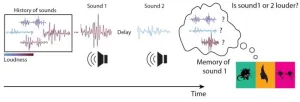
(Press-News.org) Neuroscientists have revealed that recency bias in working memory naturally leads to central tendency bias, the phenomenon where people’s (and animals’) judgements are biased towards the average of previous observations. Their findings may hint at why the phenomenon is so ubiquitous.
Researchers in the Akrami Lab at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at UCL and the Clopath Lab at Imperial College London developed a network model with a working memory module and another accounting for sensory histories. The study, published in eLife, describes how the model shows neural circuits can give rise to both recency and central tendency biases at the same time through a single mechanism.
“Psychologists first observed the central tendency bias over a century ago, but it was assumed to be a separate phenomenon to recency. Our results imply that these two biases are more related than previously thought,” said Vezha Boboeva, Senior Research Fellow at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre and first author on the paper.
Central tendency bias, also known as contraction bias, is a ubiquitous phenomenon. Imagine you are shown a bar of a given length and asked to reproduce that same bar, recalled from your memory. What we tend to do is to misremember the length, based on the bar's size, recalling longer bars as shorter and shorter bars as longer. Therefore, we judge the length of the bar as closer to the mean of the range than it is in reality. The phenomenon also occurs in other animals, including non-human primates and rodents, and happens with other modalities too, such as sound amplitudes and frequencies. This bias is believed to be a brain strategy for processing the statistical patterns of sensory information, formulated through Bayesian computation.
Recency bias, also known as short-term history bias, occurs when you fail to remember a given stimulus because the memory from the previous stimulus is still lingering in your mind.
To understand the neural processes that underpin both central tendency and recency biases, neuroscientists at SWC and Imperial College London studied the phenomena in a neural network model, highly inspired by prior results from rodents and human working memory experiments.
“My previous postdoctoral research showed that deactivating the posterior parietal cortex (PPC) attenuated contraction bias in rats performing a working memory task. We also saw that biases due to lingering memories of previous trials were reduced when PPC was deactivated, suggesting that these two mechanisms may be linked to each other,” explained Athena Akrami, Group Leader at SWC and corresponding author on the paper.
Building on this research, Boboeva and team developed a network model that replicated the previous experimental findings. In the model, short-term history effects occur due to inputs from the PPC that has a slower integration timescale as well as firing rate adaptation.
“The model shows that once you make working memory errors because of such lingering memories, contraction bias emerges naturally, without the need to make any other assumption about the average of the sensory history,” explained Boboeva.
Importantly, this new unifying model made specific predictions on how sensory statistics affect performance. The researchers used online tools to test and verify these predictions by running psychophysics experiments with human participants. The next steps are to test the model predictions about the neural dynamics by reanalysing the existing datasets and collecting new neural datal.
This research was funded by BBSRC BB/N013956/1, BB/N019008/1, Wellcome Trust 200790/Z/16/Z, Simons Foundation 564408, EPSRC EP/R035806/1, Gatsby Charitable Foundation GAT3755 and Wellcome Trust 219627/Z/19/Z.
Source:
Read the full paper in eLife: ‘Unifying Network Model Links Recency and Central Tendency Biases in Working Memory’ DOI: 10.7554/eLife.86725.3
Read the eLife Digest: ‘Recollection errors’
Media contact:
For more information or to speak to the researchers involved, please contact:
April Cashin-Garbutt
Head of Research Communications and Engagement, Sainsbury Wellcome Centre
E: a.cashin-garbutt@ucl.ac.uk T: +44 (0)20 3108 8028
About the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre
The Sainsbury Wellcome Centre (SWC) brings together world-leading neuroscientists to generate theories about how neural circuits in the brain give rise to the fundamental processes underpinning behaviour, including perception, cognition, decisions, learning and planning. Funded by the Gatsby Charitable Foundation and Wellcome, SWC is located within UCL and is closely associated with the Faculties of Life Sciences and Brain Sciences.
END
Network model unifies recency and central tendency biases
Researchers uncover interrelation between short-term history and contraction bias
2024-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ludwig Lausanne scientists identify and show how to target a key tumor defense against immune attack
2024-04-24
April 24, 2024, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has discovered how a lipid molecule found at high levels within tumors undermines the anti-cancer immune response and compromises a recently approved immunotherapy known as adoptive cell therapy (ACT) using tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, or TIL-ACT. In this individualized cell therapy, TILs—CD8+ T cells that kill cancer cells—are expanded in culture from a patient’s tumor samples and reinfused into the patient as a treatment.
Researchers led by Ludwig Lausanne’s Matteo ...
