(Press-News.org) By Leah Shaffer
A new imaging technique developed by engineers at Washington University in St. Louis can give scientists a much closer look at fibril assemblies, stacks of peptides like amyloid beta, most notably associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
These cross-β fibril assemblies are also useful building blocks within designer biomaterials for medical applications, but their resemblance to their amyloid beta cousins, whose tangles are a symptom of neurodegenerative disease, is concerning. Researchers want to learn how different sequences of these peptides are linked to their varying toxicity and function, for both naturally occurring peptides and their synthetic engineered cousins.
Now, scientists can get a close enough look at fibril assemblies to see there are notable differences in how synthetic peptides stack compared with amyloid beta. These results stem from a fruitful collaboration between lead author Matthew Lew, associate professor in the Preston M. Green Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering, and Jai Rudra, associate professor of biomedical engineering, in WashU's McKelvey School of Engineering.
“We engineer microscopes to enable better nanoscale measurements so that the science can move forward,” Lew said.
In a paper published in ACS Nano, Lew and colleagues outline how they used the Nile red chemical probe to light up cross-β fibrils. Their technique called single-molecule orientation–localization microscopy (SMOLM) uses the flashes of light from Nile red to visualize the fiber structures formed by synthetic peptides and by amyloid beta.
The bottom line: these assemblies are much more complicated and heterogenous than anticipated. But that’s good news, because it means there’s more than one way to safely stack your proteins. With better measurements and images of fibril assemblies, bioengineers can better understand the rules that dictate how protein grammar affects toxicity and biological function, leading to more effective and less toxic therapeutics.
First, scientists need to see the difference between them, something very challenging because of the tiny scale of these assemblies.
“The helical twist of these fibers is impossible to discern using an optical microscope, or even some super-resolution microscopes, because these things are just too small,” Lew said.
With high-dimensional imaging technology developed in Lew’s lab the past couple years, they are able to see the differences.
A typical fluorescence microscope uses florescent molecules as light bulbs to highlight certain aspects of a biological target. In the case of this work, they used one of those probes, Nile red, as a sensor for what was around it. As Nile red randomly explores its environment and collides with the fibrils, it emits flashes of light that they can measure to determine where the fluorescent probe is and its orientation. From that data, they can piece together the full picture of engineered fibrils that stack very differently from the natural ones like amyloid beta.
Their image of these fibril assemblies made the cover of the ACS Nano and was put together by first author Weiyan Zhou, who color-coded the image based on where the Nile reds were pointing. The resulting image is a blueish, red flowing assembly of peptides that looks like a river valley.
They plan to continue to develop techniques like SMOLM to open new avenues of studying biological structures and processes at the nanoscale.
“We are seeing things you can’t see with existing technology,” Lew said.
Weiyan Zhou, Conor L O’Neill, Tianben Ding, Oumeng Zhang, Jai S Rudra, and Matthew D Lew. Resolving the Nanoscale Structure of β-Sheet Peptide Self-Assemblies Using Single-Molecule Orientation–Localization Microscopy. ACS Nano 2024 18 (12), 8798-8810
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c11771
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under award number 2047517 to J.S.R. and by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under grant number R35GM124858 to M.D.L.
END
Imaging technique shows new details of peptide structures
2024-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson and RUSH unveil RUSH MD Anderson Cancer Center
2024-04-26
The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and RUSH University System for Health today announced a partnership to create RUSH MD Anderson Cancer Center. The partnership represents advanced clinical and operational integration in the delivery of cancer care, providing RUSH patients greater access to cancer treatments and research considered among the best in the world.
MD Anderson is one of the nation’s leading cancer centers and its team of experts is devoted exclusively to cancer patient care, research, education ...
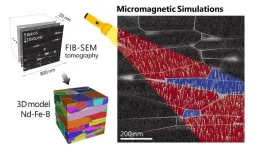
Tomography-based digital twins of Nd-Fe-b magnets
2024-04-26
1. NIMS has succeeded in simulating the magnetization reversal of Nd-Fe-B magnets using large-scale finite element models constructed based on tomographic data obtained by electron microscopy. Such simulations have shed light on microstructural features that hinder the coercivity, which quantifies a magnet’s resistance to demagnetization in opposing magnetic fields. New tomography-based models are expected to guide toward the development of sustainable permanent magnets with ultimate performance.
2. Green power generation, electric transportation, and other high-tech industries rely heavily on ...
People with rare longevity mutation may also be protected from cardiovascular disease
2024-04-26
A new study highlights possible cardiovascular health advantages in individuals with a rare condition known as growth hormone receptor deficiency (GHRD), also called Laron syndrome.
GHRD, which is characterized by the body’s impaired ability to use its own growth hormone and results in stunted growth, has been linked in mice to a record 40% longevity extension and lower risks for various age-related diseases. However, the risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with GHRD has remained ...
Mobile device location data is already used by private companies, so why not for studying human-wildlife interactions, scientists ask
2024-04-26
When did you last go anywhere without your cell phone? From maps and weather apps to social media platforms, we give consent for our phones to trace our footsteps and behavior. These curated mobility data are often used for personalized advertisements. In a commentary, published April 26 in the journal Cell Reports Sustainability, scientists argue mobility data can offer so much more—it is key to understanding human-wildlife interactions for guiding policy decisions on sustainability-related issues and should be free and accessible for research.
As ...
Test reveals mice think like babies
2024-04-26
Are mice clever enough to be strategic?
Kishore Kuchibhotla, a Johns Hopkins University neuroscientist who studies learning in humans and animals, and who has long worked with mice, wondered why rodents often performed poorly in tests when they knew how to perform well. With a simple experiment, and by acting as “a little bit of a mouse psychologist,” he and his team figured it out.
“It appears that a big part of this gap between knowledge and performance is that the animal is engaging in a form of ...
From disorder to order: flocking birds and “spinning” particles
2024-04-26
Researchers Kazuaki Takasan and Kyogo Kawaguchi of the University of Tokyo with Kyosuke Adachi of RIKEN, Japan's largest comprehensive research institution, have demonstrated that ferromagnetism, an ordered state of atoms, can be induced by increasing particle motility and that repulsive forces between atoms are sufficient to maintain it. The discovery not only extends the concept of active matter to quantum systems but also contributes to the development of novel technologies that rely on the magnetic ...
Cardiovascular risk associated with social determinants of health at individual and area levels
2024-04-26
About The Study: The findings of this study of 26,000 participants from four large U.S. studies suggest that both individual- and area-level social determinants of health may be considered in future development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment tools, particularly among Black individuals.
Authors: Yiyi Zhang, Ph.D., of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8584)
Editor’s ...
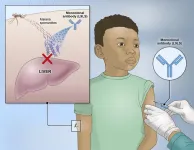
Experimental NIH malaria monoclonal antibody protective in Malian children
2024-04-26
One injected dose of an experimental malaria monoclonal antibody was 77% effective against malaria disease in children in Mali during the country’s six-month malaria season, according to the results of a mid-stage clinical trial. The trial assessed an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and results appear in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“A long-acting monoclonal antibody delivered at a single health care visit that rapidly provides high-level protection against malaria in these vulnerable populations would fulfill an unmet public health need,” said Dr. Jeanne ...
Energy trades could help resolve Nile conflict
2024-04-26
Scientists have shed light on a new, transformative approach that could help resolve a dispute over the Nile river’s water resources.
The Nile is one of the longest rivers globally and spreads over 11 countries in East Africa, supplying water, energy production, environmental quality and cultural wealth. However, the use of Nile resources has been a long-standing source of tension, often overshadowing opportunities for cooperation and mutual benefit.
But as the demand for energy, water, and food in Africa is steadily increasing, the study, led by The University of Manchester in collaboration with regional organisations, offers a glimmer of hope at a resolution.
The research, ...
Homelessness a major issue for many patients in the emergency department
2024-04-26
Housing insecurity is an issue for 1 in 20 patients who go to emergency departments at major medical centers in the Southeast, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
These patients were more likely to present with a chief complaint of suicide, to be uninsured, and to have multiple visits during the study period from Jan. 5 to May 16, 2023.
“This points to the importance of prioritizing mental health care and homeless ...