(Press-News.org) Dr. Han Joong Tark and student researcher Lee Do Geun at the Nano Hybrid Technology Research Center of Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute(KERI) have developed a new manufacturing technique for "silicon/nitrogen-doped carbon composite anode materials." These materials aim to enhance the capacity and stability of lithium-ion battery anodes.
Silicon, despite offering significantly higher energy density compared to graphite (a common anode material), suffers from a major drawback: it expands 3-4 times during charging and discharging, leading to performance degradation. To address this issue, researchers are blending silicon with graphite to balance their strengths and weaknesses.
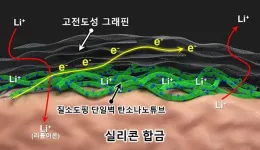
To maximize silicon content and overcome its limitations, KERI has utilized nitrogen-doped single-walled carbon nanotubes and graphene. Single-walled carbon nanotubes, being thinner and more conductive than multi-walled ones, present challenges in dispersion due to their small diameter. Leveraging their expertise in nanocarbon materials, KERI has developed a pioneering functionalization and colloidal dispersion technologies, facilitating the incorporation of nitrogen onto the carbon nanotube surface.
When applied to lithium-ion battery anodes, these nitrogen-doped single-walled carbon nanotubes accelerate lithium-ion movement to silicon, enhancing charging speed and stability across numerous charge/discharge cycles. Additionally, encapsulating the anode materials with graphene further stabilizes silicon expansion.
Through extensive testing, KERI has demonstrated that batteries utilizing their composite anode materials maintain over 82% performance after 100 charge/discharge cycles, compared to only 30% for conventional silicon composite anodes. This advancement eliminates the need for conventional conductive additives like carbon black.
The team envisions broader applications for this technology, including solid-state batteries, where lithium diffusion speed is critical. The research findings have been published in the prestigious materials journal Advanced Functional Materials. The “JCR Impact Factor” of the journal is 19, ranking in the top 3.7% of the field.
KERI has completed full-cell evaluations and patent applications for their composite anode materials, expecting strong interest from companies seeking high-capacity lithium-ion batteries. They are poised to identify potential partners for technology transfer.
KERI is a government-funded research institute under the National Research Council Science & Technology of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
END
Single-walled carbon nanotubes doped with ‘nitrogen’ enhance the performance of secondary battery anode
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
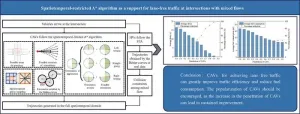
Pioneering the future of urban traffic: The revolutionary spatiotemporal-restricted a* algorithm
2024-04-24
As urban areas continue to grow, the demand for innovative solutions to alleviate traffic congestion and improve transportation efficiency has never been more urgent. A recent breakthrough study presented by researchers from the Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory as well as international research team introduces a cutting-edge approach to managing traffic at urban intersections using the spatiotemporal-restricted A* algorithm. This advanced method promises to transform how traffic is handled by optimizing the flow of both connected automated vehicles (CAVs) and human-driven vehicles (HVs) ...
First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant gives new hope to patient with terminal illness
2024-04-24
NEW YORK, NY, APRIL 24, 2024— Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman with heart and kidney failure—a confluence of advances that showcase the possibility and hope of modern medicine.
Doctors performed this feat in two stages: first surgically implanting the heart pump days before embarking on the landmark transplant, which included a gene-edited pig kidney and the pig’s thymus gland to aid against rejection. Before the procedure, patient Lisa Pisano, a New Jersey ...
FAU receives grant to examine role of pet dogs on military adolescents
2024-04-24
Florida Atlantic University Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing’s Canines Providing Assistance to Wounded Warriors (C-P.A.W.W.) has received a new grant from the Human Animal Bond Research Institute (HABRI) for research that investigates the contribution of pet dog ownership to resilience and well-being in adolescent children of military families.
