(Press-News.org)
· 73% of children with skin disease experience stigma and poor quality of life
· ‘Chronic skin conditions can be tremendously life-altering’
· Shame during childhood can affect them throughout their lives, dermatologist says
CHICAGO --- The majority of children and teens with chronic skin diseases such as acne, eczema, psoriasis, alopecia areata (hair loss) and vitiligo (pigment loss) feel stigmatized by peers for their condition and are sometimes bullied, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study. As a result, these children have a poor quality of life that includes suffering from depression, anxiety and impaired relationships with their peers.
“These chronic skin conditions can be tremendously life-altering, including shaping psychosocial development,” said corresponding author Dr. Amy Paller, chair of dermatology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a pediatric dermatologist at the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago.
Having a chronic skin disease during childhood is not uncommon. Eczema affects more than 10% of school-aged children. Among teenagers, acne affects more than 90% and psoriasis 1%.
This is the first large, multi-site study of the psychosocial impact of skin diseases in children and teens.
The study showed that 73% of 1,671 children had experienced a measurable stigma, which was strongly associated with poor quality of life.
The disease severity and visibility as rated by the child (age eight and older) was quite different from that of the doctor’s ratings, suggesting the need to ask the child about the disease and its impacts.
The study will be published April 24 in JAMA Dermatology.
The investigators used a newly developed scoring tool for stigma in school-aged children (PROMIS Pediatric Stigma) and collaborated with 31 sites in the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance to measure the extent of stigma, depression, anxiety, and poor peer relationships — and their association with an impaired quality of life.
“Stigma, which is when something false and negative is attached to an individual, can have a profound effect on children’s and teens’ mental health,” Paller said. “For example, a child with dark scales on the body can be called ‘dirty’ by other kids or a child with a hair loss issue can be shunned by other children who fear the hair loss is contagious.”
That can lead the child to internalize these thoughts, so these become their own perceptions. The false beliefs can convince other people around them that it’s true when it’s not. These kids often feel embarrassed or ashamed.”
The majority of the bullying and teasing occurs in school, Paller said.
“These painful experiences can shape a child’s personality into adulthood and erode self-confidence,” Paller said. “Children may underestimate their abilities and worry about taking social risks. They don’t feel good enough and this shame may affect them lifelong.”
Kids also may not be able to concentrate because they are worried in school, affecting their performance, Paller said.
“The study results should encourage clinicians to aggressively treat skin disorders in children and consider referral to evaluation and counseling of the child and potentially family if mental health issues occur,” Paller said.
Doctors need to ask children and parents about the impact of these diseases — stigma, mental health, how it impacts life — not just note the observable clinical manifestations.
It’s important to refer families to dermatologists for optimal treatment to decrease severity and visibility, which contribute to psychosocial impacts.”
Paller also suggested parents ask teachers to discuss the skin disease in the classroom, so other children understand it better. “Try to dimmish the stigma through education and talk about and recognize bullying,” Paller said.
The title of the article is “Stigmatization and Mental Health Impact of Chronic Pediatric Skin Disorders.”
Other Northwestern authors include Stephanie Rangel, Sarah Chamlin, David Cella and Jin-Shei Lai.
The study was funded by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance, the umbrella research organization for the field of Pediatric Dermatology
END
Children with skin diseases suffer stigma, bullying and depression
First large study to look at mental health problems in children with chronic skin conditions
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A novel universal light-based technique to control valley polarization in bulk materials
2024-04-24
Electrons inside solid materials can only take certain values of energy. The allowed energy ranges are called “bands” and the space between them, the forbidden energies, are known as “band-gaps”. Both of them together constitute the “band structure” of the material, which is a unique characteristic of each specific material.
When physicists plot the band structure, they usually see that the resulting curves resemble mountains and valleys. In fact, the technical term for a local energy maximum or minimum in the bands is called a “valley”, and the field which studies and exploits how electrons in the material ...
Vast DNA tree of life for flowering plants revealed by global science team
2024-04-24
Images
The most up-to-date understanding of the flowering plant tree of life is presented in a new study published today in the journal Nature by an international team of 279 scientists, including three University of Michigan biologists.
Using 1.8 billion letters of genetic code from more than 9,500 species covering almost 8,000 known flowering plant genera (ca. 60%), this achievement sheds new light on the evolutionary history of flowering plants and their rise to ecological dominance on Earth.
Led by scientists at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, the research team believes ...
Mini-colons revolutionize colorectal cancer research
2024-04-24
As our battle against cancer rages on, the quest for more sophisticated and realistic models to study tumor development has never been more critical. Until now, research has relied on animal models and simplified cell culture methods, which are valuable but cannot fully capture the complex interplay of factors involved in tumor development.
Even newer, more advanced models for studying cancer, such as organoids – tiny, lab-grown versions of organs – do not faithfully replicate the cell behaviors and tissue architectures seen in actual tumors.
This gap has significantly hindered our understanding ...
Lead-vacancy centers in diamond as building blocks for large-scale quantum networks
2024-04-24
Much like how electric circuits use components to control electronic signals, quantum networks rely on special components and nodes to transfer quantum information between different points, forming the foundation for building quantum systems. In the case of quantum networks, color centers in diamond, which are defects intentionally added to a diamond crystal, are crucial for generating and maintaining stable quantum states over long distances.
When stimulated by external light, these color centers in diamond emit photons carrying information about their internal electronic states, especially the spin states. The interaction between the emitted photons and the ...
JMIR Rehabilitation and Assistive Technologies announces theme issue on participatory methods in rehabilitation research
2024-04-24
JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Incorporating Participatory Methods in Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Rehab Interventions and Assistive Technologies” in its premier, open access journal JMIR Rehabilitation and Assistive Technologies (JRAT).
JRAT is a peer-reviewed journal indexed in PubMed and PubMed Central, SCOPUS, DOAJ, Web of Science, Sherpa Romeo, and EBSCO and EBSCO Essentials. This theme issue aims to showcase research that actively engages patients, caregivers, and other stakeholders (knowledge users) ...
SwRI’s Dr. Marc Janssens recognized for role in establishing cone calorimeter fire testing
2024-04-24
SAN ANTONIO — April 24, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Marc Janssens was named a “DiNenno Prize Laureate” for his role in the widespread adoption of the cone calorimeter, a fire-testing tool that accurately measures heat release and material flammability. The National Fire Protection Association® recognized the cone calorimeter with the 2024 Philip J. DiNenno Prize for its lasting impact on fire safety. Dr. Vytenis Babrauskas, a co-recipient of the prize, developed the cone ...
Modeling broader effects of wildfires in Siberia
2024-04-24
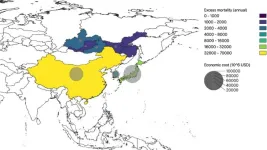
As wildfires in Siberia become more common, global climate modeling estimates significant impacts on climate, air quality, health, and economies in East Asia and across the northern hemisphere.
The global effects of increasing wildfires in Siberia have been modeled by researchers at Hokkaido University and colleagues at the University of Tokyo and Kyushu University. The results, published in the journal Earth’s Future, suggest significant and widespread effects on air quality, climate, health, and economics under the most extreme wildfire scenarios.
The authors performed global numerical simulation experiments to evaluate how the increased intensity of wildfires ...
Researchers find oldest undisputed evidence of Earth’s magnetic field
2024-04-24
A new study, led by the University of Oxford and MIT, has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth’s magnetic field, and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today. The findings have been published today in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
Without its magnetic field, life on Earth would not be possible since this shields us from harmful cosmic radiation and charged particles emitted by the Sun (the ‘solar wind’). But up to now, there has been no reliable date for when the modern magnetic field was first established.
In the new study, the researchers examined ...
Eric and Wendy Schmidt announce 2024 Schmidt Science Fellows
2024-04-24
Eric and Wendy Schmidt Announce 2024 Schmidt Science Fellows
32 exceptional early career researchers will tackle ambitious interdisciplinary science projects
The seventh cohort of the interdisciplinary program, an initiative of Schmidt Sciences, will advance research in areas ranging from healthcare and the environment to advanced materials and robotics
The 2024 Fellows, representing 17 nationalities from 26 nominating institutions across North America, Europe, and Asia, will also benefit from bespoke ...
Paclitaxel-induced immune dysfunction and activation of transcription factor AP-1 facilitate Hepatitis B virus replication
2024-04-24
Background and Aims
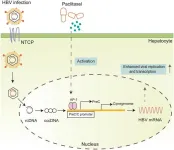
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation is commonly observed in individuals with chronic HBV infection undergoing antineoplastic drug therapy. Paclitaxel (PTX) treatment has been identified as a potential trigger for HBV reactivation. This study aimed to uncover the mechanisms of PTX-induced HBV reactivation in vitro and in vivo, which may inform new strategies for HBV antiviral treatment.
Methods
The impact of PTX on HBV replication was assessed through various methods including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, dual-luciferase reporter assay, quantitative ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Children with skin diseases suffer stigma, bullying and depressionFirst large study to look at mental health problems in children with chronic skin conditions