(Press-News.org) Marine Resource Economics (MRE) is pleased to announce the 2024 winners of the journal’s Publication of Enduring Significance Award: Kenneth Ruddle, Edvard Hviding, and Robert E. Johannes for their 1992 article, “Marine Resources Management in the Context of Customary Tenure,” and Frank Asche for his 2008 contribution entitled “Farming the Sea.”
In “Marine Resources Management in the Context of Customary Tenure,” Ruddle, Hviding, and Johannes use a case study-based analysis to show how and why customary marine sea tenure systems that rely on traditional ecological knowledge can deliver sustainable use of marine resources. Of the article’s merit, MRE editors note that it “clearly identifies the social, political, and economic principles necessary for success in these systems. The research priorities it proposes continue to anticipate and influence a growing literature on community-based fisheries management, traditional ecological knowledge, and socio-ecological systems.”
“Farming the Sea” by Frank Asche, a comparative analysis, sheds light on numerous parallels between agriculture and aquaculture. In a cross-industry comparison of production trajectories and their drivers, Asche suggests a significant potential for growth in the aquaculture industry through increasing control over the production process. The article also examines industry-specific environmental impacts, highlighting the importance of understanding the net environmental impact of aquaculture production, which can offset environmental impacts of terrestrial food production. In the words of MRE Editor-in-Chief Sunny Jardine, this “highly cited article introduces several topics for further exploration, making it an invaluable resource for contemporary aquaculture research.”
The Publication of Enduring Significance Award recognizes articles published in MRE that remain important for contemporary researchers either by significantly influencing the subsequent academic literature or by illuminating important ongoing policy issues. Two articles were selected this year; both were ahead of their time and continue to be relevant. Award winners are selected from the archive of articles published at least eight years ago in any of the journal’s sections, aside from book reviews.
END
MRE 2024 Publication of Enduring Significance Awards
2024-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UCalgary researchers quantify the connection between homelessness and mental health disorders
2024-04-18
Health-care professionals who work with people experiencing homelessness know many of the people may also be living with a mental health disorder. University of Calgary researchers wanted to better understand how often these two things are connected, and what they found surprised them.
“We found 66-to-75 per cent of people who are experiencing homelessness have an underlying mental health condition” says Dr. Dallas Seitz, MD, PhD, a psychiatrist and clinician-researcher at the Cumming School of Medicine, and senior author of the paper. “We have always ...
Fourteen years after the Gulf of Mexico oil spill, endemic fishes face an uncertain future
2024-04-18
The 2010 Gulf of Mexico Deepwater Horizon was the largest accidental oil spill in history. With almost 100 million gallons (379 million liters) of oil combined with dispersants suggested to remain in the Gulf, it is one of the worst pollution events ever. More than a decade later, its long-term effects are still not fully understood.
In a new study, researchers from Louisiana State University and Tulane University examined the endemic Gulf of Mexico fish species that may have been most impacted by the oil spill to see how their distribution has changed over the years. To get their data, they studied museum specimens from natural ...
For more open and equitable public discussions on social media, try “meronymity”
2024-04-18
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Have you ever felt reluctant to share ideas during a meeting because you feared judgment from senior colleagues? You’re not alone. Research has shown this pervasive issue can lead to a lack of diversity in public discourse, especially when junior members of a community don’t speak up because they feel intimidated.
Anonymous communication can alleviate that fear and empower individuals to speak their minds, but anonymity also eliminates important social context and can quickly skew too far in the other direction, leading to toxic or hateful speech.
MIT ...
Marine microbial populations: Potential sensors of the global change in the ocean
2024-04-18
Animal and plant populations have been extensively studied, which has helped to understand ecosystem processes and evolutionary adaptations. However, this has not been the case with microbial populations due to the impossibility of isolating, culturing and analyzing the genetic content of the different species and their individuals in the laboratory. Therefore, although it is known that populations of microorganisms include a great diversity, this remains largely uncharacterized.
Now, a new study from the Institut de Ciències del Mar (ICM-CSIC) recently published in the journal Microbiome highlights the potential of marine microbial populations as indicators ...
Metacognitive abilities like reading the emotions and attitudes of others may be more influenced by environment than genetics
2024-04-18
Twin studies have proven invaluable for teasing out the effects of both genetics and the environment on human biology. In a study published April 2 in Cell Reports, researchers studied pairs of twins to look at how the interplay of genetics and environment affect cognitive processing—the way that people think. They found that some cognitive abilities appear to be regulated more by environmental factors than by genetics.
“Past research has suggested that general intelligence—often referred to as intelligence quotient or IQ—has a heritability ranging from 50% to 80%,” says senior and corresponding author Xiaohong Wan of Beijing Normal University in China. ...
Salk Professor Satchin Panda named 2023 AAAS fellow
2024-04-18
LA JOLLA (April 18, 2024)—Salk Institute Professor Satchidananda Panda has been named a 2023 Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science. Panda is among 502 new AAAS Fellows spanning 24 scientific disciplines who were nominated by their peers for their distinguished efforts to advance science. The election recognizes his contributions to the field of chronobiology, particularly for applications to obesity and human health.
“The Salk community congratulates ...
New urine test has higher diagnostic accuracy for prostate cancer
2024-04-18
A new urine test that measures 18 genes associated with prostate cancer provides higher accuracy for detecting clinically significant cancers than PSA and other existing biomarker tests, according to a study published April 18 in JAMA Oncology. The urine test, MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2), was shown to meaningfully reduce unnecessary prostate biopsies while providing highly accurate detection of worrisome prostate cancers, the researchers concluded.
“In nearly 800 patients with an elevated PSA level, the new test was capable of ruling out the presence of clinically significant prostate cancer with remarkable accuracy. This allows patients to avoid more burdensome and ...
Floating solar’s potential to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically
2024-04-18
Milan, April 17 2024 – The study, published in Nature Energy, is among the first to explore the FPV at the continental scale, finding that FPV installed at existing major reservoirs could produce 20-100% of the electricity expected from Africa’s planned hydropower dams. Using a state-of-the-art energy planning model covering the continent’s entire energy system, the researchers found that FPV is cost-competitive with other renewables and thus a key part of Africa’s future energy mix.
"Floating solar is fast becoming cost-competitive with land-based solar, and ...
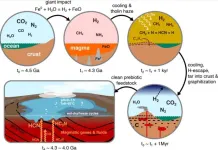
Drawing a line back to the origin of life
2024-04-18
Scientists in Cambridge University suggest molecules, vital to the development of life, could have formed from a process known as graphitisation. Once verified in the laboratory, it could allow us to try and recreate plausible conditions for life's emergence.
How did the chemicals required for life get there?
It has long been debated how the seemingly fortuitous conditions for life arose in nature, with many hypothesises reaching dead ends. However, researchers at the University of Cambridge have now modelled how these conditions could occur, producing the necessary ingredients for life in substantial ...
Data-driven music: Converting climate measurements into music
2024-04-18
A geo-environmental scientist from Japan has composed a string quartet using sonified climate data. The 6-minute-long composition—entitled “String Quartet No. 1 “Polar Energy Budget”—is based on over 30 years of satellite-collected climate data from the Arctic and Antarctic and aims to garner attention on how climate is driven by the input and output of energy at the poles. The backstory about how the composition was put together publishes April 18 in the journal iScience as part of a collection “Exploring the Art-Science Connection.”
“I strongly hope that this manuscript marks a significant turning point, transitioning ...