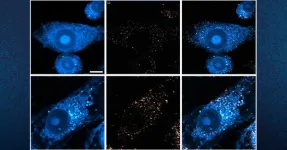
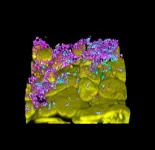
Phage therapy is being explored to treat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, but what are the direct effects of phages on the human host?
This study shows that therapeutic phages can be detected by epithelial cells of the human respiratory tract, eliciting proinflammatory responses that depend on specific phage properties and the airway microenvironment
2024-04-23
(Press-News.org)
Phage therapy is being explored to treat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, but what are the direct effects of phages on the human host?
This study shows that therapeutic phages can be detected by epithelial cells of the human respiratory tract, eliciting proinflammatory responses that depend on specific phage properties and the airway microenvironment.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002566
Article Title: Lytic bacteriophages induce the secretion of antiviral and proinflammatory cytokines from human respiratory epithelial cells
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by a Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (CFF, www.cff.org) Postdoctoral Fellowship ZAMORA20F0 and National Institute of Health (NIH, www.nih.org) grant T32AI060525 to P.F.Z.; CFF grants ARMBRU19F0 and ARMBRU22F5 and NIH grant T32HL129949 to C.R.A; and CFF grant BOMBER21P0 to J.M.B. The funders of this work did not play a role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-23
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Tuesday, April 23, 2024
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
The tobacco industry has long appealed to youth through targeted marketing that glamorizes smoking with imagery of candy-flavored products, celebrity endorsements, social settings, and other enticing tactics. That marketing approach appears to be particularly effective on social media, according to a new study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researchers.
Published in the journal Addictive Behaviors, the study found that frequent social media use was linked to an increased risk of youth using ...
2024-04-23
LAWRENCE — Locations around the globe are experiencing climate disasters on a regular basis. But some of the most marginalized populations experience disasters so often it has come to be normalized.
A new study from the University of Kansas found residents of one Seoul, South Korea, neighborhood have grown so accustomed to living through extreme climate events they have developed a “disaster subculture” that challenges both views of reality and how social agencies can help.
Joonmo Kang, assistant professor ...
2024-04-23
New York (April 23, 2024) —The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) will honor William J. Hall, MD, MACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine at the University of Rochester this year with the prestigious Nascher/Manning Award, given biannually at the AGS Annual Scientific Meeting (#AGS24 will be held virtually May 9 – 11 (pre-conference days: Tuesday & Wednesday, May 7-8).
The Nascher/Manning Award was named in honor of Ignatz Leo Nascher, MD who was the first clinician to advocate for establishing a specialty focused on the care ...
2024-04-23
STRASBOURG, France, 23 April 2024 — Why do stressed bats shed more viruses? How do some key species engineer whole landscapes? How do humans and animals work in groups to solve problems, shape behavior?
These eight research projects are among the Human Frontier Science Program’s (HFSP) 93 Research Grant and Fellowship Awards recently announced to begin in 2024.
“HFSP has funded basic research in the life sciences for the benefit of humankind, and sustainability science spans some of the most complex research imaginable,” said HFSP Chief Scientific Officer Guntram Bauer. “These investigations examine highly interrelated living systems – many ...
2024-04-23
The average wind turbine generates enough electricity in 46 minutes to power a home in the United States for an entire month, according to the United States Geological Survey. And with more than 70,800 turbines scattered throughout the country, wind power has now surpassed hydroelectric power as the largest producer of renewable energy.
With a $2 million grant from the Department of Energy, researchers from Virginia Tech are pioneering processes to make this sustainable energy source even more sustainable. The grant is part ...
2024-04-23
A new study led by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) highlights the lasting financial impact of a cancer diagnosis for many working-age adults and their families in the United States. It shows a cancer diagnosis and the time required for its treatment can result in employment disruptions, loss of household income and loss of employment-based health insurance coverage, leading to financial hardship. When combined with high out-of-pocket costs for cancer care, nearly 60% of working-age cancer survivors report at least one type of financial hardship, such as being unable to afford ...
2024-04-23
“The ultimate goal of exploiting model organisms to screen for anti-aging interventions is to identify treatments that might translate to healthy lifespan extension in humans.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 23, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 7, entitled, “The coupling between healthspan and lifespan in Caenorhabditis depends on complex interactions between compound intervention and genetic background.”
Aging is characterized by declining health that results ...
2024-04-23
USC faculty members Paul K. Newton and Nicolás Lell Benavides have been awarded prestigious Guggenheim Fellowships for 2024.
Newton, professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering and mathematics at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering, and Benavides, a lecturer at the USC Thornton School of Music, were chosen by the John Simon Guggenheim Memorial Foundation from nearly 3,000 applicants. They are among 188 inductees chosen this year for their excellence in scholarship and the arts.
“Humanity faces some profound existential challenges,” said Edward Hirsch, ...
2024-04-23
The council of the American Association for the Advancement of Science has elected USC faculty members Pinchas Cohen, Andrea Hodge, Jay Lieberman and Gaurav Sukhatme to the ranks of AAAS fellows.
The honor, which recognizes researchers whose “efforts on behalf of the advancement of science or its applications are scientifically or socially distinguished,” is among the most prized in academia.
The recognition honors excellence in research, technology, industry and government, teaching, and communicating and interpreting science to the public. The new cohort joins more than 40 of their USC peers already inducted into AAAS.
The newly elected AAAS ...
2024-04-23
Alzheimer’s disease causes significant problems with memory, thinking and behavior and is the most common form of dementia, affecting more than 50 million people around the world each year. This number is expected to triple by the year 2050.
Using their own state-of-the art imaging technologies, scientists at the University of California San Diego have now revealed how the metabolism of lipids, a class of molecule that includes fats, oils and many hormones, is changed in Alzheimer’s disease. They also revealed a new strategy to target this metabolic system with new and existing drugs. The findings are published in Cell Metabolism.
“Lipids ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Phage therapy is being explored to treat multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, but what are the direct effects of phages on the human host?
This study shows that therapeutic phages can be detected by epithelial cells of the human respiratory tract, eliciting proinflammatory responses that depend on specific phage properties and the airway microenvironment