(Press-News.org) Are mice clever enough to be strategic?
Kishore Kuchibhotla, a Johns Hopkins University neuroscientist who studies learning in humans and animals, and who has long worked with mice, wondered why rodents often performed poorly in tests when they knew how to perform well. With a simple experiment, and by acting as “a little bit of a mouse psychologist,” he and his team figured it out.
“It appears that a big part of this gap between knowledge and performance is that the animal is engaging in a form of exploration—what the animal is doing is very clever,” he said. “It’s hard to say animals are making hypotheses, but our view is that animals, like humans, can make hypotheses and they can test them and may use higher cognitive processes to do it.”
The work, which deepens our understanding of animal cognition, and could lead to identifying the neural basis for strategizing, published today in Current Biology.
Kuchibhotla’s lab previously found that animals know a lot more about tasks than they demonstrate in tests. The team had two theories about what could be behind this gap. Either the mice were making mistakes because they were stressed, or they were doing something more purposeful: exploring and testing their knowledge.
To figure it out Kuchibhotla and Ziyi Zhu, a graduate student studying neuroscience, came up with a new experiment.
Mice heard two sounds. For one sound they were supposed to turn a wheel to the left. For the other sound, they’d turn the wheel to the right. When the mice performed correctly they were rewarded.
The researchers observed how upon hearing either sound over consecutive trials, the mice would turn the wheel left for a bit, then switch to turning it right, seemingly making mistakes but actually being purposeful.
“We find that when the animal is exploring, they engage in a really simple strategy, which is, ‘I’m going to go left for a while, figure things out, and then I’m going to switch and go right for a while,’” Kuchibhotla said. “Mice are more strategic than some might believe.”
Zhu added, “Errors during animal learning are often considered as mistakes. Our work brings new insight that not all errors are the same.”
The team learned even more about the rodents’ actions by taking the reward out of the equation.
When a mouse performed correctly and wasn’t rewarded, it immediately doubled down on the correct response when retested.
“If the animal has an internal model of the task, the lack of reward should violate its expectation. And if that’s the case, it should affect the behavior on subsequent trials. And that’s exactly what we found. On subsequent trials the animal just does a lot better,” Kuchibhotla said. “The animal is like, ‘Hey, I was expecting to be rewarded, I wasn’t, so let me test my knowledge, let me use the knowledge I have and see if it’s correct.’”
If the animal didn’t have an internal model of the task, there would be no expectations to violate and the mice would keep performing poorly.
“At a very early time in learning the animal has an expectation and when we violate it, it changes its strategy,” Kuchibhotla said. “It was surprisingly strategic.”
This mouse strategizing is comparable to how nonverbal human babies learn. Both are highly exploratory and both may test hypotheses in various ways, Kuchibhotla said.
During the experiments Kuchibhotla said he became “a little bit of a mouse psychologist” to interpret their behavior. Like working with a nonverbal infant, he and Zhu had to infer the underlying mental processes from the behavior alone.
“That’s what was really fun in this project, trying to figure out what the mouse is thinking,” he said. “You have to think about it from the perspective of the animal.”
Next the team hopes to determine the neural basis for strategic thinking, and how those strategies might compare across different animals.
END
Test reveals mice think like babies
‘Surprisingly strategic’ behavior deepens our understanding of animal cognition
2024-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
From disorder to order: flocking birds and “spinning” particles
2024-04-26
Researchers Kazuaki Takasan and Kyogo Kawaguchi of the University of Tokyo with Kyosuke Adachi of RIKEN, Japan's largest comprehensive research institution, have demonstrated that ferromagnetism, an ordered state of atoms, can be induced by increasing particle motility and that repulsive forces between atoms are sufficient to maintain it. The discovery not only extends the concept of active matter to quantum systems but also contributes to the development of novel technologies that rely on the magnetic ...
Cardiovascular risk associated with social determinants of health at individual and area levels
2024-04-26
About The Study: The findings of this study of 26,000 participants from four large U.S. studies suggest that both individual- and area-level social determinants of health may be considered in future development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment tools, particularly among Black individuals.
Authors: Yiyi Zhang, Ph.D., of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8584)
Editor’s ...
