(Press-News.org) A new study shows community pharmacies may play a key role in helping people quit smoking.
The findings came out in the article Closing the Tobacco Treatment Gap, published in the 10th anniversary special issue of Pharmacy. The results provide valuable insights into the implementation of tobacco cessation services within community pharmacies while identifying barriers to further improvements.
Tobacco use remains a leading preventable cause of death. Although two thirds of people who smoke would like to quit, many individuals trying to quit on their own are not successful. To address this gap, the study explored how pharmacists and pharmacy technicians could assist in providing tobacco cessation support.
Led by researchers at UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center and other academic institutions across the country, the study involved seven independent community pharmacies in California affiliated with the Community Pharmacy Enhanced Services Network. A total of 22 California pharmacists and 26 pharmacy technicians who underwent tobacco cessation training participated.
“Community pharmacies are important partners to expand access to tobacco cessation services,” said Elisa Tong, a UC Davis Health internist and director of the cancer center’s Tobacco Cessation Policy Research Center. “By state law, pharmacists can furnish all forms of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) without a provider prescription.”
California’s law allowing pharmacists to provide the cessation tool took effect in 2014. Eligible pharmacists must complete two hours of tobacco training and follow the state-approved protocol, which consists of reviewing patients’ current tobacco use and prior quit attempts, screening for appropriateness of NRT, providing medication counseling, and addressing or referring patients for behavioral counseling. Tobacco cessation has been integrated into the curricula of California pharmacy schools since 2000, and many other training programs are available for pharmacies.
“After completing tobacco treatment training, our research showed that pharmacies successfully initiated cessation services,” said the study’s senior author Karen Hudmon from Purdue University College of Pharmacy. “Compatibility with existing workflows, staff buy-in and the crucial role of pharmacy technicians significantly helped.”
Continued research efforts are underway to study policy implementation strategies, especially for pharmacist reimbursement. California’s law authorizes Medi-Cal and private insurance to pay pharmacies for enhanced services including education and medication management.
“Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians play a pivotal role in providing effective support for tobacco treatment and other related health issues,” said Robin Corelli, a UC San Francisco pharmacy faculty member and study co-author. “Being part of the local community is important and we need sustainable models for providing these services.”
Solving barriers could help pharmacies reach more people
Given that 89% of Americans live within five miles of a community pharmacy, they can be convenient locations for receiving health care services. Pharmacists have shown to be effective in helping patients quit. They can reach uninsured and under-resourced patients as well as patients living in rural areas who might experience barriers to accessing primary care. However, the study showed certain barriers exist to making pharmacy cessation programs effective.
The research showed that billing complexities, software limitations and training gaps for handling complicated patient cases all pose challenges to successful implementation of tobacco cessation services at pharmacies.
However, the data collected implied a forward-thinking health care model where the pharmacists and their staff can play a fundamental and dynamic role in local health management, and ultimately, in cultivating a healthier population. The study serves as a valuable resource for policymakers, health care professionals and stakeholders in population health efforts to combat tobacco use.
This study was funded by the National Cancer Institute (R25 CA236637 to K Hudmon) and the Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program, which also supports the Tobacco Cessation Policy Research Center at UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The cancer center’s new Tobacco Cessation Policy Research Center will continue to examine the role of pharmacies in helping people quit smoking. The center is also studying the integration of tobacco treatment at substance use disorder facilities. Other tobacco-related research focuses on equal access to tobacco treatment provided by public insurance plans and engaging with enforcement of flavored tobacco sales restrictions.
Other authors include:
Katy Ellis Hilts of Richard M. Fairbanks School of Public Health at Indiana University; Nervana Elkhadragy of University of Wyoming School of Pharmacy; Micah Hata of College of Pharmacy, Western University of Health Sciences, Pomona; and Francis M. Vitale of College of Pharmacy, Purdue University.
END
New study confirms community pharmacies can help people quit smoking
Pharmacists may play crucial role in addressing lack of access to tobacco cessation tools
2024-04-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Book aims to re-design the up-skilling game. Rotman School author says we need a re-set in the way we think about human skill in the genAI era
2024-04-22
April 22, 2024
Book Aims to Re-Design the Up-Skilling Game. Rotman School Author Says We Need a Re-Set in the Way We Think About Human Skill in the GenAI era
Toronto – Although communicative and relational skills are currently in the greatest demand in organizations large and small, we are as educators, executives, and talent developers very far away from the kind of precision in identifying, measuring, selecting, and developing these skills that we have achieved with cognitive and technical skills. At the same time, the automation ...
Could automation, electrification of long-haul trucking reduce environmental impacts?
2024-04-22
April 22, 2024
Contact: Lori Atherton, SEAS, lorather@umich.edu
Jim Erickson, Michigan News, ericksn@umich.edu
A new University of Michigan study finds that automation and electrification of long-haul trucking can reduce urban health impacts and environmental damages.
