(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – A blood test successfully predicted knee osteoarthritis at least eight years before tell-tale signs of the disease appeared on x-rays, Duke Health researchers report.
In a study appearing April 26 in the journal Science Advances, the researchers validated the accuracy of the blood test that identifies key biomarkers of osteoarthritis. They showed that it predicted development of the disease, as well as its progression, which was demonstrated in their earlier work.
The research advances the utility of a blood test that would be superior to current diagnostic tools that often don’t identify the disease until it has caused structural damage to the joint.
“Currently, you’ve got to have an abnormal x-ray to show clear evidence of knee osteoarthritis, and by the time it shows up on x-ray, your disease has been progressing for some time,” said senior author Virginia Byers Kraus, M.D., Ph.D., a professor in the departments of Medicine, Pathology, and Orthopedic Surgery at Duke University School of Medicine. “What our blood test demonstrates is that it’s possible to detect this disease much earlier than our current diagnostics permit.”
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, afflicting an estimated 35 million adults in the U.S. and causing significant economic and societal impacts. While there are currently no cures, the success of potential new therapies could hinge on identifying the disease early and slowing its progression before it becomes debilitating.
Kraus and colleagues have focused on developing molecular biomarkers that can be used for both clinical diagnostic purposes and as a research tool to aid in the development of effective drugs. In previous studies, the blood biomarker test demonstrated 74% accuracy in predicting knee OA progression and 85% accuracy in diagnosing knee OA.
The current study further honed the test’s predictive capabilities. Using a large United Kingdom database, the researchers analyzed serum of 200 white women, half diagnosed with OA and the other half without the disease, matched by body mass index and age.
They found that a small number of biomarkers in the blood test successfully distinguished the women with knee OA from those without it, catching molecular signals of OA eight years before many of the women were diagnosed with the disease by x-ray.
“This is important because it provides more evidence that there are abnormalities in the joint that can be detected by blood biomarkers well before x-rays can detect OA,” Kraus said. “Early-stage osteoarthritis could provide a ‘window of opportunity’ in which to arrest the disease process and restore joint health.”
In addition to Kraus, study authors include Shuming Sun, Alexander Reed, Erik J. Soderblom, M Arthur Moseley, Kaile Zhou, Vaibhav Jain, Nigel Arden, and Yi-Ju Li.
The study received funding support from National Institutes of Health (R01-AR071450 and P30-AG028716).
END
Blood test finds knee osteoarthritis up to eight years before it appears on x-rays
Early detection could lead to therapies that slow progression and restore joint health
2024-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
April research news from the Ecological Society of America
2024-04-26
The Ecological Society of America (ESA) presents a roundup of four research articles recently published across its six esteemed journals. Widely recognized for fostering innovation and advancing ecological knowledge, ESA’s journals consistently feature illuminating and impactful studies. This compilation of papers explores fire hazards in Mediterranean cork oak woodlands, putting theory to work predicting where cold-blooded organisms will occur under climate change, barriers to going high-tech in rangeland management and more, showcasing the Society’s commitment to promoting cutting-edge research that furthers our understanding of the natural world.
From Ecological ...
Antimicrobial resistance crisis: “Antibiotics are not magic bullets”
2024-04-26
Dr James Gill, a Clinical Lecturer at the University of Warwick and a practising GP, will attend a pivotal event hosted at the House of Lords on Monday (April 29) focused on combating the global crisis of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Antimicrobial resistance poses a formidable threat to communities worldwide, with projections indicating that by 2050, over 10 million deaths annually could be attributed to AMR, surpassing even the toll of cancer. In the face of this escalating emergency, effective communication is paramount. Health professionals and organisations play a crucial role in disseminating accurate, accessible information to raise awareness about critical ...
Florida dolphin found with highly pathogenic avian flu: Report
2024-04-26
The case of a Florida bottlenose dolphin found with highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, or HPAIV — a discovery made by University of Florida researchers in collaboration with multiple other agencies and one of the first reports of a constantly growing list of mammals affected by this virus — has been published in Communications Biology.
The report documents the discovery, the first finding of HPAIV in a cetacean in North America, from the initial response by UF’s Marine Animal Rescue team to a report of a distressed dolphin in Dixie County, Florida, to the subsequent identification of the virus from brain and tissue samples obtained in a postmortem ...
Barcodes expand range of high-resolution sensor
2024-04-26
The same geometric quirk that lets visitors murmur messages around the circular dome of the whispering gallery at St. Paul’s Cathedral in London or across St. Louis Union Station’s whispering arch also enables the construction of high-resolution optical sensors. Whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) resonators have been used for decades to detect chemical signatures, DNA strands and even single molecules.
In the same way that the architecture of a whispering gallery bends and focuses sound waves, WGM microresonators confine and concentrate light in a tiny circular path. This enables WGM resonators ...
DOE Under Secretary for Science and Innovation visits Jefferson Lab
2024-04-26
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – On April 18, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility welcomed Under Secretary for Science and Innovation Geraldine (Geri) Richmond for a tour of the lab and briefing on its research mission, innovation and STEM programs.
Throughout the day, much of the conversation centered on a common theme of how the lab is working to ensure it is a hub of engagement, partnership, and access for researchers, students, community leaders and others. Ensuring diverse communities have access to the programs, ...
Research expo highlights student and faculty creativity
2024-04-26
Hundreds of faculty, students and business leaders flocked to The University of Texas at Arlington for its second annual Research and Innovation Expo, an event designed to showcase the University’s research efforts.
“This is an event where we can showcase our research achievements and encourage everyone to learn about and engage with other investigators outside their own fields,” said Eileen Clements, interim executive director of the UT Arlington Research Institute and an organizer of the event.
Researchers learned how ...
Imaging technique shows new details of peptide structures
2024-04-26
By Leah Shaffer
A new imaging technique developed by engineers at Washington University in St. Louis can give scientists a much closer look at fibril assemblies, stacks of peptides like amyloid beta, most notably associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
These cross-β fibril assemblies are also useful building blocks within designer biomaterials for medical applications, but their resemblance to their amyloid beta cousins, whose tangles are a symptom of neurodegenerative disease, is concerning. Researchers want ...
MD Anderson and RUSH unveil RUSH MD Anderson Cancer Center
2024-04-26
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and RUSH University System for Health today announced a partnership to create RUSH MD Anderson Cancer Center. The partnership represents advanced clinical and operational integration in the delivery of cancer care, providing RUSH patients greater access to cancer treatments and research considered among the best in the world.
MD Anderson is one of the nation’s leading cancer centers and its team of experts is devoted exclusively to cancer patient care, research, education ...
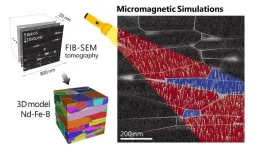
Tomography-based digital twins of Nd-Fe-b magnets
2024-04-26
1. NIMS has succeeded in simulating the magnetization reversal of Nd-Fe-B magnets using large-scale finite element models constructed based on tomographic data obtained by electron microscopy. Such simulations have shed light on microstructural features that hinder the coercivity, which quantifies a magnet’s resistance to demagnetization in opposing magnetic fields. New tomography-based models are expected to guide toward the development of sustainable permanent magnets with ultimate performance.
2. Green power generation, electric transportation, and other high-tech industries rely heavily on ...
People with rare longevity mutation may also be protected from cardiovascular disease
2024-04-26
A new study highlights possible cardiovascular health advantages in individuals with a rare condition known as growth hormone receptor deficiency (GHRD), also called Laron syndrome.
GHRD, which is characterized by the body’s impaired ability to use its own growth hormone and results in stunted growth, has been linked in mice to a record 40% longevity extension and lower risks for various age-related diseases. However, the risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with GHRD has remained ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] Blood test finds knee osteoarthritis up to eight years before it appears on x-raysEarly detection could lead to therapies that slow progression and restore joint health