Identification and exploration of transcripts involved in antibiotic resistance mechanism of two critical superbugs
2024-04-29
(Press-News.org) Background and objectives
Infectious diseases caused by pathogenic strains of bacteria are a global cause of morbidity and mortality. Hospital-acquired infections caused by Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were found vulnerable during the COVID-19 pandemic. They are also responsible for the onset of certain life-threatening infectious diseases such as cystic fibrosis, endocarditis, bacteremia, and sepsis. Looking into the importance of these two superbugs there is a strong need for extensive comparative differential gene expression analysis among the wild-type and mutant for betterment of intensive care unit patients especially as such pathogenic bacterial strains have a dangerous role in the intensive care unit.
Methods
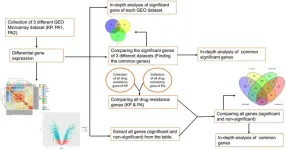
This study revealed the RNA microarray gene expression profiles of GSE24688, GSE4026, and GSE117438. The study compared all genes from three different datasets and all drug resistance genes from two divergent organisms, Klebsiella pneumonia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Results
10 numbers of shared significant genes and five drug resistance genes were obtained in this study. These putative genes may show intriguing patterns of connection with resistance mechanisms and can be used in the field of diagnostics and treatment. Our divergent analysis also revealed a very clear distinct relation between Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa at the genetic level, though they both function under antimicrobial resistance.
Conclusions
We observed interesting phenomena of nonsimilarity between common significant genes and common drug resistance genes that led to conclusions about genetic divergence due to which its physical properties have been changed but chemically involved in similar drug resistance mechanisms. Our study used a robust integrative bioinformatics analysis of microarray data to investigate the DEG of AMR superbugs. Through a comparative analysis supported by functional enrichment results, diverse pathways and distinct biological processes, molecular function, and cellular components were highlighted. Interestingly, we observed 10 common genes in all three datasets that are highly expressed and significant, five genes that are present in both KP and PA and are involved in drug resistance in both superbugs. Our findings provide a detailed account of the drug resistance gene’s divergent evolution, which could open new vistas for MDR prognosis and can be informative in antimicrobial therapeutics research. The candidate gene approach can be used to validate AMR to know the potential interesting association patterns with resistance mechanisms.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/1555-3884/GE-2023-00022
The study was recently published in the Gene Expression.
Gene Expression (GE) is an open-access journal. It was launched in 1991 by Chicago Medical School Press, and transferred to Cognizant Communication Corporation in 1994. From August 2022, GE is published by Xia & He Publishing Inc.
GE publishes peer-reviewed and high-quality original articles, reviews, editorials, commentaries, and opinions on its primary research topics including cell biology, molecular biology, genes, and genetics, especially on the cellular and molecular mechanisms of human diseases.
GE has been indexed in Medline (1991-2021), Scopus, Biological Abstracts, Biosis Previews, ProQuest, etc.
Follow us on X: https://twitter.com/xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/xia&he-publishing-inc/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-29
WASHINGTON, DC – (April 26, 2024) The effects of quantum mechanics—the laws of physics that apply at exceedingly small scales—are extremely sensitive to disturbances. This is why quantum computers must be held at temperatures colder than outer space, and only very, very small objects, such as atoms and molecules, generally display quantum properties. By quantum standards, biological systems are quite hostile environments: they’re warm and chaotic, and even their fundamental components—such as cells—are considered very large.
But ...
2024-04-29
New York, NY [April 29, 2024]—Miriam Merad, MD, PhD, a world-renowned immunologist, has been appointed Dean for Translational Research and Therapeutic Innovation of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The appointment reaffirms Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to pioneering medical progress and catalyzing the rapid advancement of research innovation.
Dr. Merad, the Mount Sinai Professor in Cancer Immunology, will also continue to serve as the founding Chair of the Department of Immunology and Immunotherapy, Director of the Marc and Jennifer Lipschultz Precision Immunology Institute, and Director ...
2024-04-29
Category 4 Hurricane Ian made landfall in Florida’s Lee County on Sept. 28, 2022, battering the region with wind speeds of 155 miles per hour and storm surge up to 13 feet – the highest storm surge documented in Southwest Florida in the past 150 years.
