Mazin to study electronic, transport & topological properties of frustrated magnets
2024-04-29
(Press-News.org)
Igor Mazin, Professor of Practice for Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Quantum Materials Center, Physics and Astronomy, is set to receive funding for the project: “Electronic, transport and topological properties of frustrated magnets.”
In this project, Mazin and his collaborators will examine frustrated magnetic systems.
Magnetic frustration lies at the core of the notion of skyrmions and quantum spin liquid.
Mazin will receive $258,480 from the National Science Foundation for this project. Funding will begin in May 2024 and will end in late April 2027.
###
ABOUT GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
George Mason University is Virginia’s largest public research university. Located near Washington, D.C., Mason enrolls more than 40,000 students from 130 countries and all 50 states. Mason has grown rapidly over the past half-century and is recognized for its innovation and entrepreneurship, remarkable diversity, and commitment to accessibility. In2023, the university launched Mason Now: Power the Possible, a one-billion-dollar comprehensive campaign to support student success, research, innovation, community, and stewardship. Learn more at gmu.edu.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-29
NEW YORK – April 25, 2024 – The TCT® 2024 Career Achievement Award will be presented to Robert A. Harrington, MD, during Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics® (TCT®), the annual scientific symposium of the Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®). TCT® will take place October 27-30 2024, in Washington, DC at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center. The award is given each year to an outstanding individual who has made extraordinary contributions to the field of interventional cardiology and has transformed ...
2024-04-29
The Tibetan plateau—the world’s highest and largest plateau—poses a challenge to the people who live there because of its extreme climate. In a new study, researchers have discovered stone artifacts that suggest that there were more cultural exchanges between those who lived on the plateau and those living on its perimeter.
“The Tibetan plateau has an average elevation of more than 4500 meters, which makes Colorado seem like it is at sea level. It’s amazing that people have been able to occupy this area on and off for at least the last 40,000 years,” said Stanley Ambrose (MME), a professor of anthropology. “Unfortunately, very little ...
2024-04-29
Oncotarget is a contributing sponsor at the 19th International p53 Workshop in Trieste, Italy, on May 13–16, 2024.
BUFFALO, NY- April 29, 2024 – Oncotarget is a contributing sponsor at the 19th International p53 Workshop, organized by the International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), which takes place from May 13–16, 2024, in Trieste, Italy.
“Groundbreaking research and cutting-edge advancements in the field of the most studied human gene and most frequently mutated gene in cancer, will take center stage at the 19th ...
2024-04-29
ITHACA, N.Y. -- New York state solar construction workers – whose numbers are expected to grow rapidly to meet climate goals – are transient, may not receive benefits and are subject to racial disparities in pay, finds a new report from the Climate Jobs Institute (CJI) at Cornell University.
“Exploring the Conditions of the New York Solar Workforce” was funded by the New York State Department of Labor and surveyed more than 260 solar installation and maintenance workers. The exploratory study is the first to focus on workers’ experiences, seeking to bridge gaps in government and industry ...
2024-04-29
The fragile qubits that make up quantum computers offer a powerful computational tool, yet also present a conundrum: How can engineers create practical, workable quantum systems out of bits that are so easily disturbed — and wiped of data — by tiny changes in their environment?
Engineers have long struggled with how to make quantum computers less error-prone, often by developing ways to detect and correct errors rather than prevent them in the first place. However, many such error-correction schemes involve duplicating information across hundreds or thousands of physical qubits at once, which quickly becomes hard to scale up in an efficient way.
Now, ...
2024-04-29
New research using live SARS-CoV-2 virus reveals an updated vaccine provides a strong immune response against previous strains and emerging variants.
The findings by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University, published in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, suggest a clear benefit in receiving updated vaccinations on a regular basis, especially among older people or those with underlying medical conditions.
“The virus is still circulating, it’s continuing to evolve, and it remains dangerous,” said co-senior author Fikadu Tafesse, Ph.D., associate professor of molecular ...
2024-04-29
Dr Carl Senior identified two types of smile – affiliative and reward – given by political leaders during the last UK general election in 2019
The eventual winner, Boris Johnson, was found to display the affiliative smile, which acts to align voter behaviour
The study is the first to look at how supporters of election losers react to the eventual winner.
New research led by Aston University’s Dr Carl Senior has found that the type of smile used by a political leader can influence voters to support them and their political agenda.
There are many different types of smile, and the ...
2024-04-29
Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers at the University Hospital Bonn (UKB), the University of Bonn and the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) have discovered a new so-called lantibiotic, namely epilancin A37. It is produced by staphylococci that colonize the skin and acts specifically against their main competitors there, the corynebacteria. This specificity is presumably mediated by a very special mechanism of action, which the researchers were able to decipher in detail. ...
2024-04-29
Quantitative study assesses how gender and race impact young athletes’ perceptions of their coaches
Across the U.S., there are over 8 million student-athletes in high school and college. Engaging in sports can contribute to physical, mental, and social benefits, and coaches can play a key role in student-athletes’ continued participation in sports.
A recent study led by UNC Greensboro’s Dr. Tsz Lun (Alan) Chu, published in Sport, Exercise, and Performance Psychology, examines how multiple aspects of a young athlete’s ...
2024-04-29
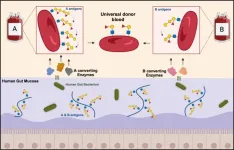
The quest to develop universal donor blood has taken a decisive step forward. Researchers at DTU and Lund University have discovered enzymes that, when mixed with red blood cells, are able to remove specific sugars that make up the A and B antigens in the human ABO blood groups. The results have been published in the scientific journal Nature Microbiology.
"For the first time, the new enzyme cocktails not only remove the well-described A and B antigens, but also extended variants previously not recognized as problematic for transfusion safety. We are close to being able to produce universal blood from group B donors, while there is still work to be done to convert ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mazin to study electronic, transport & topological properties of frustrated magnets