(Press-News.org) A novel approach to drug discovery is enabling University of Birmingham researchers to overcome the ‘valley of death’, where projects fail due to the funding gap between original research and commercial investment.
The approach, detailed in a feature published in the April issue of Drug Discovery Today, has attracted more than £4m in industry funding, grants and industry awards, on the back of just £0.2m investment from the University’s Dynamic Investment Fund (DIF).
The Birmingham Drug Discovery Hub was set up following a review that showed despite significant expertise in fields necessary for drug discovery, including a strong clinical team and two world-leading clinical trials centres, there were some excellent examples of translation but these were sporadic.
Realisation of this untapped potential became a priority for the University, and a Chair of Drug Discovery was appointed with the mission of leading and integrating drug discovery across campus. Professor Ruth Roberts, who has significant experience of drug development in industry, took on the academic lead role.
The approach defined by the BDDH had two key elements: the evaluation and management of projects by experts in drug discovery and development, and targeted resources to create a diverse, de-risked portfolio of projects that are ready for investment.
The portfolio covers projects from every part of the University which are fed into the BDDH pipeline following identification by BDDH, University of Birmingham Enterprise, the University’s Business Engagement & Research Impact and Translational Research teams, as well as from outreach events and directly from academics.
The initial triage of projects is critical. A bespoke team is assembled for each project, involving university as well as external subject matter experts. This triage is followed by a systematic ‘target-chemistry-patient’ evaluation, which identifies key risks and mitigation measures, and flushes out gaps in the data that are required before a project can enter clinical trials.
These gaps and concerns are then addressed with small, enabling investments (£5,000-£50,000) from the DIF, to fund work such as computational modelling, early chemistry or evaluation of unwanted safety risks. Academics can also bid for time from a medicinal chemistry Research Fellow, employed by the BDDH as a central resource to overcome the dependency on someone ‘knowing someone else’ within the university who is willing to help out.
Professor Roberts said: “The BDDH model tackles, head-on, the biggest challenges that arise in academic drug discovery: lack of funding between basic research and investment-ready research; lack of expertise in universities to assess value and identify data gaps; and the issue of scale in university research, which often does not meet the critical mass of expertise needed for clinical translation.”
David Coleman, CEO of University of Birmingham Enterprise, said: “Drug discovery is an important area of research for Birmingham, yet the ideas and innovations that arise can be difficult to take forward, not least because of the limited investment that is available in a sector which is highly capital intensive. The BDDH directs available resource in the most targetted way to de-risk opportunities for commercial investors or licensees, and has created an impressive portfolio that includes novel targets, small molecules, and approaches such as immune-based targeting for inflammatory diseases.”
Further examples of current BDDH projects are listed here. The BDDH also manages the Haworth Compound Collection, a curated collection of compounds synthesized in Birmingham, which display drug-like properties. The Haworth Collection includes a physical collection of more than 600 compounds and a much larger virtual collection assembled during lockdown by mining 25 years’ worth of PhD theses for suitable compounds.
For information about BDDH projects, or the Haworth Compound Collection contact Dr Angela Murray, Drug Discovery Programme Manager, email: A.J.Murray@bham.ac.uk
END
How the Birmingham Drug Discovery Hub created an investment-ready ‘drug library’
2024-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists uncover 95 regions of the genome linked to PTSD
2024-04-18
In posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), intrusive thoughts, changes in mood, and other symptoms after exposure to trauma can greatly impact a person’s quality of life. About 6 percent of people who experience trauma develop the disorder, but scientists don’t yet understand the neurobiology underlying PTSD.
Now, a new genetic study of more than 1.2 million people has pinpointed 95 loci, or locations in the genome, that are associated with risk of developing PTSD, including 80 that had not been previously identified. The study, from the PTSD working group within the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC - PTSD) together with Cohen ...
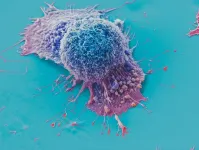
AI tool predicts responses to cancer therapy using information from each cell of the tumor
2024-04-18
With more than 200 types of cancer and every cancer individually unique, ongoing efforts to develop precision oncology treatments remain daunting. Most of the focus has been on developing genetic sequencing assays or analyses to identify mutations in cancer driver genes, then trying to match treatments that may work against those mutations.
But many, if not most, cancer patients do not benefit from these early targeted therapies. In a new study published on April 18, 2024, in the journal Nature Cancer, first author Sanju Sinha, Ph.D., assistant professor in the Cancer Molecular Therapeutics ...