In the aftermath of a disaster, rapidly assessing damage is critical for rescue, recovery and emergency planning. Damage assessments are typically conducted through field reconnaissance deployments, which can be labor-intensive, costly and risky. Moreover, field-based emergency response ...
2024-04-29
The question may be the 21st century’s version of the fable of the tortoise and the hare: Who would win in a foot race between a robot and an animal?
In a new perspective article, a team of engineers from the United States and Canada, including University of Colorado Boulder roboticist Kaushik Jayaram, set out to answer that riddle. The group analyzed data from dozens of studies and came to a resounding “no.” In almost all cases, biological organisms, such as cheetahs, cockroaches and even humans, seem to be able to outrun their robot counterparts.
The researchers, led by Samuel Burden at the University of Washington and ...
2024-04-29
NEW YORK, April 29, 2024 – The Human Immunome Project (HIP), a global nonprofit scientific initiative, released its Scientific Plan today, on World Immunology Day, the organization announced. The plan provides a detailed roadmap of how the Human Immunome Project and its network of global study sites will generate the world’s largest and most diverse immunological dataset and use these data to power publicly available AI models of the immune system.
“The immune system is the epicenter of human health, and our newly released ...
2024-04-29
Highlights:
The American Heart Association awarded four new scientific research grants to evaluate the role of race in measuring heart disease risk.
The funded studies are focused on multi-ethnic groups and studying how race, considered a social rather than biological construct, affects health risk prediction when it is incorporated as a variable in algorithms.
This research is funded by a grant from the Doris Duke Foundation to study the complex issue of how race and ethnicity, when factored into cardiovascular clinical care algorithms ...
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
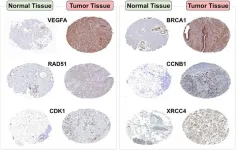
Breast cancer remains a significant global health concern, warranting further exploration into its genetic basis and potential therapeutic targets. This study aimed to elucidate the genetic associations of seven pivotal genes with breast cancer and discern their potential role in disease prognosis.
Methods
The genes VEGFA, BRCA1, RAD51, CCNB1, CHEK1, CDK1, and XRCC4 were curated from over 30 articles. Their association with breast cancer was analyzed using both in silico and in vitro techniques. The in silico assessment ...
2024-04-29
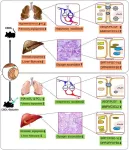
Background and Aims
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is characterized by arterial oxygenation defects due to pulmonary vascular dilation in liver disease. To date, liver transplantation remains the only effective treatment for HPS. This study aimed to explore the preventative role of baicalein in HPS development.
Methods
Sixty male rats were randomly assigned to three groups: sham, common bile duct ligation (CBDL), and baicalein, receiving intraperitoneal injections of baicalein (40 mg·kg−1·d−1, diluted in saline) for 21 days. Survival rate, liver and kidney function, and bile acid metabolism levels were evaluated. Liver and lung angiogenesis ...
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Honey is a viscous, hygroscopic liquid in nature. It has the ability to treat wounds, wrinkles, aging, and inflammation. This study’s objective was to create and characterize a nanoemulsion containing honey and evaluate its stability.
Methods
A pseudo-ternary phase diagram was retraced with several concentrations of the Smix, water, and liquid paraffin oil to formulate nanoemulsions containing honey. From the results of pre-formulation stability studies, formulation HNE-19, with a hydrophilic lipophilic balance ...
2024-04-29
As embryos, all complex organisms are partially made up of pluripotent stem cells, a term for cells that have the capacity to differentiate into any kind of cell: nerve cells, muscle cells, blood cells, skin cells, and the like. As the ultimate biological “shape-shifters,” these cells are proving key to regenerative medicine, drug development, genetic research, and related fields.
Within a pluripotent stem cell, certain genes get activated and express information that ultimately decides a cell’s fate. The first step in this expression process is called transcription, a process that turns out to be incredibly complex, in part ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Identification and exploration of transcripts involved in antibiotic resistance mechanism of two critical superbugs