Experimental NIH malaria monoclonal antibody protective in Malian children
2024-04-26
One injected dose of an experimental malaria monoclonal antibody was 77% effective against malaria disease in children in Mali during the country’s six-month malaria season, according to the results of a mid-stage clinical trial. The trial assessed an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and results appear in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“A long-acting monoclonal antibody delivered at a single health care visit that rapidly provides high-level protection against malaria in these vulnerable populations would fulfill an unmet public health need,” said Dr. Jeanne ...
Energy trades could help resolve Nile conflict
2024-04-26
Scientists have shed light on a new, transformative approach that could help resolve a dispute over the Nile river’s water resources.
The Nile is one of the longest rivers globally and spreads over 11 countries in East Africa, supplying water, energy production, environmental quality and cultural wealth. However, the use of Nile resources has been a long-standing source of tension, often overshadowing opportunities for cooperation and mutual benefit.
But as the demand for energy, water, and food in Africa is steadily increasing, the study, led by The University of Manchester in collaboration with regional organisations, offers a glimmer of hope at a resolution.
The research, ...
Homelessness a major issue for many patients in the emergency department
2024-04-26
Housing insecurity is an issue for 1 in 20 patients who go to emergency departments at major medical centers in the Southeast, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
These patients were more likely to present with a chief complaint of suicide, to be uninsured, and to have multiple visits during the study period from Jan. 5 to May 16, 2023.
“This points to the importance of prioritizing mental health care and homeless ...
Undocumented Latinx patients got COVID-19 vaccine at same rate as US citizens
2024-04-26
For undocumented Latinx patients who sought care in the emergency room during the pandemic, the reported rate of having received the COVID-19 vaccine was found to be the same as U.S. citizens, a new UCLA Health study found. These findings surprised researchers, given that COVID-19 disproportionately affected the Latinx community in infections, hospitalizations, and death.
Dr. Jesus R. Torres, lead study author and emergency medicine physician at UCLA Health, aimed to study undocumented people because they tend not to be identified in existing research even though they comprise approximately 3% of the ...
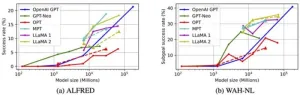
ETRI develops an automated benchmark for labguage-based task planners
2024-04-26
If instructed to “Place a cooled apple into the microwave,” how would a robot respond?
Initially, the robot would need to locate an apple, pick it up, find the refrigerator, open its door, and place the apple inside. Subsequently, it would close the refrigerator door, reopen it to retrieve the cooled apple, pick up the apple again, and close the door. Following this, the robot would need to locate the microwave, open its door, place the apple inside, and then close the microwave door. Evaluating how well these steps are executed exemplifies the essence of ...
Revolutionizing memory technology: multiferroic nanodots for low-power magnetic storage
2024-04-26
Traditional memory devices are volatile and the current non-volatile ones rely on either ferromagnetic or ferroelectric materials for data storage. In ferromagnetic devices, data is written or stored by aligning magnetic moments, while in ferroelectric devices, data storage relies on the alignment of electric dipoles. However, generating and manipulating magnetic fields is energy-intensive, and in ferroelectric memory devices, reading data destroys the polarized state, requiring the memory cell to be re-writing.
Multiferroic materials, which contain both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic orders, offer a promising solution for more efficient ...
Researchers propose groundbreaking framework for future network systems
2024-04-26
In a new study published in Engineering, Academician Wu Jiangxing’s research team unveils a theoretical framework that could revolutionize the landscape of network systems and architectures. The paper titled “Theoretical Framework for a Polymorphic Network Environment,” addresses a fundamental challenge in network design—achieving global scalability while accommodating the diverse needs of evolving services.
For decades, the quest for an ideal network capable of seamlessly scaling across various dimensions has remained elusive. The team, however, has identified a critical barrier known as the “impossible service-level ...
New favorite—smart electric wheel drive tractor: realizes efficient drive with ingenious structure and intelligent control
2024-04-26
Electric tractors are intended to be used in the field instead of traditional fuel tractors and can be used in greenhouse planting, indoor farming, mountainous operations, and other special operating scenarios. Unlike traditional fuel tractors, electric tractors have no exhaust emissions, rapid drive system response, flexible power output, or other advantages. These scenarios require electric tractors to be able to adapt to complex drive and operating environments, putting higher requirements on the design of electric tractors and their control systems. Therefore, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Test reveals mice think like babies‘Surprisingly strategic’ behavior deepens our understanding of animal cognition