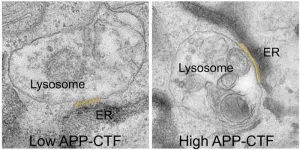
Leuven (Belgium), 16 April 2024 – Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains one of the most challenging and prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. In a new study published in Developmental Cell, researchers from the lab of Wim Annaert (VIB-KU Leuven) have identified a novel mechanism potentially connected to the early stages of AD. They demonstrated that a fragment of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), called APP-CTF, disrupts communication between cellular compartments crucial for calcium storage and waste disposal, which ...
Elite coaches leaving home as Western countries seek sport success
2024-04-15
Nations battling for Olympic success in a global sporting ‘arms race’ has led to elite coaches migrating to Western countries as they bid to escape antiquated and restrictive coaching regimes in their home countries, reveals a new study funded by the International Olympic Committee’s Olympic Studies Centre.
National teams pursuing Olympic gold medals are increasingly recruiting foreign elite coaches from the leading countries, as they try to close the gap between themselves and the top medal-winners in particular ...
Millions of gamers advance biomedical research
2024-04-15
Leveraging gamers and video game technology can dramatically boost scientific research according to a new study published today in Nature Biotechnology.
4.5 million gamers around the world have advanced medical science by helping to reconstruct microbial evolutionary histories using a minigame included inside the critically and commercially successful video game, Borderlands 3. Their playing has led to a significantly refined estimate of the relationships of microbes in the human gut. The results of this collaboration will both substantially advance our knowledge of the microbiome ...
Global North energy outsourcing demands more attention
2024-04-15
Manufacturing nations in the Global North are stockpiling energy and emission problems by outsourcing energy-intensive industrial processes to countries in the Global South, a new study reveals.
Global North countries use their advantages in capital and technology to grab a large amount of energy through outsourcing - creating a ‘false decoupling’ of energy consumption from economic growth.
But backward production technologies in the Global South tend to result in more energy consumption per unit of output – leading to greater carbon emissions ...
Mayo researchers invented a new class of AI to improve cancer research and treatments
2024-04-15
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Mayo Clinic researchers recently invented a new class of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms called hypothesis-driven AI that are a significant departure from traditional AI models which learn solely from data.
In a review published in Cancers, the researchers note that this emerging class of AI offers an innovative way to use massive datasets to help discover the complex causes of diseases such as cancer and improve treatment strategies.
"This fosters a new era in designing targeted and informed AI algorithms to solve scientific questions, ...
Machine learning could help reveal undiscovered particles within data from the Large Hadron Collider
2024-04-15
Scientists used a neural network, a type of brain-inspired machine learning algorithm, to sift through large volumes of particle collision data.
Particle physicists are tasked with mining this massive and growing store of collision data for evidence of undiscovered particles. In particular, they’re searching for particles not included in the Standard Model of particle physics, our current understanding of the universe’s makeup that scientists suspect is incomplete.
As part of the ATLAS collaboration, scientists ...
metaphacts and Dimensions launch the Dimensions Knowledge Graph, powered by metaphactory
2024-04-15
Digital Science solutions metaphacts and Dimensions are excited to announce the highly anticipated launch of the Dimensions Knowledge Graph, a large ready-made knowledge graph powering AI solutions in the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries.
The Dimensions Knowledge Graph, powered by metaphactory, is an all-in-one knowledge graph solution, ready-made for easy integration with customers’ data infrastructure and existing internal knowledge graphs. At its core is an explicitly defined and flexible semantic model that can be easily extended to include internal data (which can range from domain expert knowledge or data from internal documents) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
[Press-News.org] New research highlights effects of gentrification on urban wildlife populations across U.S. citiesData sheds light on how marginalized urban communities are further limited in their access to nature