(Press-News.org) Crowdsourcing efficiently delegates tasks to crowd workers for labeling, though their varying expertise can lead to errors. A key task is estimating worker expertise to infer true labels. However, the noise transition matrix-based methods for modeling worker expertise often overfit annotation noise due to oversimplification or inaccurate estimations.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Shao-Yuan LI published their new research on 12 Mar 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a knowledge distillation-based framework KD-Crowd, which leverages noise-model-free learning techniques to refine crowdsourcing learning. Besides, the team also proposed one f-mutual information gain-based knowledge distillation loss to prevent the student from memorizing serious mistakes of the teacher model. Compared with the existing research results, the proposed method demonstrated both on synthetic and real-world data, attains substantial improvements in performance.
Future work can focus on testing the effectiveness of this framework on regular single-source noisy label learning scenarios with complex instance-dependent noise and investigating more intrinsic patterns in crowdsourced datasets.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-023-3578-7
END
KD-crowd: A knowledge distillation framework for learning from crowds
2024-04-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can animals count?
2024-04-16
HONG KONG (16 April 2024)—A groundbreaking discovery that appears to confirm the existence of discrete number sense in rats has been announced by a joint research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) and The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK).
The findings offer a crucial animal model for investigating the neural basis of numerical ability and disability in humans, the Hong Kong-based researchers say.
This innovative study deployed a numerical learning task, brain manipulation techniques and AI modelling to tackle an ongoing debate about whether rats can count, says Professor Yung Wing-ho, Chair Professor of Cognitive Neuroscience at CityUHK, who ...
Australian media need generative AI policies to help navigate misinformation and disinformation
2024-04-16
New research into generative AI images shows only over a third of media organisations surveyed at the time of research have an image-specific AI policy in place.
The study, led by RMIT University in collaboration with Washington State University and the QUT Digital Media Research Centre, interviewed 20 photo editors or related roles from 16 leading public and commercial media organisations across Europe, Australia and the US about their perceptions of generative AI technologies in visual journalism.
Lead researcher and RMIT Senior Lecturer, Dr TJ Thomson, said while most staff interviewed ...
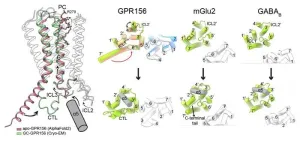
Illuminating the path to hearing recovery
2024-04-16
Professor Yunje Cho’s research team from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH, Republic of Korea) has collaborated with Professor Kwang Pyo Kim’s group from the Department of Applied Chemistry at Kyung Hee University (KHU, ROK), Professor Vsevolod Katritch’s team from the University of Southern California (USC, USA), and Professor Carol V. Robinson from the University of Oxford (UK) to uncover the mysteries surrounding a specific receptor protein associated with hearing. Their findings have recently been published in the online edition of Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
Deep ...
Unlocking the secrets of fruit quality: How anthocyanins and acidity shape consumer preferences and market value
2024-04-16
A research team reviews the critical relationship between the accumulation of anthocyanins and organic acids in fruits, highlighting how these factors influence fruit color and consumer appeal through changes in vacuolar pH. The analysis focused on the transcription factors (TFs) responsible for the co-regulation of genes affecting these quality traits, aiming to enhance fruit marketability. By establishing a genetic link and identifying the regulatory mechanisms involved, the team provides a roadmap for breeders to target specific traits for modification. Although progress has been made, the review underlines the ...
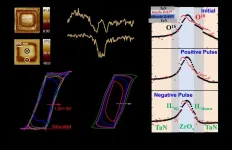
Evidence for reversible oxygen ion movement during electrical pulsing: enabler of the emerging ferroelectricity in binary oxides
2024-04-16
Ferroelectric binary oxides thin films are garnering attention for their superior compatibility over traditional perovskite-based ferroelectric materials. Its compatibility and scalability within the CMOS framework make it an ideal candidate for integrating ferroelectric devices into mainstream semiconductor components, including next-generation memory devices and various logic devices such as Ferroelectric Field-effect Transistor, and Negative Capacitance Field-effect Transistor. It has been reported that challenges ...
Revolutionizing Citrus cultivation: The superior tolerance and growth vigor of 'Shuzhen No.1' rootstock
2024-04-16
Citrus is the world’s most economically significant fruit crop, but it faces various environmental adversities that restrict its distribution. Grafting is a crucial factor in enhancing citrus productivity. Current research focuses on selecting genetically uniform rootstocks, such as trifoliate orange for its disease resistance. However, issues such as sensitivity to alkalinity and incompatibility with certain cultivars persist.
Addressing these challenges, a study (DOI: 10.48130/frures-0023-0042) published in Fruit Research on 01 February 2024, introduces 'Shuzhen No.1', a novel rootstock ...
Family and media pressure to lose weight in adolescence linked to how people value themselves almost two decades later
2024-04-16
People who as teenagers felt pressure to lose weight from family or from the media, females, people who are not heterosexual, and people experiencing socioeconomic disadvantage, are most at risk of ‘internalised’ weight stigma, new research led by the University of Bristol has found. The study is published in The Lancet Regional Health Europe today [15 April].
‘Internalised’ weight stigma, is when people apply negative obesity-related stereotypes to themselves, such as thinking they are less attractive, less competent, or less valuable as a person because of their weight. This is the first time a study has used a large UK sample to examine who is most at risk.
In ...
Despite the desire to reduce the risk of imitation, new research suggests startups should scale slowly and steadily
2024-04-16
A new study published in the Strategic Management Journal cautions startups against prioritizing early scaling, as it’s positively associated with a higher rate of firm failure — especially for platform companies. Although managers could see the potential benefits of scaling as a way to prevent competitor imitation, scaling early can also prematurely curtail learning through experimentation and committing to a business idea that lacks product-market fit.
Although a few high-growth startups such as Facebook and Uber made their fortunes by scaling early — also known as “blitzscaling” — study authors Saerom (Ronnie) Lee and ...
The Lancet: Many people with breast cancer ‘systematically left behind’ due to inaction on inequities and hidden suffering
2024-04-16
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time] / 19.30 [ET], Monday 15 April 2024**
Peer-reviewed/Literature review, Survey, and Opinion/People
Embargoed access to the papers and contact details for authors and patient advocates are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
Breast cancer is now the world’s most common cancer; at the end of 2020, 7.8 million women were alive having been diagnosed in the previous five years. In the same year, 685,000 women died from the disease. Despite significant improvements in research, treatment, and survival, gross inequities persist, and many patients ...
From opioid overdose to treatment initiation: outcomes associated with peer support in emergency departments
2024-04-16
People with a nonfatal opioid overdose who have access to a peer support program while in the emergency department are more likely to initiate treatment and less likely to have repeated overdoses, according to a Rutgers Health study.
The study is the largest study on outcomes associated with emergency department-based peer support for opioid use disorders and was published in JAMA Network Open online ahead of print in the April 2024 issue.
According to the Centers for Disease ...