For long-haul routes below 300 miles, electrification can reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas damages by 13%, or $587 million annually, according to the study. ...
European union should adopt a research-based approach to ensure the quality and safety of substances of human origin
2024-04-22
April 22, 2024
European Union Should Adopt a Research-Based Approach to Ensure the Quality and Safety of Substances of Human Origin
London/Toronto – Substances of human origin (SoHOs) such as blood, plasma, skin, corneas, and embryos play an increasing role in life-saving medical procedures. Governments around the world are reevaluating their healthcare policies to ensure of a supply of SoHOs for their population, while also considering the best-interests of both donors and patients.
A ...
Study identifies signs of repeated blast-related brain injury in active-duty United States Special Operations Forces
2024-04-22
Repeated exposure to explosive blasts has the potential to cause brain injuries, but there is currently no diagnostic test for these injuries
In a study of 30 active-duty United States SOF personnel, researchers found that increased blast exposure was associated with structural, functional, and neuroimmune changes to the brain and a decline in health-related quality of life
The researchers are now designing a larger study to develop a diagnostic test for repeated blast brain injury
United States (US) Special Operations Forces (SOF) personnel are frequently exposed to explosive blasts during training and combat. However, ...
Mount Sinai scientists discover the cellular functions of a family of proteins integral to inflammatory diseases
2024-04-22
New York, NY (April 22, 2024) – In a scientific breakthrough, Mount Sinai researchers have revealed the biological mechanisms by which a family of proteins known as histone deacetylases (HDACs) activate immune system cells linked to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other inflammatory diseases.
This discovery, reported in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), could potentially lead to the development of selective HDAC inhibitors designed to treat types of IBD such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
“Our understanding of the specific function of class II HDACs in different cell types has been limited, impeding ...
Spanish scientists identify the key cell type for strategies to prevent atherosclerosis in progeria syndrome
2024-04-22
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) is an extremely rare genetic disease that affects just 1 in every 20 million people; it is estimated that fewer than 400 children in the world have the disease. HGPS is characterized by accelerated aging, severe atherosclerosis, and premature death at an average age of about 15 years. Although people with HGPS do not normally have conventional cardiovascular risk factors (hypercholesterolemia, obesity, smoking, etc.), most patients die from the complications of atherosclerosis: myocardial ...
A new Spanish study provides the first stratification of the risk of developing dilated cardiomyopathy among symptom-free genetic carriers
2024-04-22
Dilated cardiomyopathy is the most frequent cause of heart failure in young people and is the leading cause of heart transplantation. In this disease, the heart enlarges and reduces its capacity to pump blood. People with dilated cardiomyopathy are at high risk for arrhythmias and sudden death.
In approximately 30%–40% of people with dilated cardiomyopathy, the disease is caused by a genetic mutation. When a genetic cause is identified, the patient’s family members can be studied to determine if they have also inherited the altered gene.
Family members who are carriers of the genetic mutation are at risk for developing the disease in ...
International Lawyer from the University of Warwick calls for fairness in WHO Pandemic Treaty Talks
2024-04-22
As the World Health Organization (WHO) pushes for countries to seal the Pandemic Treaty by May this year, researchers at the University of Warwick and Kings College London stress the need for fair negotiations.
The opinion piece, featured in PLOS Global Public Health journal, is led by Professor Sharifah Sekalala . The team highlights the importance of considering "Time Equity" in these talks, urging caution on setting deadlines and sharing the burden when time is tight.
Since COVID-19 hit, demands for health equity ...
International Society for Autism Research (INSAR) 23rd Annual Meeting to be held in Melbourne, Australia May 15-18, 2024
2024-04-22
The International Society for Autism Research (INSAR) will hold its 2024 Annual Meeting – the organization’s 23rd – from Wednesday, May 15 through Saturday, May 18, 2024, bringing together a global, multidisciplinary group of more than 1,200 autism researchers, clinicians, advocates, self-advocates, and students from 20 countries to exchange the latest scientific learnings and discoveries that are advancing the expanding understanding of autism and its complexities. This year’s ...
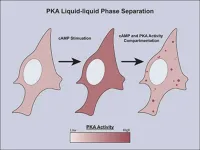
Liquid droplets shape how cells respond to change
2024-04-22
Healthy cells respond appropriately to changes in their environment. They do this by sensing what’s happening outside and relaying a command to the precise biomolecule in the precise domain that can carry out the necessary response. When the message gets to the right domain at the right time, your body stays healthy. When it ends up at the wrong place at the wrong time, you can get diseases such as diabetes or cancer.
The routes that messages take inside a cell are called signaling pathways. Cells use only a few signaling pathways to respond simultaneously to hundreds of external signals, so those pathways need to be tightly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] New study confirms community pharmacies can help people quit smokingPharmacists may play crucial role in addressing lack of access to tobacco cessation tools