The grant was awarded to a team of researchers led by Laurie Martinez, Ph.D., an assistant professor, FAU College of Nursing; and co-led by Cheryl A. Krause-Parello, Ph.D., associate vice president for research, FAU Division of Research and a research professor in the College of Nursing.
This important study will provide ...
COVID-19 pandemic alters view that doctors are obligated to provide care
2024-04-24
DURHAM, N.C. – The unique circumstances arising from the COVID-19 pandemic altered a long-held convention that doctors provide care regardless of personal risk.
In a study assessing doctors’ tolerance for refusing care to COVID-19 patients, Duke Health researchers identified a growing acceptance to withhold care because of safety concerns.
“All the papers throughout history have shown that physicians broadly believed they should treat infectious disease patients,” said the study’s lead author, Braylee Grisel, a fourth-year student at Duke University ...
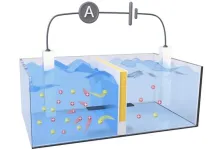
This salt battery harvests osmotic energy where the river meets the sea
2024-04-24
Estuaries — where freshwater rivers meet the salty sea — are great locations for birdwatching and kayaking. In these areas, waters containing different salt concentrations mix and may be sources of sustainable, “blue” osmotic energy. Researchers in ACS Energy Letters report creating a semipermeable membrane that harvests osmotic energy from salt gradients and converts it to electricity. The new design had an output power density more than two times higher than commercial membranes in lab demonstrations.
Osmotic energy can be generated anywhere salt gradients are ...
On the trail of deepfakes, Drexel researchers identify ‘fingerprints’ of AI-generated video
2024-04-24
In February, OpenAI released videos created by its generative artificial intelligence program Sora. The strikingly realistic content, produced via simple text prompts, is the latest breakthrough for companies demonstrating the capabilities of AI technology. It also raised concerns about generative AI’s potential to enable the creation of misleading and deceiving content on a massive scale. According to new research from Drexel University, current methods for detecting manipulated digital media will not be effective against AI-generated video; but a machine-learning approach could be the key to unmasking these synthetic creations.
In a paper accepted ...
Virtual reality can motivate people to donate to refugee crises regardless of politics
2024-04-24
PULLMAN, Wash. – Political conservatives who watched a documentary on Syrian refugees with a virtual reality headset had far more sympathy for the people depicted in the film than those who viewed the same film on a two-dimensional computer screen.
Higher sympathy levels among the conservatives who watched the VR version of the documentary, “Clouds over Sidra,” resulted in a greater willingness to donate to the crisis, according to a study on the research published in New Media & Society.
Liberal participants in the study reported high levels of sympathy and ...
Holographic displays offer a glimpse into an immersive future
2024-04-24
Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.
Holographic images have real depth because they are three dimensional, whereas monitors merely simulate depth on a 2D screen. Because we see in three dimensions, holographic images could be integrated seamlessly into our normal view of the everyday world.
The result is a virtual and augmented reality display that has the potential to be truly immersive, the kind where you can move your head ...
Novel Au-BiFeO3 nanostructures for efficient and sustainable degradation of pollutants
2024-04-24
The need for sustainable and environment-friendly solutions has accelerated the global demand for green and renewable technologies. In this regard, semiconductor photocatalysts have emerged as an attractive solution, owing to their potential in mitigating pollutants and harnessing solar energy efficiently. Photocatalysts are materials that initiate chemical reactions when exposed to light. Despite their progress, commonly used photocatalysts suffer from reduced photocatalytic activity and a narrow operation range within the visible ...
It takes two to TANGO: New strategy to tackle fibrosis and scarring
2024-04-24
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona and the University of Cologne in Germany have developed a new experimental strategy to tackle scarring and fibrosis. Experiments with patient-derived human cells and animal models showed the strategy was effective, non-toxic and its effects reversible. The findings are published today in the journal Nature Communications.
Scarring occurs from the secretion and accumulation of various components – primarily proteins known as collagens – into the space between individual cells, usually occurring as a response to injury or damage. Excessive collagen secretion can also cause the buildup of fibrotic ...