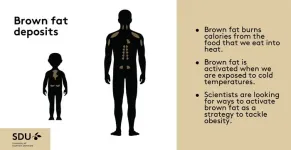
(Press-News.org) Brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue (BAT), is a type of fat in our bodies that's different from the white fat around our belly and thighs that we are more familiar with. Brown fat has a special job—it helps to burn calories from the foods that we eat into heat, which can be helpful, especially when we're exposed to cold temperatures like during winter swimming or cryotherapy. For a long time, scientists thought that only small animals like mice and newborns had brown fat. But new research shows that a certain number of adults maintain their brown fat throughout life. Because brown fat is so good at burning calories, scientists are trying to find ways to activate it safely using drugs that boost its heat-producing abilities.
A new study from the research groups of Prof. Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld from the University of Southern Denmark/the Novo Nordisk Center for Adipocyte Signaling (Adiposign) and Dagmar Wachten from the University Hospital Bonn and the University of Bonn (Germany) has found that brown fat has a previously unknown built-in mechanism that switches it off shortly after being activated. This limits its effectiveness as treatment against obesity. According to first author of the study, Hande Topel, who is a Senior Postdoc at the University of Southern Denmark and the Novo Nordisk Center for Adipocyte Signaling (Adiposign), the team has now discovered a protein responsible for this switching-off process. It is called ‘AC3-AT’.
Blocking the "off switch" opens up a new strategy
“Looking ahead, we think that finding ways to block AC3-AT could be a promising strategy for safely activating brown fat and tackling obesity and related health problems”, Hande Topel says. The research team found the switch-off protein using advanced technology predicting unknown proteins. Hande Topel explains: “When we investigated mice that genetically didn't have AC3-AT, we found that they were protected from becoming obese, partly because their bodies were simply better at burning off calories and were able to increase their metabolic rates through activating brown fat”.
Two groups of mice were fed a high-fat diet for 15 weeks, which rendered them obese. The group that had their AC3-AT protein removed, gained less weight than the control group and were metabolically healthier. “The mice that have no AC3-AT protein, also accumulated less fat in their body and increased their lean mass when compared to the control mice”, says co-author, Ronja Kardinal, who is a PhD student at the University of Bonn in the lab of Dagmar Wachten at UKB, continuing: “As AC3-AT is found not only in mice but also in humans and other species, there are direct therapeutic implications for humans”.
Hope for strategies that support weight loss
Although the prevalence of brown fat decreases as humans age, and despite grown-ups not having as much brown fat as newborns, it can still be activated, for instance by cold exposure. When it gets activated, it enhances the rate of metabolism of these individuals, which again may help to stabilize weight loss in conditions where calorie intake is (too) high.
Intriguingly, this study not only identified AC3-AT, which is a shorter, previously unknown form of the AC3protein. The researchers also identified other unknown protein/gene versions, that respond to cold exposure, similar to AC3-AT.
“However, further research is needed to elucidate the therapeutic impact of these alternative gene products and their regulatory mechanisms during BAT activation”, says co-corresponding author Prof. Dagmar Wachten, Co-Director of the Institute of Innate Immunity at the UKB and member of the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 and the Transdisciplinary Research Areas (TRA) "Modelling" and "Life & Health" at the University of Bonn.
“Understanding these kinds of molecular mechanisms not only sheds light on the regulation of brown fat but also holds promise for unraveling similar mechanisms in other cellular pathways. This knowledge can be instrumental in advancing our understanding of various diseases and in the development of novel treatments”, says co-corresponding author Prof. Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld, University of Southern Denmark.
This study was conducted in the context of the DFG Collaborative Research Center Transregio-SFB 333 "Brown and Beige Fat - Organ Interactions, Signaling Pathways and Energy Balance (BATenergy)", which is pursuing a better understanding of the different types of adipose tissue and their role in metabolic diseases and the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Adipocyte Signaling (Adiposign) at University of Southern Denmark that aims to understand fat cell dysfunction in model organisms and obese patients.
Publication: Sajjad Khani, Hande Topel, Ronja Kardinal et al; Cold-induced expression of a truncated Adenylyl Cyclase 3 acts as rheostat to brown fat function; Nature Metabolism;
DOI: 10.1038/s42255-024-01033-8; https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-024-01033-8
Scientific contact:
Prof. Dagmar Wachten
Institute for Innate Immunity at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB)
Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2, TRA "Modeling" & "Life & Health", University of Bonn
Phone: (+49) 228/ 287-51978; E-Mail: Dagmar.Wachten@ukbonn.de
Prof. Jan-Wilhelm Kornfeld
Center for Adipocyte Signaling (ADIPOSIGN)
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Southern Denmark.
