The therapeutic effects of baicalein on the hepatopulmonary syndrome in the rat model of chronic common bile duct ligation
2024-04-29
(Press-News.org) Background and Aims
Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is characterized by arterial oxygenation defects due to pulmonary vascular dilation in liver disease. To date, liver transplantation remains the only effective treatment for HPS. This study aimed to explore the preventative role of baicalein in HPS development.
Methods
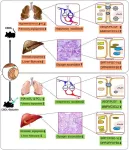
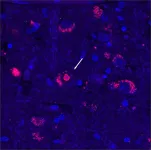
Sixty male rats were randomly assigned to three groups: sham, common bile duct ligation (CBDL), and baicalein, receiving intraperitoneal injections of baicalein (40 mg·kg−1·d−1, diluted in saline) for 21 days. Survival rate, liver and kidney function, and bile acid metabolism levels were evaluated. Liver and lung angiogenesis and hepatic glycogen staining were assessed, and the expression of relevant proteins was evaluated by immunohistochemistry.
Results
Baicalein improved survival rates and hypoxemia in rats post-CBDL, reducing angiogenic protein levels and enhancing glucose homeostasis. Compared to the untreated group, baicalein suppressed the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, placental growth factors, matrix metalloprotease 9 and C-X-C motif chemokine 2, and it increased the expression of glycemic regulatory proteins, including dipeptidyl peptidase-4, sirtuin 1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1α, and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3.
Conclusions
Baicalein significantly improves hepatic function and hypoxia in HPS rats by attenuating pathological angiogenesis in the liver and lungs, showing promise as a treatment for HPS.
Full text
https://www.xiahepublishing.com/2310-8819/JCTH-2023-00513
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.
The Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology (JCTH) is owned by the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University and published by XIA & HE Publishing Inc. JCTH publishes high quality, peer reviewed studies in the translational and clinical human health sciences of liver diseases. JCTH has established high standards for publication of original research, which are characterized by a study’s novelty, quality, and ethical conduct in the scientific process as well as in the communication of the research findings. Each issue includes articles by leading authorities on topics in hepatology that are germane to the most current challenges in the field. Special features include reports on the latest advances in drug development and technology that are relevant to liver diseases. Regular features of JCTH also include editorials, correspondences and invited commentaries on rapidly progressing areas in hepatology. All articles published by JCTH, both solicited and unsolicited, must pass our rigorous peer review process.
Follow us on X: https://twitter.com/xiahepublishing
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/xia&he-publishing-inc/
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-29
Background and objectives
Honey is a viscous, hygroscopic liquid in nature. It has the ability to treat wounds, wrinkles, aging, and inflammation. This study’s objective was to create and characterize a nanoemulsion containing honey and evaluate its stability.
Methods
A pseudo-ternary phase diagram was retraced with several concentrations of the Smix, water, and liquid paraffin oil to formulate nanoemulsions containing honey. From the results of pre-formulation stability studies, formulation HNE-19, with a hydrophilic lipophilic balance ...
2024-04-29
As embryos, all complex organisms are partially made up of pluripotent stem cells, a term for cells that have the capacity to differentiate into any kind of cell: nerve cells, muscle cells, blood cells, skin cells, and the like. As the ultimate biological “shape-shifters,” these cells are proving key to regenerative medicine, drug development, genetic research, and related fields.
Within a pluripotent stem cell, certain genes get activated and express information that ultimately decides a cell’s fate. The first step in this expression process is called transcription, a process that turns out to be incredibly complex, in part ...
2024-04-29
Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) is a state-of-the-art technique that captures and processes information across a given electromagnetic spectrum. Unlike traditional imaging techniques that capture light intensity at specific wavelengths, HSI collects a full spectrum at each pixel in an image. This rich spectral data enables the distinction between different materials and substances based on their unique spectral signatures. Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) has attracted significant attention in the food and industrial fields ...
2024-04-29
**EMBARGOED BY NATURE GENETICS UNTIL 10AM BST/ 5AM ET/ 3AM MT, APRIL 29**
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its effects on patients and their families can be severe. For most people, the first sign is difficulty walking and balancing, which gets worse as time progresses. The symptoms usually start in a person’s forties or fifties but can begin as early as the late teens. There is ...
2024-04-29
Samples reveal evidence of changes experienced by the surface of asteroid Ryugu, some probably due to micrometeoroid bombardment.
Analyzing samples retrieved from the asteroid Ryugu by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft has revealed new insights into the magnetic and physical bombardment environment of interplanetary space. The results of the study, carried out by Professor Yuki Kimura at Hokkaido University and co-workers at 13 other institutions in Japan, are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The investigations used electron waves penetrating ...
2024-04-29
Dinosaurs were as smart as reptiles but not as intelligent as monkeys, as former research suggests.
An international team of palaeontologists, behavioural scientists and neurologists have re-examined brain size and structure in dinosaurs and concluded they behaved more like crocodiles and lizards.
In a study published last year, it was claimed that dinosaurs like T. rex had an exceptionally high number of neurons and were substantially more intelligent than assumed. It was claimed that these high neuron counts could directly inform on ...
2024-04-29
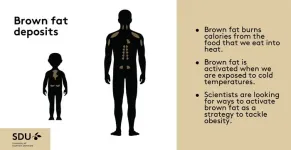
Brown fat, also known as brown adipose tissue (BAT), is a type of fat in our bodies that's different from the white fat around our belly and thighs that we are more familiar with. Brown fat has a special job—it helps to burn calories from the foods that we eat into heat, which can be helpful, especially when we're exposed to cold temperatures like during winter swimming or cryotherapy. For a long time, scientists thought that only small animals like mice and newborns had brown fat. But new research shows that a certain number of adults maintain their brown fat throughout life. Because brown fat is so good at burning calories, scientists ...
2024-04-29
Tech Extension Co., Ltd. (referred to hereinafter as TEX)[1] and Tech Extension Taiwan Co., Ltd. (referred to hereinafter as TEX-T)[2] have agreed with Innolux Corporation (referred to hereinafter as INNOLUX)[3] to build in a cleanroom of INNOLUX a manufacturing line intended for next-generation 3D integration[4] based on the Bumpless Build Cube (BBCube[5]), which is a technology achieved through the Tokyo Institute of Technology WOW Alliance[6].
TEX will transfer WOW technology[7] and COW technology[8], which are both based on the BBCube technology platform, to this manufacturing line intended for next-generation 3D integration. ...
2024-04-29
Physicists have been hoping for this moment for a long time: for many years, scientists all around the world have been searching for a very specific state of thorium atomic nuclei that promises revolutionary technological applications. It could be used, for example, to build an nuclear clock that could measure time more precisely than the best atomic clocks available today. It could also be used to answer completely new fundamental questions in physics - for example, the question of whether the constants of nature are actually constant or whether they change in space ...
2024-04-29
The mysteries of how memory works are explained in a new book that suggests anyone can boost their powers of recall – and that losing your keys is normal.
Dr Megan Sumeracki and Dr Althea Need Kaminske say storing and retrieving information is far more complex than people think. Extremes of memory such as photographic or savant are also very rare despite their regular portrayal in films.
Their new book The Psychology of Memory outlines simple recollection-boosting techniques to improve learning – or to help remember names and numbers.
Forgetting is normal
The authors highlight how a degree ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The therapeutic effects of baicalein on the hepatopulmonary syndrome in the rat model of chronic common bile duct ligation