CEOs’ human concern translates into higher stock price
2024-04-18
Compassionate leadership has tangible benefits: CEOs’ expressions of empathy correlate with positive stock performance, a study led by the University of Zurich shows. The researchers analyzed data from conference calls between CEOs and financial analysts during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic prompted an unprecedented financial crisis. Between 24 February 2020, and 20 March 2020, the value of U.S. companies on the stock market decreased significantly, surpassing the decline during the 2008-2009 financial crisis.
At the onset of the pandemic, several CEOs made statements ...
Smoking-related deaths could be reduced if people attending lung cancer screening are offered stop-smoking support
2024-04-18
A new study has found that by offering stop smoking support as part of the national lung cancer screening programme, there is potential to save lives, and dedicated funding must be considered by policy makers.
The results of the study, published in the European Respiratory Journal, showed that offering stop smoking support at the same time and in the same place as lung screening, resulted in a high uptake of support across a range of demographic characteristics.
This has the potential to reduce smoking-related illness and death in a high-risk ...
Quick decisions in soccer enhanced by brain’s ability to suppress actions
2024-04-18
To pass or not to pass, that is the question faced by soccer players the world over in every match. It might be unsurprising that higher skilled players exhibit better execution of actions than lower skilled ones, but now an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research team has evidence that the neural process to suppress actions also plays an important role.
Research Center for Urban Health and Sports Assistant Professor Takahiro Matsutake and colleagues conducted an experiment to see how three levels of soccer players perform when faced with the same tasks.
The ...
Recycling CFRP waste is a challenge, but we've found a way to make it work
2024-04-18
Carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) are lighter and stronger than metal and are used in a variety of industries, including aviation, aerospace, automotive, marine, and sporting goods. In recent years, it has also been applied to new industries such as air mobility, which has led to an increase in its use and a waste disposal problem. However, CFRP is not naturally degradable, and high-temperature incineration methods emit toxic substances and cause environmental pollution, so it is urgent to develop ...
Advanced nuclear magnetic resonance technique developed to reveal precise structural and dynamical details in zeolites
2024-04-18
Zeolites are widely used in many industries. There is still a need to fully understand their intrinsic catalytic nature due to the complexity of the hydroxyl-aluminum moieties.
Atomic-scale analysis of local environments for the hydroxyl species is essential for revealing the intrinsic catalytic activity of zeolites and guiding the design of high-performance catalysts. However, many unfavorable factors prohibit the elucidation of their fine structures such as low quantity, meta-stable property, structural similarity, ...
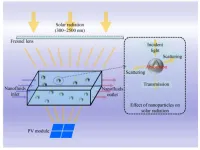
Advancing performance assessment of a spectral beam splitting hybrid PV/T system with water-based SiO2 nanofluid
2024-04-18
As the globe grapples with the urgent need to shift from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources, solar power stands as a beacon of hope. However, a significant challenge has been to efficiently capture and utilize the full spectrum of sunlight. Traditional photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into electricity but can't use the entire solar spectrum, especially the infrared part which is often wasted as heat. To address this, photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) systems have been developed. These hybrid systems ...
Researchers realize target protein stability analysis by time-resolved ultraviolet photodissociation mass spectrometry
2024-04-18
How mutations impact protein stability and structure dynamics is crucial for understanding the molecular mechanism of the disease and the targeted drug design. However, probing the molecular details of mutation-induced subtle structure dynamics is still challenging.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WANG Fangjun from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a time-resolved native mass spectrometry (TR-nMS) strategy coupled with ultraviolet photodissociation (UVPD) analysis. This ...
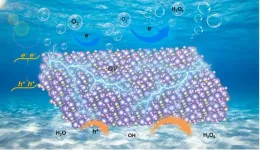
Oxygen vacancies mediated ultrathin Bi4O5Br2 nanosheets as efficient piezocatalyst for synthesis of H2O2 from pure water
2024-04-18
As an important chemical raw material, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is widely applied in various aspects of industry and life. The industrial anthraquinone method for H2O2 production has the serious flaws, such as high pollution and energy consumption. By using ubiquitous mechanical energy, piezocatalytic H2O2 evolution has been proven as a promising strategy, but its progress is hindered by unsatisfied energy conversion efficiency.
Bi4O5Br2 is regarded as a highly attractive photocatalytic material due to its unique sandwich ...