(Press-News.org) **EMBARGOED BY NATURE GENETICS UNTIL 10AM BST/ 5AM ET/ 3AM MT, APRIL 29**
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its effects on patients and their families can be severe. For most people, the first sign is difficulty walking and balancing, which gets worse as time progresses. The symptoms usually start in a person’s forties or fifties but can begin as early as the late teens. There is no known cure. And, until now, there was no known cause.
Now, after 25 years of uncertainty, a multinational study led by Stefan Pulst, M.D., Dr. med., professor and chair of neurology, and K. Pattie Figueroa, a project manager in neurology, both in the Spencer Fox Eccles School of Medicine at University of Utah, has conclusively identified the genetic difference that causes SCA4, bringing answers to families and opening the door to future treatments. Their results are published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Genetics.
Solving a genetic enigma
SCA4’s pattern of inheritance had long made it clear that the disease was genetic, and previous research had located the gene responsible to a specific region of one chromosome. But that region proved extraordinarily difficult for researchers to analyze: full of repeated segments that look like parts of other chromosomes, and with an unusual chemical makeup that makes most genetic tests fail.
To pinpoint the change that causes SCA4, Figueroa and Pulst, along with the rest of the research team, used a recently developed advanced sequencing technology. By comparing DNA from affected and unaffected people from several Utah families, they found that in SCA4 patients, a section in a gene called ZFHX3 is much longer than it should be, containing an extra-long string of repetitive DNA.
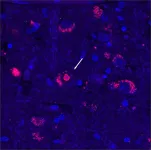
Isolated human cells that have the extra-long version of ZFHX3 show signs of being sick—they don’t seem able to recycle proteins as well as they should, and some of them contain clumps of stuck-together protein.
“This mutation is a toxic expanded repeat and we think that it actually jams up how a cell deals with unfolded or misfolded proteins,” says Pulst, the last author on the study. Healthy cells need to constantly break down non-functional proteins. Using cells from SCA4 patients, the group showed that the SCA4-causing mutation gums up the works of cells’ protein-recycling machinery in a way that could poison nerve cells.
Hope for the future
Intriguingly, something similar seems to be happening in another form of ataxia, SCA2, which also interferes with protein recycling. The researchers are currently testing a potential therapy for SCA2 in clinical trials, and the similarities between the two conditions raise the possibility that the treatment might benefit patients with SCA4 as well.
Finding the genetic change that leads to SCA4 is essential to develop better treatments, Pulst says. “The only step to really improve the life of patients with inherited disease is to find out what the primary cause is. We now can attack the effects of this mutation potentially at multiple levels.”
But while treatments will take a long time to develop, simply knowing the cause of the disease can be incredibly valuable for families affected by SCA4, says Figueroa, the first author on the study. People in affected families can learn whether they have the disease-causing genetic change or not, which can help inform life decisions such as family planning. “They can come and get tested and they can have an answer, for better or for worse,” Figueroa says.
The researchers emphasize that their discoveries would not have been possible without the generosity of SCA4 patients and their families, whose sharing of family records and biological samples allowed them to compare the DNA of affected and unaffected individuals. “Different branches of the family opened up not just their homes but their history to us,” Figueroa says. Family records were complete enough that the researchers were able to trace the origins of the disease in Utah back through history to a pioneer couple who moved to Salt Lake Valley in the 1840s.
Since meeting so many families with the disease, studying SCA4 has become a personal quest, Figueroa adds. “I’ve been working on SCA4 directly since 2010 when the first family approached me, and once you go to their homes and get to know them, they’re no longer the number on the DNA vial. These are people you see every day… You can’t walk away. This is not just science. This is somebody’s life.”
# # #
This research was published in Nature Genetics as “GGC expansion in ZFHX3 causes SCA4 and impairs autophagy.”
This work was performed in collaboration with researchers from University of Tübingen, University of Lübeck and Kiel University, University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf, and Veterans Administration Medical Center, Albany, NY.
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health under award number R35127253 and the DFG-funded INST 37/1049-1.
END
After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
2024-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Probing the effects of interplanetary space on asteroid Ryugu
2024-04-29
Samples reveal evidence of changes experienced by the surface of asteroid Ryugu, some probably due to micrometeoroid bombardment.
Analyzing samples retrieved from the asteroid Ryugu by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft has revealed new insights into the magnetic and physical bombardment environment of interplanetary space. The results of the study, carried out by Professor Yuki Kimura at Hokkaido University and co-workers at 13 other institutions in Japan, are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The investigations used electron waves penetrating ...
T. rex not as smart as previously claimed, scientists find
2024-04-29
Dinosaurs were as smart as reptiles but not as intelligent as monkeys, as former research suggests.
An international team of palaeontologists, behavioural scientists and neurologists have re-examined brain size and structure in dinosaurs and concluded they behaved more like crocodiles and lizards.
In a study published last year, it was claimed that dinosaurs like T. rex had an exceptionally high number of neurons and were substantially more intelligent than assumed. It was claimed that these high neuron counts could directly inform on ...
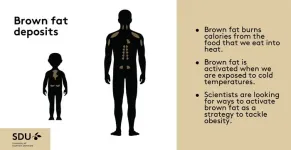
Breakthrough in brown fat research: Researchers from Denmark and Germany have found brown fat’s “off-switch”
2024-04-29
Brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue (BAT), is a type of fat in our bodies that's different from the white fat around our belly and thighs that we are more familiar with. Brown fat has a special job—it helps to burn calories from the foods that we eat into heat, which can be helpful, especially when we're exposed to cold temperatures like during winter swimming or cryotherapy. For a long time, scientists thought that only small animals like mice and newborns had brown fat. But new research shows that a certain number of adults maintain their brown fat throughout life. Because brown fat is so good at burning calories, scientists ...
Tech Extension Co. and Tech Extension Taiwan to build next-generation 3D integration manufacturing lines using Tokyo Tech's BBCube Technology
2024-04-29
Tech Extension Co., Ltd. (referred to hereinafter as TEX)[1] and Tech Extension Taiwan Co., Ltd. (referred to hereinafter as TEX-T)[2] have agreed with Innolux Corporation (referred to hereinafter as INNOLUX)[3] to build in a cleanroom of INNOLUX a manufacturing line intended for next-generation 3D integration[4] based on the Bumpless Build Cube (BBCube[5]), which is a technology achieved through the Tokyo Institute of Technology WOW Alliance[6].
TEX will transfer WOW technology[7] and COW technology[8], which are both based on the BBCube technology platform, to this manufacturing line intended for next-generation 3D integration. ...
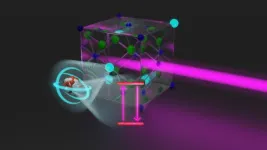
Atomic nucleus excited with laser: a breakthrough after decades
2024-04-29
Physicists have been hoping for this moment for a long time: for many years, scientists all around the world have been searching for a very specific state of thorium atomic nuclei that promises revolutionary technological applications. It could be used, for example, to build an nuclear clock that could measure time more precisely than the best atomic clocks available today. It could also be used to answer completely new fundamental questions in physics - for example, the question of whether the constants of nature are actually constant or whether they change in space ...
Losing keys and everyday items ‘not always sign of poor memory’
2024-04-29
The mysteries of how memory works are explained in a new book that suggests anyone can boost their powers of recall – and that losing your keys is normal.
Dr Megan Sumeracki and Dr Althea Need Kaminske say storing and retrieving information is far more complex than people think. Extremes of memory such as photographic or savant are also very rare despite their regular portrayal in films.
Their new book The Psychology of Memory outlines simple recollection-boosting techniques to improve learning – or to help remember names and numbers.
Forgetting is normal
The authors highlight how a degree ...
People with opioid use disorder less likely to receive palliative care at end of life
2024-04-29
Compared with people without opioid use disorder, those with opioid use disorder were less likely to receive palliative care in clinics and in their homes, and were dying at younger ages of causes other than opioid use, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231419.
“The majority of conversations about the opioid crisis focus on the high number of opioid toxicity deaths. The unfortunate reality is that people with opioid use disorder ...
New Durham University study reveals mystery of decaying exoplanet orbits
2024-04-29
-With images-
A new study led by researchers at Durham University has uncovered a novel mechanism that could solve a long-standing mystery about decaying planetary orbits around stars like our Sun.
The study, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, proposes that stellar magnetic fields play a crucial role in dissipating the gravitational tides responsible for the orbital decay of ‘hot Jupiter’ exoplanets.
Hot Jupiters are massive, gaseous planets similar to Jupiter that orbit extraordinarily close to their parent stars, taking only a few days to complete ...
The threat of polio paralysis may have disappeared, but enterovirus paralysis is just as dangerous and surveillance and testing systems are desperately needed
2024-04-29
Consistently high vaccination rates and global health surveillance programmes have helped eliminate poliomyelitis (polio) in almost all countries of the world, except Afghanistan and Pakistan. Yet non-polio enteroviruses can also lead to the same devastating symptoms of ‘acute flaccid paralysis’ (AFP), but the world is lacking formal surveillance systems to trace and control these viruses with paralytic potential.
In a presentation at this year’s ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) (Barcelona 27-30 April), Prof Thea Kølsen Fischer, Nordsjællands Hospital & University of Copenhagen, Denmark will highlight the continuous dangers that ...
Study shows ChatGPT failed when challenging ESCMID guideline for treating brain abscesses
2024-04-29
With artificial intelligence (AI) poised to become a fundamental part of clinical research and decision making, many still question the accuracy of ChatGPT, a sophisticated AI language model, to support complex diagnostic and treatment processes.
Now a new study, being presented at this year’s ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April), which pitted ChatGPT against the ESCMID guideline for the management of brain abscesses, found that while ChatGPT seems able to give recommendations on key questions about diagnosis and treatment in most cases, some of the AI model’s ...