Phone: +45 9350 7481; E-Mail: janwilhelmkornfeld@bmb.sdu.dk
END
Tech Extension Co., Ltd. (referred to hereinafter as TEX)[1] and Tech Extension Taiwan Co., Ltd. (referred to hereinafter as TEX-T)[2] have agreed with Innolux Corporation (referred to hereinafter as INNOLUX)[3] to build in a cleanroom of INNOLUX a manufacturing line intended for next-generation 3D integration[4] based on the Bumpless Build Cube (BBCube[5]), which is a technology achieved through the Tokyo Institute of Technology WOW Alliance[6].
TEX will transfer WOW technology[7] and COW technology[8], which are both based on the BBCube technology platform, to this manufacturing line intended for next-generation 3D integration. ...
Physicists have been hoping for this moment for a long time: for many years, scientists all around the world have been searching for a very specific state of thorium atomic nuclei that promises revolutionary technological applications. It could be used, for example, to build an nuclear clock that could measure time more precisely than the best atomic clocks available today. It could also be used to answer completely new fundamental questions in physics - for example, the question of whether the constants of nature are actually constant or whether they change in space ...
The mysteries of how memory works are explained in a new book that suggests anyone can boost their powers of recall – and that losing your keys is normal.
Dr Megan Sumeracki and Dr Althea Need Kaminske say storing and retrieving information is far more complex than people think. Extremes of memory such as photographic or savant are also very rare despite their regular portrayal in films.
Their new book The Psychology of Memory outlines simple recollection-boosting techniques to improve learning – or to help remember names and numbers.
Forgetting is normal
The authors highlight how a degree ...
Compared with people without opioid use disorder, those with opioid use disorder were less likely to receive palliative care in clinics and in their homes, and were dying at younger ages of causes other than opioid use, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231419.
“The majority of conversations about the opioid crisis focus on the high number of opioid toxicity deaths. The unfortunate reality is that people with opioid use disorder ...
-With images-
A new study led by researchers at Durham University has uncovered a novel mechanism that could solve a long-standing mystery about decaying planetary orbits around stars like our Sun.
The study, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, proposes that stellar magnetic fields play a crucial role in dissipating the gravitational tides responsible for the orbital decay of ‘hot Jupiter’ exoplanets.
Hot Jupiters are massive, gaseous planets similar to Jupiter that orbit extraordinarily close to their parent stars, taking only a few days to complete ...
Consistently high vaccination rates and global health surveillance programmes have helped eliminate poliomyelitis (polio) in almost all countries of the world, except Afghanistan and Pakistan. Yet non-polio enteroviruses can also lead to the same devastating symptoms of ‘acute flaccid paralysis’ (AFP), but the world is lacking formal surveillance systems to trace and control these viruses with paralytic potential.
In a presentation at this year’s ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) (Barcelona 27-30 April), Prof Thea Kølsen Fischer, Nordsjællands Hospital & University of Copenhagen, Denmark will highlight the continuous dangers that ...
With artificial intelligence (AI) poised to become a fundamental part of clinical research and decision making, many still question the accuracy of ChatGPT, a sophisticated AI language model, to support complex diagnostic and treatment processes.
Now a new study, being presented at this year’s ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April), which pitted ChatGPT against the ESCMID guideline for the management of brain abscesses, found that while ChatGPT seems able to give recommendations on key questions about diagnosis and treatment in most cases, some of the AI model’s ...
**Note: the release below is from the ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
New research presented at the ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) has found substantial levels of resistance to critically important antibiotics in meat sold for human and animal consumption. The study is by Dr Jordan Sealey, Professor Matthew Avison and colleagues from the University of Bristol, UK.
Meat sold for consumption by humans and companion animals in the UK is regulated by the UK Government Food Standards Agency (FSA) to ensure it falls within bacterial limits deemed ...
With the creation of safe and efficacious vaccines to target human papillomavirus in the first decade of this century, WHO has an ambitious target to lower cervical cancer incidence (mostly caused by HPV) and mortality by 30% by 2030, meaning each country has a target of vaccinating 90% of girls by age 15, 70% of women receiving a high precision screening test at least at age 35 and 45 years of age, and 90% of all women requiring treatment at any age to receive it. The targets are aspirational and as yet, it appears no country has been ...
It’s time to take a new approach to addressing negative messaging about vaccines, including avoiding the use of the term “anti-vaxxers”, say the researchers.
**ECCMID has now changed name to ESCMID Global, please credit ESCMID Global Congress in all future stories**
There was a marked increase in negativity about vaccines on Twitter after COVID-19 vaccines became available, the ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April) will hear.
The analysis also found that spikes in the number of negative tweets coincided with announcements ...