Can climate change accelerate transmission of malaria? Pioneering research sheds light on impacts of temperature
2024-04-24
In 2022, an estimated 249 million malaria cases killed 608,000 people in 85 countries worldwide including the United States, according to the World Health Organization.
Malaria continues to pose a considerable public health risk in tropical and subtropical areas, where it impacts human health and economic progress.
Despite concerns about the potential impact of climate change on increasing malaria risk, there is still limited understanding of how temperature affects malaria transmission – until now.
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite that spreads from bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. If left untreated in humans, malaria can cause severe symptoms, ...
A new attempt to identify salt gland development and salt resistance genes of Limonium bicolor ——Identification of bHLH gene family and its function analysis in salt gland development
2024-04-24
The secondary salinization of saline-alkali land is increasing globally. It is of strategic significance to explore the salt-tolerant molecular mechanism of halophytes and cultivate saline-alkali resistant crops for the improvement of saline-alkali land. The recretohalophyte Limonium bicolor has a unique salt-secreting structure, salt gland, which can directly excrete Na+ out of the body to effectively avoid salt stress. Exploring the development mechanism of salt gland structure in recretohalophyte is of great significance for analyzing the development of plant epidermis structure and improving the salt-resistant mechanism of plants.
Recently, Wang ...
The SAPIENS Podcast named finalist at the 16th Annual Shorty Awards
2024-04-24
SAPIENS: A Podcast for Everything Human has been named as a 16th Annual Shorty Awards finalist in the Science and Technology Podcast Category.
The Shorty Awards honor the best work in digital and social media by the most creative and influential brands, agencies, organizations, and individuals whose work has excelled in creativity, strategy, and effectiveness.
SAPIENS’s work has demonstrated outstanding performance across the judging criteria, which makes it a top contender for a Shorty Award in a most competitive year. The work is also eligible for ...
Startup financing gender gaps greater in societies where women are more empowered
2024-04-24
Commercial bankers provide capital to fund the operations and growth of businesses. However, as these lenders evaluate entrepreneurs who apply for loans, gender bias leads to women being denied more often than their male counterparts.
Estimates show a $1.7 trillion financing gap worldwide for small- and medium-sized enterprises owned by women.
Studies show that when women do secure business loans, the amounts tend to be smaller, have higher interest rates and require more collateral, which restricts the economic potential of women-led ventures. However, findings ...
Postpartum depression after adolescent stress shows a dysregulated HPA axis: a cross-species translational study
2024-04-24
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Adverse life events are a known and predominant risk factor for postpartum depression in women after delivery of their baby. Furthermore, the postpartum depression in women who have experienced adverse life events tends to be refractory to treatment.
In a study using a mouse model and human subjects, researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Johns Hopkins Medicine show that stress from adolescent social isolation in mice elicits a prolonged elevation of corticosterone levels and glucocorticoid signaling, which in turn results ...
When studies conflict: building a decision-support system for clinicians
2024-04-24
One day you hear that red wine is good for your heart. The next day, it’s not. The same goes for chocolate. And coffee. The see-saw of contradicting information isn’t anything new, but what happens when clinicians hear conflicting studies about a medication they use for their patients? Researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania are hoping to use, among other methods, a variety of artificial intelligence to help sort that out.
Ellen Caniglia, ScD, an assistant professor of Epidemiology and Enrique Schisterman, PhD, a professor and the chair of the Department of Biostatistics, Epidemiology, and Informatics (DBEI), ...
Artificial sweetener has potential to damage gut
2024-04-24
New research has discovered that neotame, one of the new generation of artificial sweeteners, is capable of damaging the human intestine and causing illness.
The study is the first to show that neotame can cause previously healthy gut bacteria to become diseased and invade the gut wall – potentially leading to health issues including irritable bowel syndrome and sepsis – and also cause a breakdown of the epithelial barrier, which forms part of the gut wall.
The research, which is published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition and was carried out at Anglia Ruskin ...
Gene-based therapy restores cellular development and function in brain cells from people with Timothy syndrome
2024-04-24
In a proof-of-concept study, researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of a potential new therapy for Timothy syndrome, an often life-threatening and rare genetic disorder that affects a wide range of bodily systems, leading to severe cardiac, neurological, and psychiatric symptoms as well as physical differences such as webbed fingers and toes. The treatment restored typical cellular function in 3D structures created from cells of people with Timothy syndrome, known as organoids, which can mimic the function of cells ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for April 24, 2024
2024-04-24
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments at MD Anderson offer insights into a novel targeted therapy for rare cancers, the role of enhancer RNAs in cell differentiation, novel biomarkers for the prognosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer, imaging signatures to stratify ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Network model unifies recency and central tendency biasesResearchers uncover interrelation between short-term history and contraction bias