The relationship between viral replication and the severity of hepatic necroinflammatory damage changed before HBeAg loss in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
2024-04-22
(Press-News.org) Background and Aims
Disease progression of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is driven by the interactions between viral replication and the host immune response against the infection. This study aimed to clarify the relationship between HBV replication and hepatic inflammation during disease progression.
Methods
Two cross-sectional, one validation cohort, and meta-analyses were used to explore the relationship between HBV replication and liver inflammation. Spearman analysis, multiple linear regression, and logistic regression were used to explore the relationship between variables.
Results
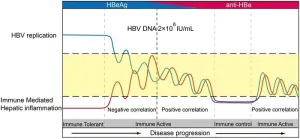
In the cross-sectional cohorts A and B including 1,350 chronic hepatitis B patients, Spearman analysis revealed a negative relationship between HBV replication (such as HBV DNA) and liver inflammation (such as ALT) in HBeAg-positive patients with higher HBV DNA >2×106 IU/mL (rho=−0.160 and −0.042) which turned to be positive in HBeAg-positive patients with HBV DNA ≤2×106 IU/mL (rho=0.278 and 0.260) and HBeAg-negative patients (rho=0.450 and 0.363). After adjustment for sex, age, and anti-HBe, results from logistic regression and multiple linear regression showed the opposite relationship still existed in HBeAg-positive patients with different DNA levels; the opposite relationship in HBeAg-positive patients with different DNA levels was validated in a third cohort; the opposite relationship in patients with different HBeAg status was partially confirmed by meta-analysis (overall R: −0.004 vs 0.481).
Conclusions
These results suggested a negative relationship between viral replication and liver inflammation in HBeAg-positive patients with high HBV DNA, which changed to a positive relationship for those HBeAg-positive patients with DNA less than 2×106 IU/mL and HBeAg-negative patients.
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2023-00378
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
Follow us on X: https://twitter.com/xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/xia&he-publishing-inc/
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-22
Nathan Sleeter, Research Assistant Professor, History and Art History, Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media (RRCHNM), is set to receive funding for: “American Indian Science and Engineering Society (AISES) at 50 website.”
RRCHNM researchers will develop a website that will tell the story of AISES’s first 50 years, its founding mission, its growth, and the individuals who have been part of its work supporting American Indians in STEM. Sleeter will serve as project director.
The researchers will also conduct and record oral history ...
2024-04-22
Farhang Alem, Interim Director of the Biomedical Research Laboratory, Institute for Biohealth Innovation, received funding for: “PRNT Analysis of Samples from Athari BioSciences.”
Researchers with the Biomedical Research Laboratory will perform Plaque Reduction Neutralization Tests (PRNTs) on Athari patient serum samples with parameters defined by Athari. They will also produce and deliver a report containing all patient serum sample titer results for SARS-CoV-2.
PRNT analysis is a serological test that utilizes the ability of a specific antibody to neutralize a virus, and in turn, prevent the virus ...
2024-04-22
Clarifying the cause of a skin disease led to the discovery of a new disease-causing gene, a new category of diseases, and new perspectives for both counseling and therapy. The Kobe University discovery is the first time that epigenetic silencing, the “switching off” of an otherwise intact gene, has been recognized as the cause for a skin disease.
Porokeratosis is a skin disease that leads to the development of annular or circular, red and itchy lesions. In some individuals, these develop all over the body, in some localized in lines, and in some only in one or very few spots. Kobe University dermatologist KUBO Akiharu previously ...
2024-04-22
About The Study: Preoperative use of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in patients undergoing emergency surgery was not associated with a higher risk of postoperative respiratory complications compared with patients not using GLP-1 RAs. The results of this study suggest that liberalizing withholding guidelines for GLP-1 RAs preoperatively should be considered.
Authors: Anjali A. Dixit, M.D., M.P.H., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, ...
2024-04-22
In a world with rapidly aging societies, there’s a need for a detailed understanding of the cause and progression of diseases associated with aging. Skeletal muscle is the key motor system in the human body and plays a pivotal role in body metabolic regulation. With increased age, particularly in individuals over 80 years old, skeletal muscles suffer from sarcopenia, a progressive loss of muscle mass and function. Sarcopenia not only increases the individual’s disability but also plays a role in the rapid decline of general functions in the elderly, making them frailer. The underlying ...
2024-04-22
About The Study: Modest decreases in developmental screening scores suggest reason for cautious optimism about the development of a generation of U.S. children exposed to the COVID-19 pandemic in this study including 50,000 children. Continued attention to developmental surveillance is critical since the long-term population- and individual-level implications of these changes are unclear.
Authors: Sara B. Johnson, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
2024-04-22
About The Study: The findings of this study indicated that initiation of antihypertensive medication was associated with elevated risks of fractures and falls among older long-term care nursing home residents in the Veterans Health Administration. These risks were numerically higher among residents with dementia, higher baseline blood pressures values, and no recent antihypertensive medication use. Caution and additional monitoring are advised when initiating antihypertensive medication in this vulnerable population.
Authors: Chintan V. Dave, Pharm.D., Ph.D., of Rutgers University in New Brunswick, ...
2024-04-22
Primary health care, conditional cash transfers and social pensions have prevented 1.4 million deaths of all ages in Brazil over the past two decades, according to a study coordinated by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. If expanded, these programmes could avert an additional 1.3 million deaths and 6.6 million hospitalisations by 2030.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated poverty and social inequalities worldwide, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). In addition, the economic consequences of the ongoing war in Ukraine and ...
2024-04-22
Scientists believe the environment immediately surrounding a black hole is tumultuous, featuring hot magnetized gas that spirals in a disk at tremendous speeds and temperatures. Astronomical observations show that within such a disk, mysterious flares occur up to several times a day, temporarily brightening and then fading away. Now a team led by Caltech scientists has used telescope data and an artificial intelligence (AI) computer-vision technique to recover the first three-dimensional video showing what such flares could look like around Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*, pronounced sadge-ay-star), the ...
2024-04-22
DALLAS, April 22, 2024 — The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service, and the National Football League (NFL), in collaboration with its 32 NFL clubs, are challenging kids to get moving to support mental and physical health with the latest installment of NFL PLAY 60 Fitness Break broadcast series leading up to the live Draft coverage from Detroit. On Thursday, April 25 at 1 p.m. ET/ 12 p.m. CT/ 10 a.m. PT the NFL PLAY 60 Draft Fitness Break broadcast will assist kids in getting their daily 60 minutes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The relationship between viral replication and the severity of hepatic necroinflammatory damage changed before HBeAg loss in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection