(Press-News.org) A new study, led by the University of Oxford and MIT, has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth’s magnetic field, and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today. The findings have been published today in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
Without its magnetic field, life on Earth would not be possible since this shields us from harmful cosmic radiation and charged particles emitted by the Sun (the ‘solar wind’). But up to now, there has been no reliable date for when the modern magnetic field was first established.
In the new study, the researchers examined an ancient sequence of iron-containing rocks from Isua, Greenland. Iron particles effectively act as tiny magnets that can record both magnetic field strength and direction when the process of crystallization locks them in place. The researchers found that rocks dating from 3.7 billion years ago captured a magnetic field strength of at least 15 microtesla comparable to the modern magnetic field (30 microtesla).
These results provide the oldest estimate of the strength of Earth’s magnetic field derived from whole rock samples, which provide a more accurate and reliable assessment than previous studies which used individual crystals.
Lead researcher Professor Claire Nichols (Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford) said: ‘Extracting reliable records from rocks this old is extremely challenging, and it was really exciting to see primary magnetic signals begin to emerge when we analysed these samples in the lab. This is a really important step forward as we try and determine the role of the ancient magnetic field when life on Earth was first emerging.’
Whilst the magnetic field strength appears to have remained relatively constant, the solar wind is known to have been significantly stronger in the past. This suggests that the protection of Earth’s surface from the solar wind has increased over time, which may have allowed life to move onto the continents and leave the protection of the oceans.
Earth's magnetic field is generated by mixing of the molten iron in the fluid outer core, driven by buoyancy forces as the inner core solidifies, which create a dynamo. During Earth’s early formation, the solid inner core had not yet formed, leaving open questions about how the early magnetic field was sustained. These new results suggest the mechanism driving Earth’s early dynamo was similarly efficient to the solidification process that generates Earth’s magnetic field today.
Understanding how Earth’s magnetic field strength has varied over time is also key for determining when Earth’s inner, solid core began to form. This will help us to understand how rapidly heat is escaping from Earth’s deep interior, which is key for understanding processes such as plate tectonics.
A significant challenge in reconstructing Earth’s magnetic field so far back in time is that any event which heats the rock can alter preserved signals. Rocks in the Earth’s crust often have long and complex geological histories which erase previous magnetic field information. However, the Isua Supracrustal Belt has a unique geology, sitting on top of thick continental crust which protects it from extensive tectonic activity and deformation. This allowed the researchers to build a clear body of evidence supporting the existence of the magnetic field 3.7 billion years ago.
The results may also provide new insights into the role of our magnetic field in shaping the development of Earth’s atmosphere as we know it, particularly regarding atmospheric escape of gases. A currently unexplained phenomenon is the loss of the unreactive gas xenon from our atmosphere more than 2.5 billion years ago. Xenon is relatively heavy and therefore unlikely to have simply drifted out of our atmosphere. Recently, scientists have begun to investigate the possibility that charged xenon particles were removed from the atmosphere by the magnetic field.
In the future, researchers hope to expand our knowledge of Earth’s magnetic field prior to the rise of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere around 2.5 billion years ago by examining other ancient rock sequences in Canada, Australia, and South Africa. A better understanding of the ancient strength and variability of Earth’s magnetic field will help us to determine whether planetary magnetic fields are critical for hosting life on a planetary surface and their role in atmospheric evolution.
Notes to editors:
For media enquiries and interview requests, contact Dr Charlie Rex: charlie.rex@earth.ox.ac.uk
The study ‘Possible Eoarchean records of the geomagnetic field preserved in the Isua Supracrustal Belt, southern west Greenland’ will be published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth at 14:00 BST / 09:00 ET Wednesday 24 April at https://doi.org/10.1029/2023JB027706. To view a copy of the paper before this under embargo, contact Dr Charlie Rex: charlie.rex@earth.ox.ac.uk
Images relating to the study that can be used to illustrate articles are available with figure captions: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1alvO0QLhVxEbIWJHOO3K60H2sDq3aii7/edit?usp=sharing&ouid=105232552213541807800&rtpof=true&sd=true Original photos can be downloaded here: https://photos.app.goo.gl/3kY56LtUzoRn9e1v6 These are for editorial purposes only and must be credited. They must NOT be sold on to third parties.
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the eighth year running, and number 3 in the QS World Rankings 2024. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and teaching excellence and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 300 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past five years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
END
Researchers find oldest undisputed evidence of Earth’s magnetic field
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Eric and Wendy Schmidt announce 2024 Schmidt Science Fellows
2024-04-24
Eric and Wendy Schmidt Announce 2024 Schmidt Science Fellows
32 exceptional early career researchers will tackle ambitious interdisciplinary science projects
The seventh cohort of the interdisciplinary program, an initiative of Schmidt Sciences, will advance research in areas ranging from healthcare and the environment to advanced materials and robotics
The 2024 Fellows, representing 17 nationalities from 26 nominating institutions across North America, Europe, and Asia, will also benefit from bespoke ...
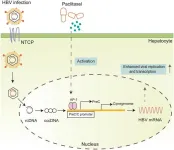
Paclitaxel-induced immune dysfunction and activation of transcription factor AP-1 facilitate Hepatitis B virus replication
2024-04-24
Background and Aims
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation is commonly observed in individuals with chronic HBV infection undergoing antineoplastic drug therapy. Paclitaxel (PTX) treatment has been identified as a potential trigger for HBV reactivation. This study aimed to uncover the mechanisms of PTX-induced HBV reactivation in vitro and in vivo, which may inform new strategies for HBV antiviral treatment.
Methods
The impact of PTX on HBV replication was assessed through various methods including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, dual-luciferase reporter assay, quantitative ...
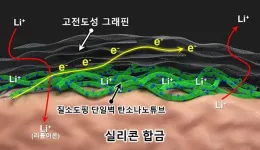
Single-walled carbon nanotubes doped with ‘nitrogen’ enhance the performance of secondary battery anode
2024-04-24
Dr. Han Joong Tark and student researcher Lee Do Geun at the Nano Hybrid Technology Research Center of Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute(KERI) have developed a new manufacturing technique for "silicon/nitrogen-doped carbon composite anode materials." These materials aim to enhance the capacity and stability of lithium-ion battery anodes.
Silicon, despite offering significantly higher energy density compared to graphite (a common anode material), suffers from a major drawback: it expands 3-4 times during charging and discharging, leading to performance degradation. To address this issue, researchers are blending ...
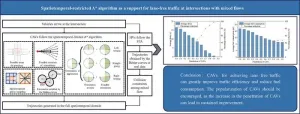
Pioneering the future of urban traffic: The revolutionary spatiotemporal-restricted a* algorithm
2024-04-24
As urban areas continue to grow, the demand for innovative solutions to alleviate traffic congestion and improve transportation efficiency has never been more urgent. A recent breakthrough study presented by researchers from the Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory as well as international research team introduces a cutting-edge approach to managing traffic at urban intersections using the spatiotemporal-restricted A* algorithm. This advanced method promises to transform how traffic is handled by optimizing the flow of both connected automated vehicles (CAVs) and human-driven vehicles (HVs) ...
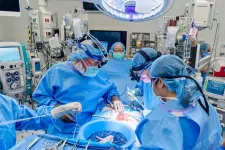
First-ever combined heart pump and pig kidney transplant gives new hope to patient with terminal illness
2024-04-24
NEW YORK, NY, APRIL 24, 2024— Surgeons at NYU Langone Health performed the first-ever combined mechanical heart pump and gene-edited pig kidney transplant surgery in a 54-year-old woman with heart and kidney failure—a confluence of advances that showcase the possibility and hope of modern medicine.
Doctors performed this feat in two stages: first surgically implanting the heart pump days before embarking on the landmark transplant, which included a gene-edited pig kidney and the pig’s thymus gland to aid against rejection. Before the procedure, patient Lisa Pisano, a New Jersey ...
FAU receives grant to examine role of pet dogs on military adolescents
2024-04-24
Florida Atlantic University Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing’s Canines Providing Assistance to Wounded Warriors (C-P.A.W.W.) has received a new grant from the Human Animal Bond Research Institute (HABRI) for research that investigates the contribution of pet dog ownership to resilience and well-being in adolescent children of military families.
The grant was awarded to a team of researchers led by Laurie Martinez, Ph.D., an assistant professor, FAU College of Nursing; and co-led by Cheryl A. Krause-Parello, Ph.D., associate vice president for research, FAU Division of Research and a research professor in the College of Nursing.
This important study will provide ...
COVID-19 pandemic alters view that doctors are obligated to provide care
2024-04-24
DURHAM, N.C. – The unique circumstances arising from the COVID-19 pandemic altered a long-held convention that doctors provide care regardless of personal risk.
In a study assessing doctors’ tolerance for refusing care to COVID-19 patients, Duke Health researchers identified a growing acceptance to withhold care because of safety concerns.
“All the papers throughout history have shown that physicians broadly believed they should treat infectious disease patients,” said the study’s lead author, Braylee Grisel, a fourth-year student at Duke University ...
This salt battery harvests osmotic energy where the river meets the sea
2024-04-24
Estuaries — where freshwater rivers meet the salty sea — are great locations for birdwatching and kayaking. In these areas, waters containing different salt concentrations mix and may be sources of sustainable, “blue” osmotic energy. Researchers in ACS Energy Letters report creating a semipermeable membrane that harvests osmotic energy from salt gradients and converts it to electricity. The new design had an output power density more than two times higher than commercial membranes in lab demonstrations.
Osmotic energy can be generated anywhere salt gradients are ...
On the trail of deepfakes, Drexel researchers identify ‘fingerprints’ of AI-generated video
2024-04-24
In February, OpenAI released videos created by its generative artificial intelligence program Sora. The strikingly realistic content, produced via simple text prompts, is the latest breakthrough for companies demonstrating the capabilities of AI technology. It also raised concerns about generative AI’s potential to enable the creation of misleading and deceiving content on a massive scale. According to new research from Drexel University, current methods for detecting manipulated digital media will not be effective against AI-generated video; but a machine-learning approach could be the key to unmasking these synthetic creations.
In a paper accepted ...
Virtual reality can motivate people to donate to refugee crises regardless of politics
2024-04-24
PULLMAN, Wash. – Political conservatives who watched a documentary on Syrian refugees with a virtual reality headset had far more sympathy for the people depicted in the film than those who viewed the same film on a two-dimensional computer screen.
Higher sympathy levels among the conservatives who watched the VR version of the documentary, “Clouds over Sidra,” resulted in a greater willingness to donate to the crisis, according to a study on the research published in New Media & Society.
Liberal participants in the study reported high levels of sympathy and ...